
Big Rip
Encyclopedia
The Big Rip is a cosmological
hypothesis
first published in 2003, about the ultimate fate of the universe
, in which the matter of the universe
, from stars and galaxies to atoms and subatomic particles, is progressively torn apart by the expansion of the universe
at a certain time in the future. Theoretically, the scale factor
of the universe becomes infinite at a finite time in the future.
in the universe
. The key value is the equation of state
parameter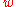 , the ratio
, the ratio
between the dark energy pressure and its energy density
. At < −1, the universe will eventually be pulled apart. Such energy is called phantom energy
< −1, the universe will eventually be pulled apart. Such energy is called phantom energy
, an extreme form of quintessence
.
A universe dominated by phantom energy expands at an ever-increasing rate. However, this implies that the size of the observable universe
is continually shrinking; the distance to the edge of the observable universe which is moving away at the speed of light from any point moves ever closer. When the size of the observable universe becomes smaller than any particular structure, no interaction by any of the fundamental forces (gravitational, electromagnetic
, weak, or strong
) can occur between the most remote parts of the structure. When these interactions become impossible, the structure is "ripped apart". The model implies that after a finite time there will be a final singularity, called the "Big Rip", in which all distances diverge to infinite values.
The authors of this hypothesis, led by Robert Caldwell of Dartmouth College
, calculate the time from the present to the end of the universe as we know it for this form of energy to be
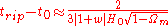
where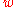 is defined above, H0 is Hubble's constant and Ωm is the present value of the density of all the matter in the universe.
is defined above, H0 is Hubble's constant and Ωm is the present value of the density of all the matter in the universe.
In their paper, the authors consider an example with = −1.5, H0 = 70 km/s/Mpc and Ωm = 0.3, in which case the end of the universe is approximately 22 billion years from the present. This is not considered a prediction, but a hypothetical example. The authors note that evidence indicates
= −1.5, H0 = 70 km/s/Mpc and Ωm = 0.3, in which case the end of the universe is approximately 22 billion years from the present. This is not considered a prediction, but a hypothetical example. The authors note that evidence indicates 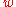 to be very close to −1 in our universe, which makes
to be very close to −1 in our universe, which makes  the dominating term in the equation. The closer that the quantity (1 +
the dominating term in the equation. The closer that the quantity (1 + 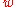 ) is to zero, the closer the denominator is to zero and the further the Big Rip is in the future. If
) is to zero, the closer the denominator is to zero and the further the Big Rip is in the future. If 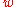 were exactly equal to −1, the Big Rip could not happen, regardless of the values of H0 or Ωm.
were exactly equal to −1, the Big Rip could not happen, regardless of the values of H0 or Ωm.
In their scenario for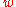 = −1.5, the galaxies would first be separated from each other. About 60 million years before the end, gravity would be too weak to hold the Milky Way
= −1.5, the galaxies would first be separated from each other. About 60 million years before the end, gravity would be too weak to hold the Milky Way
and other individual galaxies together. Approximately three months before the end, the solar system
(or systems similar to our own at this time, as the fate of our own solar system 7.5 billion years in the future is questionable) would be gravitationally unbound. In the last minutes, stars and planets would be torn apart, and an instant before the end, atom
s would be destroyed.
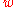 < −1,
< −1, 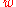 = −1, and
= −1, and 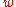 > −1.
> −1.
Physical cosmology
Physical cosmology, as a branch of astronomy, is the study of the largest-scale structures and dynamics of the universe and is concerned with fundamental questions about its formation and evolution. For most of human history, it was a branch of metaphysics and religion...
hypothesis
Hypothesis
A hypothesis is a proposed explanation for a phenomenon. The term derives from the Greek, ὑποτιθέναι – hypotithenai meaning "to put under" or "to suppose". For a hypothesis to be put forward as a scientific hypothesis, the scientific method requires that one can test it...
first published in 2003, about the ultimate fate of the universe
Ultimate fate of the universe
The ultimate fate of the universe is a topic in physical cosmology. Many possible fates are predicted by rival scientific theories, including futures of both finite and infinite duration....
, in which the matter of the universe
Universe
The Universe is commonly defined as the totality of everything that exists, including all matter and energy, the planets, stars, galaxies, and the contents of intergalactic space. Definitions and usage vary and similar terms include the cosmos, the world and nature...
