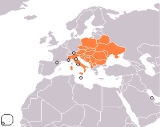
Central European Initiative
Encyclopedia
Central Europe
Central Europe or alternatively Middle Europe is a region of the European continent lying between the variously defined areas of Eastern and Western Europe...
an Initiative (CEI) is a forum of regional cooperation in Central, Eastern and South Eastern Europe
Europe
Europe is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting...
, counting 18 member states. It was formed in Budapest
Budapest
Budapest is the capital of Hungary. As the largest city of Hungary, it is the country's principal political, cultural, commercial, industrial, and transportation centre. In 2011, Budapest had 1,733,685 inhabitants, down from its 1989 peak of 2,113,645 due to suburbanization. The Budapest Commuter...
in 1989.
History
The Central European Initiative or CEI http://www.ceinet.org, is the largest and oldest forum of regional cooperation in Central, Eastern and South Eastern Europe. It now counts 18 member states: AlbaniaAlbania
Albania , officially known as the Republic of Albania , is a country in Southeastern Europe, in the Balkans region. It is bordered by Montenegro to the northwest, Kosovo to the northeast, the Republic of Macedonia to the east and Greece to the south and southeast. It has a coast on the Adriatic Sea...
, Austria
Austria
Austria , officially the Republic of Austria , is a landlocked country of roughly 8.4 million people in Central Europe. It is bordered by the Czech Republic and Germany to the north, Slovakia and Hungary to the east, Slovenia and Italy to the south, and Switzerland and Liechtenstein to the...
, Belarus
Belarus
Belarus , officially the Republic of Belarus, is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe, bordered clockwise by Russia to the northeast, Ukraine to the south, Poland to the west, and Lithuania and Latvia to the northwest. Its capital is Minsk; other major cities include Brest, Grodno , Gomel ,...
, Bosnia and Herzegovina
Bosnia and Herzegovina
Bosnia and Herzegovina , sometimes called Bosnia-Herzegovina or simply Bosnia, is a country in Southern Europe, on the Balkan Peninsula. Bordered by Croatia to the north, west and south, Serbia to the east, and Montenegro to the southeast, Bosnia and Herzegovina is almost landlocked, except for the...
, Bulgaria
Bulgaria
Bulgaria , officially the Republic of Bulgaria , is a parliamentary democracy within a unitary constitutional republic in Southeast Europe. The country borders Romania to the north, Serbia and Macedonia to the west, Greece and Turkey to the south, as well as the Black Sea to the east...
, Croatia
Croatia
Croatia , officially the Republic of Croatia , is a unitary democratic parliamentary republic in Europe at the crossroads of the Mitteleuropa, the Balkans, and the Mediterranean. Its capital and largest city is Zagreb. The country is divided into 20 counties and the city of Zagreb. Croatia covers ...
, the Czech Republic
Czech Republic
The Czech Republic is a landlocked country in Central Europe. The country is bordered by Poland to the northeast, Slovakia to the east, Austria to the south, and Germany to the west and northwest....
, Hungary
Hungary
Hungary , officially the Republic of Hungary , is a landlocked country in Central Europe. It is situated in the Carpathian Basin and is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine and Romania to the east, Serbia and Croatia to the south, Slovenia to the southwest and Austria to the west. The...
, Italy
Italy
Italy , officially the Italian Republic languages]] under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, Italy's official name is as follows:;;;;;;;;), is a unitary parliamentary republic in South-Central Europe. To the north it borders France, Switzerland, Austria and...
, Macedonia
Republic of Macedonia
Macedonia , officially the Republic of Macedonia , is a country located in the central Balkan peninsula in Southeast Europe. It is one of the successor states of the former Yugoslavia, from which it declared independence in 1991...
, Moldova
Moldova
Moldova , officially the Republic of Moldova is a landlocked state in Eastern Europe, located between Romania to the West and Ukraine to the North, East and South. It declared itself an independent state with the same boundaries as the preceding Moldavian Soviet Socialist Republic in 1991, as part...
