
Biological exponential growth
Encyclopedia
Biological exponential growth is the exponential growth of biological organisms. When the resources availability is unlimited in the habitat
, the population
of an organism
living in the habitat grows in an exponential
or geometric fashion.
Resource availability is obviously essential for the unimpeded growth of a population. Ideally, when resources in the habitat are unlimited, each species has the ability to realise fully its innate potential to grow in number, as Charles Darwin
observed while developing his theory of natural selection
.
If, in a hypothetical population of size N, the birth rates (per capita) are represented as b and death rates (per capita) as d, then the increase or decrease in N during a time period t will be:
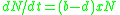
(b-d) is called the 'intrinsic rate of natural increase' and is a very important parameter chosen for assessing the impacts of any biotic or abiotic factor
on population growth.
Any species growing exponentially under unlimited resource conditions can reach enormous population densities
in a short time. Darwin showed how even a slow growing animal like the elephant
could reach an enormous population if there were unlimited resources for its growth in its habitat.
If birth giving takes two parents we get Nurgaliev's law
.
Habitat
* Habitat , a place where a species lives and grows*Human habitat, a place where humans live, work or play** Space habitat, a space station intended as a permanent settlement...
, the population
Population
A population is all the organisms that both belong to the same group or species and live in the same geographical area. The area that is used to define a sexual population is such that inter-breeding is possible between any pair within the area and more probable than cross-breeding with individuals...
of an organism
Organism
In biology, an organism is any contiguous living system . In at least some form, all organisms are capable of response to stimuli, reproduction, growth and development, and maintenance of homoeostasis as a stable whole.An organism may either be unicellular or, as in the case of humans, comprise...
living in the habitat grows in an exponential
Exponential growth
Exponential growth occurs when the growth rate of a mathematical function is proportional to the function's current value...
or geometric fashion.
Resource availability is obviously essential for the unimpeded growth of a population. Ideally, when resources in the habitat are unlimited, each species has the ability to realise fully its innate potential to grow in number, as Charles Darwin
Charles Darwin
Charles Robert Darwin FRS was an English naturalist. He established that all species of life have descended over time from common ancestry, and proposed the scientific theory that this branching pattern of evolution resulted from a process that he called natural selection.He published his theory...
observed while developing his theory of natural selection
Natural selection
Natural selection is the nonrandom process by which biologic traits become either more or less common in a population as a function of differential reproduction of their bearers. It is a key mechanism of evolution....
.
If, in a hypothetical population of size N, the birth rates (per capita) are represented as b and death rates (per capita) as d, then the increase or decrease in N during a time period t will be:
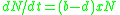
(b-d) is called the 'intrinsic rate of natural increase' and is a very important parameter chosen for assessing the impacts of any biotic or abiotic factor
Abiotic components
In biology and ecology, abiotic components are non-living chemical and physical factors in the environment which affect ecosystems. Abiotic phenomena underlie all of biology. Abiotic factors, while generally downplayed, can have enormous impact on ramonds evolution...
on population growth.
Any species growing exponentially under unlimited resource conditions can reach enormous population densities
Population density
Population density is a measurement of population per unit area or unit volume. It is frequently applied to living organisms, and particularly to humans...
in a short time. Darwin showed how even a slow growing animal like the elephant
Elephant
Elephants are large land mammals in two extant genera of the family Elephantidae: Elephas and Loxodonta, with the third genus Mammuthus extinct...
could reach an enormous population if there were unlimited resources for its growth in its habitat.
If birth giving takes two parents we get Nurgaliev's law
Nurgaliev's law
In population dynamics, Nurgaliev's law is an equation that describes the rate of change of the size of a population at a given time, in terms of the current population size...
.