, from stars and galaxies to atoms and subatomic particles, is progressively torn apart by the expansion of the universe
Metric expansion of space
The metric expansion of space is the increase of distance between distant parts of the universe with time. It is an intrinsic expansion—that is, it is defined by the relative separation of parts of the universe and not by motion "outward" into preexisting space...
at a certain time in the future. Theoretically, the scale factor
Scale factor (Universe)
The scale factor or cosmic scale factor parameter of the Friedmann equations is a function of time which represents the relative expansion of the universe. It is sometimes called the Robertson-Walker scale factor...
of the universe becomes infinite at a finite time in the future.
Definition and overview
The hypothesis relies crucially on the type of dark energyDark energy
In physical cosmology, astronomy and celestial mechanics, dark energy is a hypothetical form of energy that permeates all of space and tends to accelerate the expansion of the universe. Dark energy is the most accepted theory to explain recent observations that the universe appears to be expanding...
in the universe
Universe
The Universe is commonly defined as the totality of everything that exists, including all matter and energy, the planets, stars, galaxies, and the contents of intergalactic space. Definitions and usage vary and similar terms include the cosmos, the world and nature...
. The key value is the equation of state
Equation of state (cosmology)
In cosmology, the equation of state of a perfect fluid is characterized by a dimensionless number \! w, equal to the ratio of its pressure \! p to its energy density \! \rho: \! w=p/\rho...
parameter
 , the ratio
, the ratioRatio
In mathematics, a ratio is a relationship between two numbers of the same kind , usually expressed as "a to b" or a:b, sometimes expressed arithmetically as a dimensionless quotient of the two which explicitly indicates how many times the first number contains the second In mathematics, a ratio is...
between the dark energy pressure and its energy density
Energy density
Energy density is a term used for the amount of energy stored in a given system or region of space per unit volume. Often only the useful or extractable energy is quantified, which is to say that chemically inaccessible energy such as rest mass energy is ignored...
. At
 < −1, the universe will eventually be pulled apart. Such energy is called phantom energy
< −1, the universe will eventually be pulled apart. Such energy is called phantom energyPhantom energy
Phantom energy is a hypothetical form of dark energy with equation of state \! w Phantom energy is a hypothetical form of dark energy with equation of state...
, an extreme form of quintessence
Quintessence (physics)
In physics, quintessence is a hypothetical form of dark energy postulated as an explanation of observations of an accelerating universe. It has been proposed by some physicists to be a fifth fundamental force...
.
A universe dominated by phantom energy expands at an ever-increasing rate. However, this implies that the size of the observable universe
Observable universe
In Big Bang cosmology, the observable universe consists of the galaxies and other matter that we can in principle observe from Earth in the present day, because light from those objects has had time to reach us since the beginning of the cosmological expansion...
is continually shrinking; the distance to the edge of the observable universe which is moving away at the speed of light from any point moves ever closer. When the size of the observable universe becomes smaller than any particular structure, no interaction by any of the fundamental forces (gravitational, electromagnetic
Electromagnetism
Electromagnetism is one of the four fundamental interactions in nature. The other three are the strong interaction, the weak interaction and gravitation...
, weak, or strong
Strong interaction
In particle physics, the strong interaction is one of the four fundamental interactions of nature, the others being electromagnetism, the weak interaction and gravitation. As with the other fundamental interactions, it is a non-contact force...
) can occur between the most remote parts of the structure. When these interactions become impossible, the structure is "ripped apart". The model implies that after a finite time there will be a final singularity, called the "Big Rip", in which all distances diverge to infinite values.
The authors of this hypothesis, led by Robert Caldwell of Dartmouth College
Dartmouth College
Dartmouth College is a private, Ivy League university in Hanover, New Hampshire, United States. The institution comprises a liberal arts college, Dartmouth Medical School, Thayer School of Engineering, and the Tuck School of Business, as well as 19 graduate programs in the arts and sciences...
