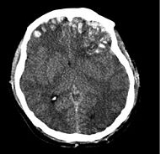
Cerebral contusion
Encyclopedia
Cerebral contusion, Latin
contusio cerebri, a form of traumatic brain injury
, is a bruise
of the brain
tissue. Like bruises in other tissues, cerebral contusion can be associated with multiple microhemorrhages, small blood vessel
leaks into brain tissue. Contusion occurs in 20–30% of severe head injuries
. A cerebral laceration
is a similar injury except that, according to their respective definitions, the pia
-arachnoid
membranes are torn over the site of injury in laceration and are not torn in contusion. The injury can cause a decline in mental function in the long term and in the emergency setting may result in brain herniation
, a life-threatening condition in which parts of the brain are squeezed past parts of the skull. Thus treatment aims to prevent dangerous rises in intracranial pressure
, the pressure within the skull.
Contusions are likely to heal on their own without medical intervention.
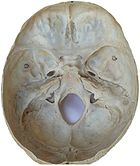 Often caused by a blow to the head, contusions commonly occur in coup or contre-coup injuries
Often caused by a blow to the head, contusions commonly occur in coup or contre-coup injuries
. In coup injuries, the brain is injured directly under the area of impact, while in contrecoup injuries it is injured on the side opposite the impact.
Contusions occur primarily in the cortical
tissue, especially under the site of impact or in areas of the brain located near sharp ridges on the inside of the skull. The brain may be contused when it collides with bony protuberances on the inside surface of the skull. The protuberances are located on the inside of the skull under the frontal
and temporal lobe
s and on the roof of the ocular orbit
. Thus, the tips of the frontal and temporal lobes located near the bony ridges in the skull are areas where contusions frequently occur and are most severe. For this reason, attention, emotional and memory problems, which are associated with damage to frontal and temporal lobes, are much more common in head trauma survivors than are syndromes associated with damage to other areas of the brain.
, are especially likely to cause increases in intracranial pressure
(ICP) and concomitant crushing of delicate brain tissue.
Contusions typically form in a wedge-shape with the widest part in the outermost part of the brain.
The distinction between contusion and intracerebral hemorrhage is blurry because both involve bleeding within the brain tissue; however, an arbitrary cutoff exists that the injury is a contusion if two thirds or less of the tissue involved is blood and a hemorrhage otherwise.
The contusion may cause swelling of the surrounding brain tissue, which may be irritated by toxins released in the contusion. The swelling is worst at around four to six days after the injury.
Extensive contusion associated with subdural hematoma
is called burst lobe
. Cases of a burst frontal or temporal lobe are associated with high mortality
and morbidity.
Old or remote contusions are associated with resorption of the injured tissue, resulting in various degrees of cavitation, in addition to the presence of a golden-yellow discoloration due to residual hemosiderin. These remote contusions are often referred to as plaque jaune or yellow plaque.
, basal ganglia
, thalamus
and areas near the third ventricle
. The hemorrhages can occur as the result of brain herniation
, which can cause arteries to tear and bleed. A type of diffuse brain injury, multiple petechial hemorrhages are not always visible using current imaging techniques like CT and MRI scans. This may be the case even if the injury is quite severe, though these may show up days after the injury. Hemorrhages may be larger than in normal contusions if the injury is quite severe. This type of injury has a poor prognosis if the patient is coma
tose, even with no apparent causes for the coma.
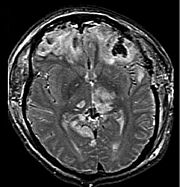 Since cerebral swelling presents a danger to the patient, treatment of cerebral contusion aims to prevent swelling. Measures to avoid swelling include prevention of hypotension
Since cerebral swelling presents a danger to the patient, treatment of cerebral contusion aims to prevent swelling. Measures to avoid swelling include prevention of hypotension
(low blood pressure), hyponatremia
(insufficient sodium), and hypercapnia
(increased carbon dioxide
in the blood). Due to the danger of increased intracranial pressure, surgery may be necessary to reduce it. People with cerebral contusion may require intensive care and close monitoring.
Latin
Latin is an Italic language originally spoken in Latium and Ancient Rome. It, along with most European languages, is a descendant of the ancient Proto-Indo-European language. Although it is considered a dead language, a number of scholars and members of the Christian clergy speak it fluently, and...
contusio cerebri, a form of traumatic brain injury
Traumatic brain injury
Traumatic brain injury , also known as intracranial injury, occurs when an external force traumatically injures the brain. TBI can be classified based on severity, mechanism , or other features...
