CD14
Encyclopedia
Cluster of differentiation 14 also known as CD14 is a human gene
.
The protein
encoded by this gene is a component of the innate immune system
. CD14 exists in two forms. Either it is anchored into the membrane by a glycosylphosphatidylinositol tail (mCD14) or it appears in a soluble form (sCD14). Soluble CD14 either appears after shedding of mCD14 (48 KDa
) or is directly secreted from intracellular vesicles (56 KDa).
CD14 takes its name from its inclusion in the cluster of differentiation
group of cell surface marker proteins.
CD14 was the first described pattern recognition receptor
.
TLR 4
and MD-2) for the detection of bacterial lipopolysaccharide
(LPS). CD14 can bind LPS only in the presence of lipopolysaccharide-binding protein
(LBP).
Although LPS is considered its main ligand
, CD14 also recognizes other pathogen-associated molecular patterns.
and monocyte
s and is sufficient in low concentrations to confer LPS-responsiveness to cells that otherwise do not express CD14. sCD14 is also present in human milk, where it is believed to regulate microbial growth in the infant gut.
One type of cell is the dendritic cell
, where differentiation is encouraged by cytokines. Examples of cytokines that will cause dendritic cell differentiation includes GM-CSF and IL-4.
with Lipopolysaccharide-binding protein
.
Gene
A gene is a molecular unit of heredity of a living organism. It is a name given to some stretches of DNA and RNA that code for a type of protein or for an RNA chain that has a function in the organism. Living beings depend on genes, as they specify all proteins and functional RNA chains...
.
The protein
Protein
Proteins are biochemical compounds consisting of one or more polypeptides typically folded into a globular or fibrous form, facilitating a biological function. A polypeptide is a single linear polymer chain of amino acids bonded together by peptide bonds between the carboxyl and amino groups of...
encoded by this gene is a component of the innate immune system
Innate immune system
The innate immune system, also known as non-specific immune system and secondary line of defence, comprises the cells and mechanisms that defend the host from infection by other organisms in a non-specific manner...
. CD14 exists in two forms. Either it is anchored into the membrane by a glycosylphosphatidylinositol tail (mCD14) or it appears in a soluble form (sCD14). Soluble CD14 either appears after shedding of mCD14 (48 KDa
KDA
KDA may refer to:* Karachi Development Authority* Kongsberg Defence & Aerospace* Kotelawala Defence Academy* Kramer Design Associates* Lithium diisopropylamide, KDA is the potassium analogue of lithium diisopropylamideOr kDa may refer to:...
) or is directly secreted from intracellular vesicles (56 KDa).
CD14 takes its name from its inclusion in the cluster of differentiation
Cluster of differentiation
The cluster of differentiation is a protocol used for the identification and investigation of cell surface molecules present on white blood cells, providing targets for immunophenotyping of cells...
group of cell surface marker proteins.
CD14 was the first described pattern recognition receptor
Pattern recognition receptor
Pattern recognition receptors are a primitive part of the immune system. They are proteins expressed by cells of the innate immune system to identify pathogen-associated molecular patterns , which are associated with microbial pathogens or cellular stress, as well as damage-associated molecular...
.
Function
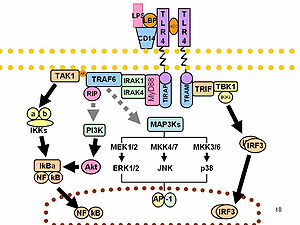
CD14 acts as a co-receptor (along with the Toll-like receptorToll-like receptor
Toll-like receptors are a class of proteins that play a key role in the innate immune system. They are single, membrane-spanning, non-catalytic receptors that recognize structurally conserved molecules derived from microbes...
TLR 4
TLR 4
Toll-like receptor 4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TLR4 gene. TLR 4 is a toll-like receptor. It detects lipopolysaccharide from Gram-negative bacteria and is thus important in the activation of the innate immune system...
and MD-2) for the detection of bacterial lipopolysaccharide
Lipopolysaccharide
Lipopolysaccharides , also known as lipoglycans, are large molecules consisting of a lipid and a polysaccharide joined by a covalent bond; they are found in the outer membrane of Gram-negative bacteria, act as endotoxins and elicit strong immune responses in animals.-Functions:LPS is the major...
(LPS). CD14 can bind LPS only in the presence of lipopolysaccharide-binding protein
Lipopolysaccharide-binding protein
Lipopolysaccharide-binding protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the LBP gene.LBP is a soluble acute-phase protein that binds to bacterial lipopolysaccharide to elicit immune responses by presenting the LPS to important cell surface pattern recognition receptors called CD14 and...
(LBP).
Although LPS is considered its main ligand
Ligand
In coordination chemistry, a ligand is an ion or molecule that binds to a central metal atom to form a coordination complex. The bonding between metal and ligand generally involves formal donation of one or more of the ligand's electron pairs. The nature of metal-ligand bonding can range from...
, CD14 also recognizes other pathogen-associated molecular patterns.

Tissue distribution
CD14 is expressed mainly by macrophages and (at 10 times lesser extent) by neutrophil granulocytes. It is also expressed by dendritic cells. A soluble form sCD14 is secreted by the liverLiver
The liver is a vital organ present in vertebrates and some other animals. It has a wide range of functions, including detoxification, protein synthesis, and production of biochemicals necessary for digestion...
and monocyte
Monocyte
Monocytes are a type of white blood cell and are part of the innate immune system of vertebrates including all mammals , birds, reptiles, and fish. Monocytes play multiple roles in immune function...
s and is sufficient in low concentrations to confer LPS-responsiveness to cells that otherwise do not express CD14. sCD14 is also present in human milk, where it is believed to regulate microbial growth in the infant gut.
Differentiation
CD14+ cells are monocytes that can differentiate into a host of different cells. (A '+' sign refers to the presence of the CD14 protein on a cell. )One type of cell is the dendritic cell
Dendritic cell
Dendritic cells are immune cells forming part of the mammalian immune system. Their main function is to process antigen material and present it on the surface to other cells of the immune system. That is, dendritic cells function as antigen-presenting cells...
, where differentiation is encouraged by cytokines. Examples of cytokines that will cause dendritic cell differentiation includes GM-CSF and IL-4.
Interactions
CD14 has been shown to interactProtein-protein interaction
Protein–protein interactions occur when two or more proteins bind together, often to carry out their biological function. Many of the most important molecular processes in the cell such as DNA replication are carried out by large molecular machines that are built from a large number of protein...
with Lipopolysaccharide-binding protein
Lipopolysaccharide-binding protein
Lipopolysaccharide-binding protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the LBP gene.LBP is a soluble acute-phase protein that binds to bacterial lipopolysaccharide to elicit immune responses by presenting the LPS to important cell surface pattern recognition receptors called CD14 and...
.

