
Average True Range
Encyclopedia
Average True Range is a technical analysis
volatility
indicator originally developed by J. Welles Wilder, Jr. for commodities. The indicator does not provide an indication of price trend
, simply the degree of price volatility
.
The average true range is an N-day exponential moving average of the true range values. Wilder recommended a 14-period smoothing.
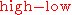 . The true range extends it to yesterday's closing price if it was outside of today's range.
. The true range extends it to yesterday's closing price if it was outside of today's range.
The true range is the largest of the:
The idea of ranges is that they show the commitment or enthusiasm of traders. Large or increasing ranges suggest traders prepared to continue to bid up or sell down a stock through the course of the day. Decreasing range suggests waning interest.
Technical analysis
In finance, technical analysis is security analysis discipline for forecasting the direction of prices through the study of past market data, primarily price and volume. Behavioral economics and quantitative analysis incorporate technical analysis, which being an aspect of active management stands...
volatility
Volatility (finance)
In finance, volatility is a measure for variation of price of a financial instrument over time. Historic volatility is derived from time series of past market prices...
indicator originally developed by J. Welles Wilder, Jr. for commodities. The indicator does not provide an indication of price trend
Market trend
A market trend is a putative tendency of a financial market to move in a particular direction over time. These trends are classified as secular for long time frames, primary for medium time frames, and secondary for short time frames...
, simply the degree of price volatility
Volatility (finance)
In finance, volatility is a measure for variation of price of a financial instrument over time. Historic volatility is derived from time series of past market prices...
.
The average true range is an N-day exponential moving average of the true range values. Wilder recommended a 14-period smoothing.
Calculation
The range of a day's trading is simply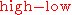 . The true range extends it to yesterday's closing price if it was outside of today's range.
. The true range extends it to yesterday's closing price if it was outside of today's range.The true range is the largest of the:
- Most recent period's high less the most recent period's low
- Absolute value of the most recent period's high less the previous close
- Absolute value of the most recent period's low less the previous close
The idea of ranges is that they show the commitment or enthusiasm of traders. Large or increasing ranges suggest traders prepared to continue to bid up or sell down a stock through the course of the day. Decreasing range suggests waning interest.
Applicability to futures contracts vs. stocks
Since true range and ATR are calculated by subtracting prices, the volatility they compute does not change when historical prices are backadjusted by adding or subtracting a constant to every price. Backadjustments are often employed when splicing together individual monthly futures contracts to form a continuous futures contract spanning a long period of time. However the standard procedures used to compute volatility of stock prices, such as the standard deviation of logarithmic price ratios, are not invariant to (addition of a constant). Thus futures traders and analysts typically use one method (ATR) to calculate volatility, while stock traders and analysts typically use another (SD of log price ratios).External links
- Measure Volatility With Average True Range at investopedia.com
- Enter Profitable Territory With Average True Range at investopedia.com
- Average True Range (ATR) at stockcharts.com
- Average True Range (ATR) at surefiretradingchallenge.com
- ATR-Filtered SMA System at surefiretradingchallenge.com


