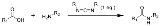
Carbodiimide
Encyclopedia
A carbodiimide or a methanediimine is a functional group
consisting of the formula RN=C=NR. Carbodiimides hydrolyze to form urea
s, which makes them uncommon in nature.
of urea
s or from thiourea
s. They are also formed by treating organic isocyanates with suitable catalysts (generally based on phosphine oxide
s); in this process, carbon dioxide
evolves from the isocyanate.
organic chemistry
, compounds containing the carbodiimide functionality are dehydration agents and are often used to activate carboxylic acid
s towards amide
or ester
formation. Additives, such as N-hydroxybenzotriazole or N-hydroxysuccinimide
, are often added to increase yields and decrease side reactions.
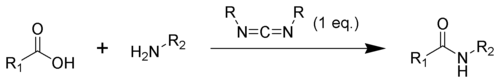 Carbodiimides can also react with amine
Carbodiimides can also react with amine
s to form guanidine
s.
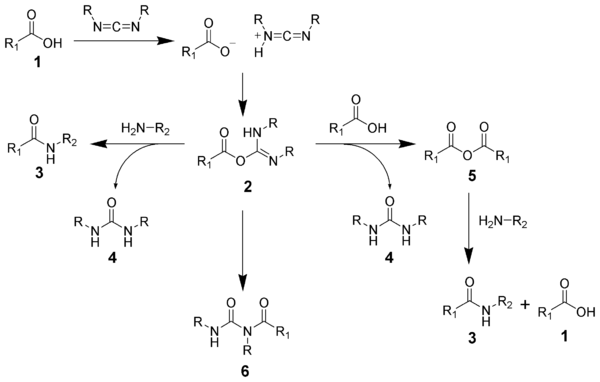
with an activated leaving group. The O-acylisourea will react with amines to give the desired amide 3 and urea 4.
The side reaction of the O-acylisourea 2 produce both desired and undesired products. The O-acylisourea 2 can react with an additional carboxylic acid 1 to give an acid anhydride 5, which can react further to give the desired amide 3. The main undesired reaction pathway involves the rearrangement of the O-acylisourea 2 to the stable N-acylurea 6. The use of solvents with low-dielectric constants such as dichloromethane
or chloroform
can minimize this side reaction.
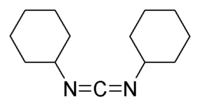
DCC (acronym for N,N'-dicyclohexylcarbodiimide
) was one of the first carbodiimides developed. It is widely used for amide and ester formation, especially for solid-phase
peptide
synthesis. DCC has achieved popularity mainly because of its high yielding amide coupling reactions and the fact that it is quite inexpensive.
However, DCC does have some serious drawbacks, and its use is often avoided unless necessary, for several reasons:
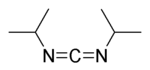
DIC (acronym for N,N'-diisopropylcarbodiimide) was developed as an alternative to DCC. DIC is identical to DCC in nearly every way except:
Functional group
In organic chemistry, functional groups are specific groups of atoms within molecules that are responsible for the characteristic chemical reactions of those molecules. The same functional group will undergo the same or similar chemical reaction regardless of the size of the molecule it is a part of...
consisting of the formula RN=C=NR. Carbodiimides hydrolyze to form urea
Urea
Urea or carbamide is an organic compound with the chemical formula CO2. The molecule has two —NH2 groups joined by a carbonyl functional group....
s, which makes them uncommon in nature.
