Audio power
Encyclopedia
Audio power is the electrical power
transferred from an audio amplifier
to a loudspeaker
, measured in watt
s. The electrical power delivered to the loudspeaker, together with its sensitivity
, determines the sound power level generated (with the rest being converted to heat).
Amplifiers are limited in the electrical energy they can amplify, while loudspeakers are limited in the electrical energy they can convert to sound energy without distorting the audio signal or destroying themselves. These power rating
s are important to consumers finding compatible products and comparing competitors.
Amplifiers are valued in part by their power output capacity. And in the interest of being able to advertise a higher power output number, manufacturers in the US (and elsewhere) began to take advantage of the highly variable nature of most audio signals (especially musical sources) and to cite the peak output (quite brief and rarely sustainable for long) as the amplifier power. There being no standards, imaginative approaches came to be so common that the US Federal Trade Commission
intervened in the market and required all amplifier manufacturers to use an engineering based measure (root-mean square) in addition to any other value they might cite.
Amplifiers, being electronic devices, have power limitations deriving from both their electrical and mechanical properties. All amplifiers produce heat as a byproduct of their operation, and if that heat is generated too fast, temperatures will rise high enough to damage components. In addition, for any given electrical load, higher power means higher voltage and current delivered, and either may exceed the capacity of one or more amplifier components.
There are no similar loudspeaker power handling measurement methods in the US; the problem is much harder as many loudspeaker systems have very different power handling capacities at different frequencies (eg, tweeters which handle high frequency signals are physically small and easily damaged, while woofers which handle low frequency signals are larger and more robust) in addition to the previously cited great variation in the power levels inherent in musical signals presented to a loudspeaker.
For loudspeakers, there is also a thermal and a mechanical aspect to maximum power handling. Not all energy delivered to a loudspeaker is emitted as sound. In fact, most is converted to heat, and that heat must not rise too high or damage will follow. High level signals over a prolonged period can cause thermal damage, some of which will be immediately obvious, but much will have the effect of reducing longevity or performance margin. In addition, loudspeaker components have mechanical limits which can be exceeded by even a very brief power peak; an example is the most common sort of loudspeaker driver, which cannot move in or out
more than some limit without mechanical damage.
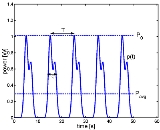
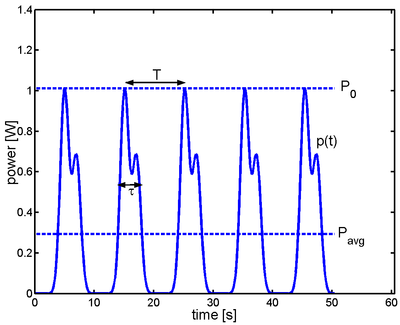 Since the instantaneous power of an AC
Since the instantaneous power of an AC
waveform varies over time, AC power
, which includes audio power, is typically measured as an average over time. It is based on this formula: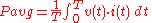
For a purely resistive load, a simpler equation can be used, based on the root mean square
(RMS) values of the voltage and current waveforms:
In the case of a steady sinusoidal tone (not music) into a purely resistive load, this can be calculated from the peak amplitude of the voltage
waveform (which is easier to measure with an oscilloscope
) and the load's resistance:
Though a speaker is not purely resistive, these equations are often used to approximate power measurements for such a system.

Thus the output of an inexpensive car audio amplifier is limited by the voltage of the alternator. In most actual car systems, the amplifiers are connected in a bridge-tied load
configuration, and speaker impedances are no higher than 4 Ω. High-power car amplifiers use a DC-to-DC converter to generate a higher supply voltage.
(RMS), a method for measuring AC voltage or current.
In its 1974 Amplifier Rule meant to combat the unrealistic power claims made by many hi-fi amplifier manufacturers, the FTC
prescribed continuous power measurements performed with sine wave signals on advertising and specification citations for amplifiers sold in the US. Typically, an amplifier's power specifications are calculated by measuring its RMS output voltage, with a continuous sine wave signal, at the onset of clipping—defined arbitrarily as a stated percentage of total harmonic distortion (THD)—into specified load resistances. Typical loads used are 8 and 4 ohms per channel; many amplifiers used in professional audio are also specified at 2 ohms.
Continuous power measurements do not actually describe the highly varied signals found in audio equipment but are widely regarded as a reasonable way of describing an amplifier's maximum output capability. Most amplifiers are capable of higher power if driven further into clipping, with corresponding increases in harmonic distortion, so the continuous power output rating cited for an amplifier should be understood to be the maximum power (at or below a particular acceptable amount of harmonic distortion) in the frequency band of interest. For audio equipment, this is nearly always the nominal frequency range of human hearing, 20Hz to 20 kHz. Other electronic equipment is intended to handle other frequency bands.
In loudspeakers, thermal capacities of the voice coils and magnet structures largely determine continuous power handling ratings. However, at the lower end of a loudspeaker's usable frequency range, its power handling might necessarily be derated because of mechanical excursion limits. For example, a subwoofer
rated at 100 watts
may be able to handle 100 watts of power at 80 hertz
, but at 25 hertz it might not be able to handle nearly as much power since such frequencies would, for some drivers in some enclosures, force the driver beyond its mechanical limits much before reaching 100 watts from the amplifier. The continuous ("RMS") value is also referred to as the nominal value, there being a regulatory requirement to use it.
