
Cavity quantum electrodynamics
Encyclopedia
Cavity quantum electrodynamics
(cavity QED) is the study of the interaction between light confined in a reflective cavity and atoms or other particles, under conditions where the quantum nature of light photon
s is significant. It could in principle be used to construct a quantum computer
.
The case of a single 2-level atom in the cavity is mathematically described by the Jaynes-Cummings model
, and undergoes vacuum Rabi oscillation
s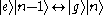 , that is between an excited atom and n-1 photons, and a ground state atom and n photons.
, that is between an excited atom and n-1 photons, and a ground state atom and n photons.
If the cavity is on resonance with the atomic transition, a half-cycle of oscillation starting with no photons coherently swaps the atom qubit's state onto the cavity field's,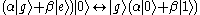 , and can be repeated to swap it back again; this could be used as a single photon source (starting with an excited atom), or as an interface between an atom or trapped ion quantum computer and optical quantum communication.
, and can be repeated to swap it back again; this could be used as a single photon source (starting with an excited atom), or as an interface between an atom or trapped ion quantum computer and optical quantum communication.
Other interaction durations create entanglement
between the atom and cavity field; for example, a quarter-cycle on resonance starting from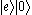 gives the maximally entangled state
gives the maximally entangled state  . This can in principle be used as a quantum computer
. This can in principle be used as a quantum computer
, mathematically equivalent to a trapped ion quantum computer with cavity photons replacing phonons.
Quantum electrodynamics
Quantum electrodynamics is the relativistic quantum field theory of electrodynamics. In essence, it describes how light and matter interact and is the first theory where full agreement between quantum mechanics and special relativity is achieved...
(cavity QED) is the study of the interaction between light confined in a reflective cavity and atoms or other particles, under conditions where the quantum nature of light photon
Photon
In physics, a photon is an elementary particle, the quantum of the electromagnetic interaction and the basic unit of light and all other forms of electromagnetic radiation. It is also the force carrier for the electromagnetic force...
s is significant. It could in principle be used to construct a quantum computer
Quantum computer
A quantum computer is a device for computation that makes direct use of quantum mechanical phenomena, such as superposition and entanglement, to perform operations on data. Quantum computers are different from traditional computers based on transistors...
.
The case of a single 2-level atom in the cavity is mathematically described by the Jaynes-Cummings model
Jaynes-Cummings model
The Jaynes–Cummings model is a theoretical model in quantum optics. It describes the system of a two-level atom interacting with a quantized mode of an optical cavity, with or without the presence of light...
, and undergoes vacuum Rabi oscillation
Vacuum Rabi oscillation
A vacuum Rabi oscillation is a damped oscillation of an initially excited atom coupled to an electromagnetic resonator or cavity in which the atom alternately emits photon into a single-mode electromagnetic cavity and reabsorbs them. The atom interacts with a single-mode field confined to a limited...
s
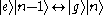 , that is between an excited atom and n-1 photons, and a ground state atom and n photons.
, that is between an excited atom and n-1 photons, and a ground state atom and n photons.If the cavity is on resonance with the atomic transition, a half-cycle of oscillation starting with no photons coherently swaps the atom qubit's state onto the cavity field's,
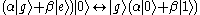 , and can be repeated to swap it back again; this could be used as a single photon source (starting with an excited atom), or as an interface between an atom or trapped ion quantum computer and optical quantum communication.
, and can be repeated to swap it back again; this could be used as a single photon source (starting with an excited atom), or as an interface between an atom or trapped ion quantum computer and optical quantum communication.Other interaction durations create entanglement
Quantum entanglement
Quantum entanglement occurs when electrons, molecules even as large as "buckyballs", photons, etc., interact physically and then become separated; the type of interaction is such that each resulting member of a pair is properly described by the same quantum mechanical description , which is...
between the atom and cavity field; for example, a quarter-cycle on resonance starting from
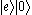 gives the maximally entangled state
gives the maximally entangled state  . This can in principle be used as a quantum computer
. This can in principle be used as a quantum computerQuantum computer
A quantum computer is a device for computation that makes direct use of quantum mechanical phenomena, such as superposition and entanglement, to perform operations on data. Quantum computers are different from traditional computers based on transistors...
, mathematically equivalent to a trapped ion quantum computer with cavity photons replacing phonons.