, calculate the time from the present to the end of the universe as we know it for this form of energy to be
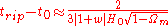
where
 is defined above, H0 is Hubble's constant and Ωm is the present value of the density of all the matter in the universe.
is defined above, H0 is Hubble's constant and Ωm is the present value of the density of all the matter in the universe.In their paper, the authors consider an example with
 = −1.5, H0 = 70 km/s/Mpc and Ωm = 0.3, in which case the end of the universe is approximately 22 billion years from the present. This is not considered a prediction, but a hypothetical example. The authors note that evidence indicates
= −1.5, H0 = 70 km/s/Mpc and Ωm = 0.3, in which case the end of the universe is approximately 22 billion years from the present. This is not considered a prediction, but a hypothetical example. The authors note that evidence indicates  to be very close to −1 in our universe, which makes
to be very close to −1 in our universe, which makes  the dominating term in the equation. The closer that the quantity (1 +
the dominating term in the equation. The closer that the quantity (1 +  ) is to zero, the closer the denominator is to zero and the further the Big Rip is in the future. If
) is to zero, the closer the denominator is to zero and the further the Big Rip is in the future. If  were exactly equal to −1, the Big Rip could not happen, regardless of the values of H0 or Ωm.
were exactly equal to −1, the Big Rip could not happen, regardless of the values of H0 or Ωm.In their scenario for
 = −1.5, the galaxies would first be separated from each other. About 60 million years before the end, gravity would be too weak to hold the Milky Way
= −1.5, the galaxies would first be separated from each other. About 60 million years before the end, gravity would be too weak to hold the Milky WayMilky Way
The Milky Way is the galaxy that contains the Solar System. This name derives from its appearance as a dim un-resolved "milky" glowing band arching across the night sky...
and other individual galaxies together. Approximately three months before the end, the solar system
Solar System
The Solar System consists of the Sun and the astronomical objects gravitationally bound in orbit around it, all of which formed from the collapse of a giant molecular cloud approximately 4.6 billion years ago. The vast majority of the system's mass is in the Sun...
(or systems similar to our own at this time, as the fate of our own solar system 7.5 billion years in the future is questionable) would be gravitationally unbound. In the last minutes, stars and planets would be torn apart, and an instant before the end, atom
Atom
The atom is a basic unit of matter that consists of a dense central nucleus surrounded by a cloud of negatively charged electrons. The atomic nucleus contains a mix of positively charged protons and electrically neutral neutrons...
s would be destroyed.
Experimental data
According to the latest cosmological data available, the uncertainties are still too large to discriminate among the three cases < −1,
< −1,  = −1, and
= −1, and  > −1.
> −1.See also
- List of astronomical topics
- Heat-death of the Universe
- Big CrunchBig CrunchIn physical cosmology, the Big Crunch is one possible scenario for the ultimate fate of the universe, in which the metric expansion of space eventually reverses and the universe recollapses, ultimately ending as a black hole singularity.- Overview :...
- Big BounceBig BounceThe Big Bounce is a theoretical scientific model of the formation of the known universe. It is implied by the cyclic model or oscillatory universe interpretation of the Big Bang where the first cosmological event was the result of the collapse of a previous universe.- Expansion and contraction...
- Big Freeze
- Accelerating universeAccelerating universeThe accelerating universe is the observation that the universe appears to be expanding at an increasing rate, which in formal terms means that the cosmic scale factor a has a positive second derivative, implying that the velocity at which a given galaxy is receding from us should be continually...
- Ultimate fate of the UniverseUltimate fate of the universeThe ultimate fate of the universe is a topic in physical cosmology. Many possible fates are predicted by rival scientific theories, including futures of both finite and infinite duration....
- Phantom energyPhantom energyPhantom energy is a hypothetical form of dark energy with equation of state \! w Phantom energy is a hypothetical form of dark energy with equation of state...
- Cyclic ModelCyclic modelA cyclic model is any of several cosmological models in which the universe follows infinite, self-sustaining cycles. For example, the oscillating universe theory briefly considered by Albert Einstein in 1930 theorized a universe following an eternal series of oscillations, each beginning with a...
- Dark energyDark energyIn physical cosmology, astronomy and celestial mechanics, dark energy is a hypothetical form of energy that permeates all of space and tends to accelerate the expansion of the universe. Dark energy is the most accepted theory to explain recent observations that the universe appears to be expanding...

