
CPT theorem
Encyclopedia
In quantum field theory
the CPT theorem states that any canonical (that is, local and Lorentz-covariant
) quantum field theory is invariant under the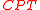 operation, which is a combination of three discrete transformations: charge conjugation
operation, which is a combination of three discrete transformations: charge conjugation  , parity transformation
, parity transformation 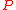 , and time reversal
, and time reversal
 . It was first proved by G.Lüders
. It was first proved by G.Lüders
, W.Pauli
and J.Bell
in the framework of Lagrangian field theory.
At present,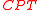 is the sole combination of
is the sole combination of  ,
, 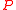 ,
,  observed as an exact symmetry of nature at the fundamental level.
observed as an exact symmetry of nature at the fundamental level.
Quantum field theory
Quantum field theory provides a theoretical framework for constructing quantum mechanical models of systems classically parametrized by an infinite number of dynamical degrees of freedom, that is, fields and many-body systems. It is the natural and quantitative language of particle physics and...
the CPT theorem states that any canonical (that is, local and Lorentz-covariant
Principle of covariance
In physics, the principle of covariance emphasizes formulation of physical laws using only those physical quantities the measurements of which the observers in different frames of reference could unambiguously correlate....
) quantum field theory is invariant under the
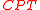 operation, which is a combination of three discrete transformations: charge conjugation
operation, which is a combination of three discrete transformations: charge conjugation  , parity transformation
, parity transformation 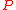 , and time reversal
, and time reversalT-symmetry
T Symmetry is the symmetry of physical laws under a time reversal transformation: T: t \mapsto -t.Although in restricted contexts one may find this symmetry, the observable universe itself does not show symmetry under time reversal, primarily due to the second law of thermodynamics.Time asymmetries...
 . It was first proved by G.Lüders
. It was first proved by G.LüdersGerhart Lüders
Gerhart Lüders was a German theoretical physicist who worked mainly in quantum field theory and was well known for the discovery and a general proof of the CPT theorem...
, W.Pauli
Wolfgang Pauli
Wolfgang Ernst Pauli was an Austrian theoretical physicist and one of the pioneers of quantum physics. In 1945, after being nominated by Albert Einstein, he received the Nobel Prize in Physics for his "decisive contribution through his discovery of a new law of Nature, the exclusion principle or...
and J.Bell
John Stewart Bell
John Stewart Bell FRS was a British physicist from Northern Ireland , and the originator of Bell's theorem, a significant theorem in quantum physics regarding hidden variable theories.- Early life and work :...
in the framework of Lagrangian field theory.
At present,
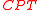 is the sole combination of
is the sole combination of  ,
, 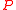 ,
,  observed as an exact symmetry of nature at the fundamental level.
observed as an exact symmetry of nature at the fundamental level.