, is a bruise
Bruise
A bruise, also called a contusion, is a type of relatively minor hematoma of tissue in which capillaries and sometimes venules are damaged by trauma, allowing blood to seep into the surrounding interstitial tissues. Bruises can involve capillaries at the level of skin, subcutaneous tissue, muscle,...
of the brain
Brain
The brain is the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals—only a few primitive invertebrates such as sponges, jellyfish, sea squirts and starfishes do not have one. It is located in the head, usually close to primary sensory apparatus such as vision, hearing,...
tissue. Like bruises in other tissues, cerebral contusion can be associated with multiple microhemorrhages, small blood vessel
Blood vessel
The blood vessels are the part of the circulatory system that transports blood throughout the body. There are three major types of blood vessels: the arteries, which carry the blood away from the heart; the capillaries, which enable the actual exchange of water and chemicals between the blood and...
leaks into brain tissue. Contusion occurs in 20–30% of severe head injuries
Head injury
Head injury refers to trauma of the head. This may or may not include injury to the brain. However, the terms traumatic brain injury and head injury are often used interchangeably in medical literature....
. A cerebral laceration
Cerebral laceration
A cerebral laceration is a type of traumatic brain injury that occurs when the tissue of the brain is mechanically cut or torn. The injury is similar to a cerebral contusion; however, according to their respective definitions, the pia-arachnoid membranes are torn over the site of injury in...
is a similar injury except that, according to their respective definitions, the pia
Pia mater
Pia mater often referred to as simply the pia, is the delicate innermost layer of the meninges, the membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord. The word finds its roots in Latin, meaning literally "tender mother." The other two meningeal membranes are the dura mater and the arachnoid mater....
-arachnoid
Arachnoid mater
The arachnoid mater, literally from Latin "spider -like mother", is one of the three meninges, the membranes that cover the brain and spinal cord...
membranes are torn over the site of injury in laceration and are not torn in contusion. The injury can cause a decline in mental function in the long term and in the emergency setting may result in brain herniation
Brain herniation
Brain herniation, also known as cistern obliteration, is a deadly side effect of very high intracranial pressure that occurs when the brain shifts across structures within the skull...
, a life-threatening condition in which parts of the brain are squeezed past parts of the skull. Thus treatment aims to prevent dangerous rises in intracranial pressure
Intracranial pressure
Intracranial pressure is the pressure inside the skull and thus in the brain tissue and cerebrospinal fluid . The body has various mechanisms by which it keeps the ICP stable, with CSF pressures varying by about 1 mmHg in normal adults through shifts in production and absorption of CSF...
, the pressure within the skull.
Contusions are likely to heal on their own without medical intervention.
Signs and symptoms
The symptoms of a cerebral contusion (bruising on the brain) depend on the severity of the injury, ranging from minor to severe. Individuals may experience a headache; confusion; sleepiness; dizziness; loss of consciousness; nausea and vomiting; seizures; and difficulty with coordination and movement. They may also have difficulty with memory, vision, speech, hearing, managing emotions, and thinking. Signs depend on the contusion's location in the brain.Causes

Coup contrecoup injury
In head injury, a coup injury occurs under the site of impact with an object, and a contrecoup injury occurs on the side opposite the area that was impacted. Coup and contrecoup injury is associated with cerebral contusion, a type of traumatic brain injury in which the brain is bruised. Coup and...
. In coup injuries, the brain is injured directly under the area of impact, while in contrecoup injuries it is injured on the side opposite the impact.
Contusions occur primarily in the cortical
Cerebral cortex
The cerebral cortex is a sheet of neural tissue that is outermost to the cerebrum of the mammalian brain. It plays a key role in memory, attention, perceptual awareness, thought, language, and consciousness. It is constituted of up to six horizontal layers, each of which has a different...
tissue, especially under the site of impact or in areas of the brain located near sharp ridges on the inside of the skull. The brain may be contused when it collides with bony protuberances on the inside surface of the skull. The protuberances are located on the inside of the skull under the frontal
Frontal lobe
The frontal lobe is an area in the brain of humans and other mammals, located at the front of each cerebral hemisphere and positioned anterior to the parietal lobe and superior and anterior to the temporal lobes...
and temporal lobe
Temporal lobe
The temporal lobe is a region of the cerebral cortex that is located beneath the Sylvian fissure on both cerebral hemispheres of the mammalian brain....
s and on the roof of the ocular orbit
Orbit (anatomy)
In anatomy, the orbit is the cavity or socket of the skull in which the eye and its appendages are situated. "Orbit" can refer to the bony socket, or it can also be used to imply the contents...
. Thus, the tips of the frontal and temporal lobes located near the bony ridges in the skull are areas where contusions frequently occur and are most severe. For this reason, attention, emotional and memory problems, which are associated with damage to frontal and temporal lobes, are much more common in head trauma survivors than are syndromes associated with damage to other areas of the brain.
Features
Contusions, which are frequently associated with edemaEdema
Edema or oedema ; both words from the Greek , oídēma "swelling"), formerly known as dropsy or hydropsy, is an abnormal accumulation of fluid beneath the skin or in one or more cavities of the body that produces swelling...