, Montenegro
Montenegro
Montenegro Montenegrin: Crna Gora Црна Гора , meaning "Black Mountain") is a country located in Southeastern Europe. It has a coast on the Adriatic Sea to the south-west and is bordered by Croatia to the west, Bosnia and Herzegovina to the northwest, Serbia to the northeast and Albania to the...
, Poland
Poland
Poland , officially the Republic of Poland , is a country in Central Europe bordered by Germany to the west; the Czech Republic and Slovakia to the south; Ukraine, Belarus and Lithuania to the east; and the Baltic Sea and Kaliningrad Oblast, a Russian exclave, to the north...
, Romania
Romania
Romania is a country located at the crossroads of Central and Southeastern Europe, on the Lower Danube, within and outside the Carpathian arch, bordering on the Black Sea...
, Serbia
Serbia
Serbia , officially the Republic of Serbia , is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central and Southeast Europe, covering the southern part of the Carpathian basin and the central part of the Balkans...
, Slovakia
Slovakia
The Slovak Republic is a landlocked state in Central Europe. It has a population of over five million and an area of about . Slovakia is bordered by the Czech Republic and Austria to the west, Poland to the north, Ukraine to the east and Hungary to the south...
, Slovenia
Slovenia
Slovenia , officially the Republic of Slovenia , is a country in Central and Southeastern Europe touching the Alps and bordering the Mediterranean. Slovenia borders Italy to the west, Croatia to the south and east, Hungary to the northeast, and Austria to the north, and also has a small portion of...
and Ukraine
Ukraine
Ukraine is a country in Eastern Europe. It has an area of 603,628 km², making it the second largest contiguous country on the European continent, after Russia...
.
The origin of the Central European Initiative lies in the creation of the Quadragonale in Budapest on 11 November 1989 whose founding fathers were Italy, Austria, Hungary and the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (SFRY).
The Initiative aimed at overcoming the division in blocks by re-establishing cooperation links, among countries of different political orientations and economic structures.
At the first Summit in Venice in 1990, Czechoslovakia was admitted and the Initiative was renamed Pentagonale. In 1991, with the admission of Poland it became the Hexagonale.
The organisation was renamed Central European Initiative (CEI) in 1992. On the same occasion, Macedonia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Croatia and Slovenia were admitted as Member States.
The Czech Republic and Slovakia were admitted to the CEI in 1993 following the dissolution of Czechoslovakia. In 1996 Albania, Belarus, Bulgaria, Moldova, Romania and Ukraine joined the CEI as full-fledged members.
The current membership derives from the adhesion of the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (afterwards State Union of Serbia and Montenegro and later on Serbia) in 2000 and of Montenegro in 2006.
The CEI headquarters are based in Trieste (Italy) since 1996.
Mission
The CEI aims at achieving cohesion in areas of mutual interest and at assisting its non-EU member countries in consolidating their economic and social development. In this regard, the CEI Plan of Action defines the organisation’s priorities within the established areas of cooperation.Once predominantly oriented towards policy dialogue, the CEI has progressively added economic growth and human development as pillars of cooperation with a focus on capacity building, sharing experience and know-how transfer.
A number of CEI activities and projects are also strategically developed within EU programmes as well as with other international and regional organisations. The CEI also cooperates with other organisations such as the RCC, BSEC, the OSCE etc.
Areas of Cooperation:
Climate, Environment and Sustainable Energy, Enterprise Development including Tourism, Human Resource Development, Information Society and Media, Intercultural Cooperation including Minorities, Multimodal Transport, Science and Technology, Sustainable Agriculture, Interregional and Cross-Border Cooperation.
Structures
The CEI operates through various structures:– Annual Meeting of the Heads of Government (CEI Summit).
– Annual Meeting of the Ministers of Foreign Affairs (MFA Meeting).
– Regular meetings of the CEI Committee of National Coordinators (CNC).
