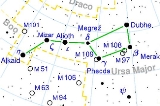
Big Dipper
Overview
Saptarshi
The Saptarishi are the seven rishis who are extolled at many places in the Vedas and Hindu literature. The Vedic Samhitas never actually enumerate these rishis by name, though later Vedic texts such as the Brahmanas and Upanisads do so. They are regarded in the Vedas as the patriarchs of the...
), is an asterism
Asterism (astronomy)
In astronomy, an asterism is a pattern of stars recognized on Earth's night sky. It may form part of an official constellation, or be composed of stars from more than one. Like constellations, asterisms are in most cases composed of stars which, while they are visible in the same general direction,...
of seven star
Star
A star is a massive, luminous sphere of plasma held together by gravity. At the end of its lifetime, a star can also contain a proportion of degenerate matter. The nearest star to Earth is the Sun, which is the source of most of the energy on Earth...
s that has been recognized as a distinct grouping in many cultures from time immemorial. The component stars are the seven brightest of the formal constellation
Constellation
In modern astronomy, a constellation is an internationally defined area of the celestial sphere. These areas are grouped around asterisms, patterns formed by prominent stars within apparent proximity to one another on Earth's night sky....
Ursa Major
Ursa Major
Ursa Major , also known as the Great Bear, is a constellation visible throughout the year in most of the northern hemisphere. It can best be seen in April...
.
The Plough is significant because the North Star (Polaris
Polaris
Polaris |Alpha]] Ursae Minoris, commonly North Star or Pole Star, also Lodestar) is the brightest star in the constellation Ursa Minor. It is very close to the north celestial pole, making it the current northern pole star....
), the current northern
True north
True north is the direction along the earth's surface towards the geographic North Pole.True geodetic north usually differs from magnetic north , and from grid north...
pole star
Pole star
The term "Pole Star" usually refers to Polaris, which is the current northern pole star, also known as the North Star.In general, however, a pole star is a visible star, especially a prominent one, that is approximately aligned with the Earth's axis of rotation; that is, a star whose apparent...
on Earth
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun, and the densest and fifth-largest of the eight planets in the Solar System. It is also the largest of the Solar System's four terrestrial planets...
, can be found using it. Polaris
Polaris
Polaris |Alpha]] Ursae Minoris, commonly North Star or Pole Star, also Lodestar) is the brightest star in the constellation Ursa Minor. It is very close to the north celestial pole, making it the current northern pole star....
is part of the "Little Dipper", Ursa Minor
Ursa Minor
Ursa Minor , also known as the Little Bear, is a constellation in the northern sky. Like the Great Bear, the tail of the Little Bear may also be seen as the handle of a ladle, whence the name Little Dipper...
.
In Hindu astronomy
Hindu astronomy
Historical Indian astronomy develops as a discipline of Vedanga or one of the "auxiliary disciplines" associated with the study of the Vedas.The oldest extant text of astronomy is the treatise by Lagadha, dated to the Mauryan era ....
, it is referred to as Sapta Rishi, meaning the "Seven (Great) Sages
Saptarshi
The Saptarishi are the seven rishis who are extolled at many places in the Vedas and Hindu literature. The Vedic Samhitas never actually enumerate these rishis by name, though later Vedic texts such as the Brahmanas and Upanisads do so. They are regarded in the Vedas as the patriarchs of the...
".
Throughout eastern Asia, these stars compose the Northern Dipper.
Unanswered Questions