Carbodiimide formation
Carbodiimides are formed by dehydrationDehydration reaction
In chemistry and the biological sciences, a dehydration reaction is usually defined as a chemical reaction that involves the loss of water from the reacting molecule. Dehydration reactions are a subset of elimination reactions...
of urea
Urea
Urea or carbamide is an organic compound with the chemical formula CO2. The molecule has two —NH2 groups joined by a carbonyl functional group....
s or from thiourea
Thiourea
Thiourea is an organosulfur compound of with the formula SC2 . It is structurally similar to urea, except that the oxygen atom is replaced by a sulfur atom, but the properties of urea and thiourea differ significantly. Thiourea is a reagent in organic synthesis. "Thioureas" refers to a broad...
s. They are also formed by treating organic isocyanates with suitable catalysts (generally based on phosphine oxide
Phosphine oxide
Phosphine oxides are either inorganic phosphorus compounds such as phosphoryl trichloride or organophosphorus compounds with the formula OPR3, where R = alkyl or aryl...
s); in this process, carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a naturally occurring chemical compound composed of two oxygen atoms covalently bonded to a single carbon atom...
evolves from the isocyanate.
Uses of carbodiimides
In syntheticOrganic synthesis
Organic synthesis is a special branch of chemical synthesis and is concerned with the construction of organic compounds via organic reactions. Organic molecules can often contain a higher level of complexity compared to purely inorganic compounds, so the synthesis of organic compounds has...
organic chemistry
Organic chemistry
Organic chemistry is a subdiscipline within chemistry involving the scientific study of the structure, properties, composition, reactions, and preparation of carbon-based compounds, hydrocarbons, and their derivatives...
, compounds containing the carbodiimide functionality are dehydration agents and are often used to activate carboxylic acid
Carboxylic acid
Carboxylic acids are organic acids characterized by the presence of at least one carboxyl group. The general formula of a carboxylic acid is R-COOH, where R is some monovalent functional group...
s towards amide
Amide
In chemistry, an amide is an organic compound that contains the functional group consisting of a carbonyl group linked to a nitrogen atom . The term refers both to a class of compounds and a functional group within those compounds. The term amide also refers to deprotonated form of ammonia or an...
or ester
Ester
Esters are chemical compounds derived by reacting an oxoacid with a hydroxyl compound such as an alcohol or phenol. Esters are usually derived from an inorganic acid or organic acid in which at least one -OH group is replaced by an -O-alkyl group, and most commonly from carboxylic acids and...
formation. Additives, such as N-hydroxybenzotriazole or N-hydroxysuccinimide
N-Hydroxysuccinimide
N-Hydroxysuccinimide is a compound with a molecular weight of 115.09 and a melting point of 95 °C.As it is slightly acidic, it is an irritant to skin, eyes and mucous membranes....
, are often added to increase yields and decrease side reactions.

Amine
Amines are organic compounds and functional groups that contain a basic nitrogen atom with a lone pair. Amines are derivatives of ammonia, wherein one or more hydrogen atoms have been replaced by a substituent such as an alkyl or aryl group. Important amines include amino acids, biogenic amines,...
s to form guanidine
Guanidine
Guanidine is a crystalline compound of strong alkalinity formed by the oxidation of guanine. It is used in the manufacture of plastics and explosives. It is found in urine as a normal product of protein metabolism. The molecule was first synthesized in 1861 by the oxidative degradation of an...
s.
Amide formation mechanism
The formation of an amide using a carbodiimide is straightforward, but with several side reactions complicating the subject. The acid 1 will react with the carbodiimide to produce the key intermediate: the O-acylisourea 2, which can be viewed as a carboxylic esterEster
Esters are chemical compounds derived by reacting an oxoacid with a hydroxyl compound such as an alcohol or phenol. Esters are usually derived from an inorganic acid or organic acid in which at least one -OH group is replaced by an -O-alkyl group, and most commonly from carboxylic acids and...
with an activated leaving group. The O-acylisourea will react with amines to give the desired amide 3 and urea 4.
The side reaction of the O-acylisourea 2 produce both desired and undesired products. The O-acylisourea 2 can react with an additional carboxylic acid 1 to give an acid anhydride 5, which can react further to give the desired amide 3. The main undesired reaction pathway involves the rearrangement of the O-acylisourea 2 to the stable N-acylurea 6. The use of solvents with low-dielectric constants such as dichloromethane
Dichloromethane
Dichloromethane is an organic compound with the formula CH2Cl2. This colorless, volatile liquid with a moderately sweet aroma is widely used as a solvent. Although it is not miscible with water, it is miscible with many organic solvents...
or chloroform
Chloroform
Chloroform is an organic compound with formula CHCl3. It is one of the four chloromethanes. The colorless, sweet-smelling, dense liquid is a trihalomethane, and is considered somewhat hazardous...
can minimize this side reaction.