, are especially likely to cause increases in intracranial pressure
Intracranial pressure
Intracranial pressure is the pressure inside the skull and thus in the brain tissue and cerebrospinal fluid . The body has various mechanisms by which it keeps the ICP stable, with CSF pressures varying by about 1 mmHg in normal adults through shifts in production and absorption of CSF...
(ICP) and concomitant crushing of delicate brain tissue.
Contusions typically form in a wedge-shape with the widest part in the outermost part of the brain.
The distinction between contusion and intracerebral hemorrhage is blurry because both involve bleeding within the brain tissue; however, an arbitrary cutoff exists that the injury is a contusion if two thirds or less of the tissue involved is blood and a hemorrhage otherwise.
The contusion may cause swelling of the surrounding brain tissue, which may be irritated by toxins released in the contusion. The swelling is worst at around four to six days after the injury.
Extensive contusion associated with subdural hematoma
Subdural hematoma
A subdural hematoma or subdural haematoma , also known as a subdural haemorrhage , is a type of haematoma, a form of traumatic brain injury. Blood gathers within the outermost meningeal layer, between the dura mater, which adheres to the skull, and the arachnoid mater, which envelops the brain...
is called burst lobe
Burst lobe
Burst lobe is a term used to describe an intracranial hemorrhage, specifically affecting a brain lobe and characterized by an intracerebral hemorrhage in continuity with a subdural hemorrhage. This term is used as well to described a connection between intra-axial and extra-axial intracranial...
. Cases of a burst frontal or temporal lobe are associated with high mortality
Mortality rate
Mortality rate is a measure of the number of deaths in a population, scaled to the size of that population, per unit time...
and morbidity.
Old or remote contusions are associated with resorption of the injured tissue, resulting in various degrees of cavitation, in addition to the presence of a golden-yellow discoloration due to residual hemosiderin. These remote contusions are often referred to as plaque jaune or yellow plaque.
Multiple petechial hemorrhages
Numerous small contusions from broken capillaries that occur in grey matter under the cortex are called multiple petechial hemorrhages or multifocal hemorrhagic contusion. Caused by shearing injuries at the time of impact, these contusions occur especially at the junction between grey and white matter and in the upper brain stemBrain stem
In vertebrate anatomy the brainstem is the posterior part of the brain, adjoining and structurally continuous with the spinal cord. The brain stem provides the main motor and sensory innervation to the face and neck via the cranial nerves...
, basal ganglia
Basal ganglia
The basal ganglia are a group of nuclei of varied origin in the brains of vertebrates that act as a cohesive functional unit. They are situated at the base of the forebrain and are strongly connected with the cerebral cortex, thalamus and other brain areas...
, thalamus
Thalamus
The thalamus is a midline paired symmetrical structure within the brains of vertebrates, including humans. It is situated between the cerebral cortex and midbrain, both in terms of location and neurological connections...
and areas near the third ventricle
Ventricular system
The ventricular system is a set of structures containing cerebrospinal fluid in the brain. It is continuous with the central canal of the spinal cord.-Components:The system comprises four ventricles:* right and left lateral ventricles* third ventricle...
. The hemorrhages can occur as the result of brain herniation
Brain herniation
Brain herniation, also known as cistern obliteration, is a deadly side effect of very high intracranial pressure that occurs when the brain shifts across structures within the skull...
, which can cause arteries to tear and bleed. A type of diffuse brain injury, multiple petechial hemorrhages are not always visible using current imaging techniques like CT and MRI scans. This may be the case even if the injury is quite severe, though these may show up days after the injury. Hemorrhages may be larger than in normal contusions if the injury is quite severe. This type of injury has a poor prognosis if the patient is coma
Coma
In medicine, a coma is a state of unconsciousness, lasting more than 6 hours in which a person cannot be awakened, fails to respond normally to painful stimuli, light or sound, lacks a normal sleep-wake cycle and does not initiate voluntary actions. A person in a state of coma is described as...
tose, even with no apparent causes for the coma.
Treatment

Hypotension
In physiology and medicine, hypotension is abnormally low blood pressure, especially in the arteries of the systemic circulation. It is best understood as a physiologic state, rather than a disease. It is often associated with shock, though not necessarily indicative of it. Hypotension is the...
(low blood pressure), hyponatremia
Hyponatremia
Hyponatremia is an electrolyte disturbance in which the sodium concentration in the serum is lower than normal. In the vast majority of cases, hyponatremia occurs as a result of excess body water diluting the serum sodium and is not due to sodium deficiency. Sodium is the dominant extracellular...
(insufficient sodium), and hypercapnia
Hypercapnia
Hypercapnia or hypercapnea , also known as hypercarbia, is a condition where there is too much carbon dioxide in the blood...
(increased carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a naturally occurring chemical compound composed of two oxygen atoms covalently bonded to a single carbon atom...
in the blood). Due to the danger of increased intracranial pressure, surgery may be necessary to reduce it. People with cerebral contusion may require intensive care and close monitoring.