The CNC, composed of representatives of Foreign Ministries of all Member States, is the body responsible for the management of CEI cooperation and the implementation of CEI programmes and projects.
Meetings at ministerial as well as expert level are also convened upon the initiative of the annually rotating CEI Presidency.
Working bodies such as the Networks of Focal Points, designated in specific sectors by the governments of its 18 Member States, operate in each CEI area of activity.
The CEI - Executive Secretariat (CEI-ES), is the only permanent CEI body and was established in Trieste in 1996. It provides administrative and conceptual support to the decision-making and operational structures of the CEI.
The Secretariat for CEI Projects (CEI-PS), established in 1991 at the European Bank for Reconstruction and Development (EBRD), maintains offices both in Trieste and London and carries out investment and project-related activities.
Participation in EU programmes started in 2004, with the aim to foster territorial cooperation among CEI countries – with particular attention to the involvement of non-EU CEI Member States in EU funded projects - and to expand existing experience in CEI’s priority areas.
Financial support for the functioning of the Secretariat is provided by Italy.
Another important element of the CEI is the cooperation promoted among the Parliaments of the CEI Member States or what is known as the CEI Parliamentary Dimension. Relations are also maintained among the Chambers of Commerce of the Region.
Secretary General
As of 1 January 2010, Ambassador Gerhard Pfanzelter (Austria) has taken up his duties as Secretary General.CEI Presidencies
– 1989 Hungary.
– 1990 Italy.
– 1991 SFR Yugoslavia.
– 1992 Austria.
– 1993 Hungary.
– 1994 Italy.
– 1995 Poland.
– 1996 Austria.
– 1997 Bosnia and Herzegovina.
– 1998 Croatia.
– 1999 Czech Republic.
– 2000 Hungary.
– 2001 Italy.
– 2002 Macedonia.
– 2003 Poland.
– 2004 Slovenia.
– 2005 Slovakia.
– 2006 Albania.
– 2007 Bulgaria.
– 2008 Moldova.
– 2009 Romania.
– 2010 Montenegro.
- 2011 Serbia
Membership
Founding members: (1989) (1989)
(1989)  (1989)
(1989)  (1989-1992)
(1989-1992)Joined later: (1990-1992) (1991)
 (1992) (1992) (1992)
(1992) (1992) (1992)  (1993) (1993)
(1993) (1993)  (1993)
(1993)  (1995) (1995) (1995)
(1995) (1995) (1995)  (1996) (1995)
(1996) (1995)  (1995) (2000) (2 August 2006)
(1995) (2000) (2 August 2006)See also
- Central EuropeCentral EuropeCentral Europe or alternatively Middle Europe is a region of the European continent lying between the variously defined areas of Eastern and Western Europe...
, Southeastern Europe - Southeast European Cooperation ProcessSoutheast European Cooperation ProcessThe South East European Co-operation Process was launched on Bulgaria's initiative in 1996. At the Bulgaria-chaired meeting in Sofia, the SEE countries laid the foundations for regional co-operation for the purposes of creating an atmosphere of trust, good neighbourly relations and stability.A...
(SEECP) - Central European Free Trade AgreementCentral European Free Trade AgreementThe Central European Free Trade Agreement is a trade agreement between non-EU countries in Southeast Europe.-Members:As of 1 May 2007, the parties of the CEFTA agreement are: Albania, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Croatia, Macedonia, Moldova, Montenegro, Serbia and UNMIK on behalf of Kosovo.Former...
(CEFTA) - Southeast European Cooperative InitiativeSoutheast European Cooperative InitiativeThe Southeast European Cooperative Initiative, or the SECI, has been an initiative that, under the auspices of men like Erhard Busek and Richard Schifter, has been successful in providing stability in an unstable region and has found support in international organizations and countries...
(SECI) - Black Sea Economic Co-operation (BSEC)
- Adriatic-Ionian Initiative (AII)
- Regional Cooperation Council (RCC)