DCC

DCC (acronym for N,N'-dicyclohexylcarbodiimide
Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide
N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide is an organic compound with chemical formula C13H22N2 whose primary use is to couple amino acids during artificial peptide synthesis. Under standard conditions, it exists in the form of white crystals with a heavy, sweet odor. The low melting point of this material...
) was one of the first carbodiimides developed. It is widely used for amide and ester formation, especially for solid-phase
Solid-phase synthesis
In chemistry, solid-phase synthesis is a method in which molecules are bound on a bead and synthesized step-by-step in a reactant solution; compared with normal synthesis in a liquid state, it is easier to remove excess reactant or byproduct from the product. In this method, building blocks are...
peptide
Peptide
Peptides are short polymers of amino acid monomers linked by peptide bonds. They are distinguished from proteins on the basis of size, typically containing less than 50 monomer units. The shortest peptides are dipeptides, consisting of two amino acids joined by a single peptide bond...
synthesis. DCC has achieved popularity mainly because of its high yielding amide coupling reactions and the fact that it is quite inexpensive.
However, DCC does have some serious drawbacks, and its use is often avoided unless necessary, for several reasons:
- The byproduct N,N'-dicyclohexylurea is mostly removed by filtration, but trace amounts remain and are often difficult to remove.
- DCC is incompatible with traditional solid-phase peptide synthesisPeptide synthesisIn organic chemistry, peptide synthesis is the production of peptides, which are organic compounds in which multiple amino acids are linked via amide bonds which are also known as peptide bonds...
. The formed N,N'-dicyclohexylureaDicyclohexylureaDicyclohexylurea is an organic compound, specifically, a urea. It is the byproduct of the reaction of dicyclohexylcarbodiimide with amines or alcohols. It may be prepared by the reaction of cyclohexylamine and S,S-dimethyl dithiocarbonate....
is mostly insoluble and is difficult to separate from the peptidePeptidePeptides are short polymers of amino acid monomers linked by peptide bonds. They are distinguished from proteins on the basis of size, typically containing less than 50 monomer units. The shortest peptides are dipeptides, consisting of two amino acids joined by a single peptide bond...
resinResinResin in the most specific use of the term is a hydrocarbon secretion of many plants, particularly coniferous trees. Resins are valued for their chemical properties and associated uses, such as the production of varnishes, adhesives, and food glazing agents; as an important source of raw materials...
. - DCC is a potent allergenAllergenAn allergen is any substance that can cause an allergy. In technical terms, an allergen is a non-parasitic antigen capable of stimulating a type-I hypersensitivity reaction in atopic individuals....
, repeated contact with skin increases the probability of sensitization to the compound. Clinical reports of individuals who cannot enter rooms where peptide coupling agents are used have been reported.
DIC
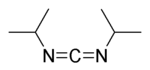
DIC (acronym for N,N'-diisopropylcarbodiimide) was developed as an alternative to DCC. DIC is identical to DCC in nearly every way except:
- As a liquid, DIC is easier to handle than DCC (which is a waxy solid).
- The product, N,N'-diisopropylurea, is soluble in organic solvents and is easily removed by extraction. Hence, DIC is more often used in solid-phase synthesisSolid-phase synthesisIn chemistry, solid-phase synthesis is a method in which molecules are bound on a bead and synthesized step-by-step in a reactant solution; compared with normal synthesis in a liquid state, it is easier to remove excess reactant or byproduct from the product. In this method, building blocks are...
. - DIC is far less likely than DCC to cause an allergic reaction.

