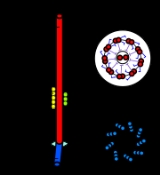
Basal body
Overview
Organelle
In cell biology, an organelle is a specialized subunit within a cell that has a specific function, and is usually separately enclosed within its own lipid bilayer....
formed from a centriole
Centriole
A Centriole is a barrel-shaped cell structure found in most animal eukaryotic cells, though it is absent in higher plants and most fungi. The walls of each centriole are usually composed of nine triplets of microtubules...
, and a short cylindrical array of microtubules. It is found at the base of a eukaryotic undulipodium
Undulipodium
An undulipodium or 9+2 organelle is an intracellular projection of a eukaryotic cell containing a microtubule array. Both eukaryotic flagella and eukaryotic cilia are considered undulipodia....
(cilium
Cilium
A cilium is an organelle found in eukaryotic cells. Cilia are slender protuberances that project from the much larger cell body....
or flagellum
Flagellum
A flagellum is a tail-like projection that protrudes from the cell body of certain prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, and plays the dual role of locomotion and sense organ, being sensitive to chemicals and temperatures outside the cell. There are some notable differences between prokaryotic and...
) and serves as a nucleation site for the growth of the axoneme
Axoneme
Numerous eukaryotic cells carry whip-like appendages whose inner core consists of a cytoskeletal structure called the axoneme....
microtubules. Centrioles, from which basal bodies are derived, act as anchoring sites for proteins that in turn anchor microtubules within centrosomes, one type of microtubule organizing center
Microtubule organizing center
The microtubule-organizing center is a structure found in eukaryotic cells from which microtubules emerge. MTOCs have two main functions: the organization of eukaryotic flagella and cilia and the organization of the mitotic and meiotic spindle apparatus, which separate the chromosomes during cell...
(MTOC). These microtubules provide structure and facilitate movement of vesicles and organelles within many eukaryotic cells.

