
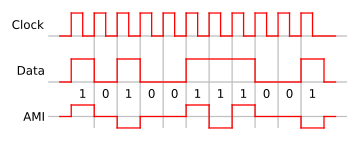
Bipolar encoding
Encyclopedia
Line code
In telecommunication, a line code is a code chosen for use within a communications system for baseband transmission purposes...
(a method of encoding digital information to make it resistant to certain forms of signal loss during transmission). A duobinary signal is such an encoding.
Advantages
A binary 0 is encoded as zero volts as in unipolar encodingUnipolar encoding
Unipolar encoding is a line code. A positive voltage represents a binary 1, and zero volts indicates a binary 0. It is the simplest line code, directly encoding the bitstream, and is analogous to on-off keying in modulation....
. A binary 1 is encoded alternately as a positive voltage and a negative voltage. This prevents a significant build-up of DC
Direct current
Direct current is the unidirectional flow of electric charge. Direct current is produced by such sources as batteries, thermocouples, solar cells, and commutator-type electric machines of the dynamo type. Direct current may flow in a conductor such as a wire, but can also flow through...
, as the positive and negative pulses average to zero volts. Little or no DC-component is considered an advantage because the cable may then be used for longer distances and to carry power for intermediate equipment such as line repeater
Repeater
A repeater is an electronic device that receives asignal and retransmits it at a higher level and/or higher power, or onto the other side of an obstruction, so that the signal can cover longer distances.-Description:...
s. The DC-component can be easily and cheaply removed before the signal reaches the decoding circuitry.
Bipolar encoding is preferable to non-return-to-zero
Non-return-to-zero
In telecommunication, a non-return-to-zero line code is a binary code in which 1's are represented by one significant condition and 0's are represented by some other significant condition , with no other neutral or rest condition. The pulses have more energy than a RZ code...
where signal transitions are required to maintain synchronization between the transmitter and receiver. Other systems must synchronize using some form of out-of-band communication, or add frame synchronization
Frame synchronization
While receiving a stream of framed data, frame synchronization is the process by which incoming frame alignment signals, i.e., distinctive bit sequences , are identified, i.e., distinguished from data bits, permitting the data bits within the frame to be extracted for decoding or retransmission...
sequences that don't carry data to the signal. These alternative approaches require either an additional transmission medium for the clock signal or a loss of performance due to overhead, respectively. A bipolar encoding is an often good compromise: runs of ones will not cause a lack of transitions, however long sequences of zeroes are still an issue. Long sequences of zero bits result in no transitions and a loss of synchronization. Where frequent transitions are a requirement, a self-clocking encoding such as return-to-zero
Return-to-zero
For the Delp/Goudreau band, see RTZReturn-to-zero describes a line code used in telecommunications signals in which the signal drops to zero between each pulse. This takes place even if a number of consecutive 0's or 1's occur in the signal. The signal is self-clocking...
or some other more complicated line code
Line code
In telecommunication, a line code is a code chosen for use within a communications system for baseband transmission purposes...
may be more appropriate, though they introduce significant overhead.
Alternate mark inversion
When used on a T-carrierT-carrier
In telecommunications, T-carrier, sometimes abbreviated as T-CXR, is the generic designator for any of several digitally multiplexed telecommunications carrier systems originally developed by Bell Labs and used in North America, Japan, and South Korea....
, the code is known as alternate mark inversion because, in this context, a binary '1' is referred to as a "mark", while a binary '0' is called a "space". The coding was used extensively in first-generation PCM
Pulse-code modulation
Pulse-code modulation is a method used to digitally represent sampled analog signals. It is the standard form for digital audio in computers and various Blu-ray, Compact Disc and DVD formats, as well as other uses such as digital telephone systems...
networks, and is still commonly seen on older multiplexing
Multiplexing
The multiplexed signal is transmitted over a communication channel, which may be a physical transmission medium. The multiplexing divides the capacity of the low-level communication channel into several higher-level logical channels, one for each message signal or data stream to be transferred...
equipment today, but successful transmission relies on no long runs of zeroes being present. No more than 15 consecutive zeros should ever be sent to ensure synchronization. The modification of bit 7 causes a change to voice that is undetectable by the human ear, but it is an unacceptable corruption of a data stream. Data channels are required to use some other form of pulse-stuffing, such as always setting bit 8 to '1', in order to maintain a sufficient density of ones. If the characteristics of the input data do not follow the pattern that every eighth bit is '1', the coder using alternate mark inversion adds a '1' after seven consecutive zeros to maintain synchronisation. On the decoder side, this extra '1' added by the coder is removed, resulting that the correct data arrives for the receiver. Due to this, the data sent between the coder and the decoder is longer than the original data by less than 1% on average. Of course, this lowers the effective data throughput to 56 kbit/s per channel.
Error detection
Another benefit of bipolar encoding compared to unipolar is error detection. In the T-carrier example, the bipolar signals are regenerated at regular intervals so that signals diminished by distance are not just amplified, but detected and recreated anew. Weakened signals corrupted by noise could cause errors, a mark interpreted as zero, or zero as positive or negative mark. Every single-bit error results in a violation of the bipolar rule. Each such bipolar violationBipolar violation
A bipolar violation, bipolarity violation, or BPV, is a violation of the bipolar encoding rules where two pulses of the same polarity occur without an intervening pulse of the opposite polarity. This indicates an error in the transmission of the signal.T-carrier and E-carrier signals are...
(BPV) is an indication of a transmission error. (The location of BPV is not necessarily the location of the original error).
Other T1 encoding schemes
For data channels, in order to avoid the need of always setting bit 8 to 1, as described above, other T1 encoding schemes (Modified AMI codeModified AMI code
Modified AMI codes are Alternate Mark Inversion line codes in which bipolar violations may be deliberately inserted to maintain system synchronization. There are several types of modified AMI codes, used in various T-carrier and E-carrier systems....
s) ensure regular transitions regardless of the data being carried. In this way, data throughput of 64 kbit/s per channel is achieved. B8ZS is a newer format for North America, where HDB3 is the original line coding type used in Europe and Japan.
A very similar encoding scheme, with the logical positions reversed, is also used and is often referred to as pseudoternary encoding. This encoding is otherwise identical.
See also
- MLT-3 encodingMLT-3 encodingMLT-3 encoding is a line code that uses three voltage levels...
- polar encoding