Exercise physiologists measure peak power in their evaluation of human energy-generating capacities. Peak power also refers to the time of day when there is the most demand for electricity, requiring more power from the electrical grid. Some plans for creating a more energy-efficient infrastructure call for power plants which are only online during peak times. Peak power here refers to the maximum amount of power an electronic component can possibly handle for an instant without damage. Because of the highly dynamic nature of many audio signals (eg, music, which accounts for an alternative name, music power) there is some sense in attempting to characterize the ability of equipment to handle quickly changing power levels. But, how small an instant is a matter of some variation from observer to observer and so a peak power rating is necessarily more than a little indeterminate.
It always produces a higher value than the continuous ("RMS") figure, however, and so has been tempting to use in advertising. Generally, whatever the definition of instant used, distortion is also higher for an instant. For instance, an amplifier (especially a surround sound
receiver), may be rated at 1,000 watts peak power, but the harmonic distortion level might be 10 percent under those conditions. Peak power is also referred to as max power or PMPO (Peak Music Power Output).
Peak power is a common way to rate the power handling electronics, especially loudspeaker
s and amplifiers. It is a very impractical and exaggerated rating used by manufacturers to make their products seem much more powerful than they actually are. Peak power refers to the maximum amount of power something can handle before damage. In speakers, the peak power rating (also referred to as "max power" or Peak Music Power Output (PMPO), is often five or six times greater than the continuous ("RMS") rating.
Ambiguity: Among amplifiers, the peak power rating is fairly ambiguous as it varies depending on "acceptable" maximum harmonic distortion. For example, the peak power output rating of surround sound
receivers is often taken at 10 percent THD
. The highest generally acceptable level of total harmonic distortion
is considered to be 0.1%. Hence, two max power output ratings are sometimes provided, one at 0.1% THD, and another at 10% THD.
to rate the power of an audio system. Total system power refers to the total power consumption
of the unit, rather than the power handling of the speakers
or the power output of the amplifier
. This can be viewed as a somewhat deceptive marketing
ploy, as the total power consumption of the unit will of course be greater than any of its other power ratings, except for, perhaps, the peak power of the amplifier, which is essentially an exaggerated value anyway. Shelf stereo
s and surround sound
receivers are often rated using total system power.
One way to use total system power to get a more accurate estimate of power is to consider the amplifier class which would give an educated guess of the power output by considering the efficiency of the class. For example, class AB amplifiers are around 25 or 50% efficiency while Class D amps are much higher; around 80% or more efficiency. A very exceptional efficiency for a specific Class D amp, the ROHM
BD5421efs, operates at 90% efficiency.
In some cases, an audio device may be measured by the total system power of all its loudspeakers by adding all their peak power ratings. Many home theater in a box
systems are rated this way. Often low-end home theater systems' power ratings are taken at a high level of harmonic distortion as well; as high as 10%, which would be noticeable.
output of an audio amplifier – or the power
handling of a loudspeaker – is continuous average sine wave
power. The peak power of a sine wave of RMS value X is √2*X; conversely, the RMS value of a sine wave of peak X is (1/√2)*X. For a resistive load, the average power is the product of the RMS current and RMS voltage.
Harmonic distortion increases with power output; the maximum continuous power output of an amplifier is always stated at a given percentage of distortion, say 1% THD+N at 1 kHz. Considerably more power can be delivered if distortion is allowed to increase; some manufacturers quote maximum power at a higher distortion, like 10%, making their equipment appear more powerful than if measured at an acceptable distortion level.
In the US on May 3, 1974, the Amplifier Rule CFR 16 Part 432 (39 FR 15387) was instated by the Federal Trade Commission
(FTC) requiring audio power and distortion ratings for home entertainment equipment to be measured in a defined manner with power stated in RMS terms. (See more in the section Standards at the end of this article). The erroneous term "watts RMS" is actually used in CE regulations.
, of interest more to advertising copy-writers than to consumers. The term PMPO has never been defined in any standard, but it is often taken to be the sum of some sort of peak power for each amplifier in a system. Different manufacturers use different definitions, so that the ratio of PMPO to continuous power output varies widely; it is not possible to convert from one to the other. Most amplifiers can sustain their PMPO for only a very short time, if at all; loudspeakers are not designed to withstand their stated PMPO for anything but a momentary peak without serious damage.
" varies logarithmically
with output power (other inversely proportionate factors are; frequency, number and material of objects through which the sound waves must travel, as well as distance between source and receiver) a given change in output power produces a much smaller change in perceived loudness. Consequently it is useful and accurate to express perceived loudness in the logarithmic decibel
(dB) scale.
An increase/decrease of 3 dB corresponds to a doubling/halving of power. The sensitivity of loudspeakers,rather than merely the often-quoted power-handling capacity, is important. Many high quality domestic speakers have a sensitivity of 84 dB for 1 W at 1 meter, but professional speakers can have a figure of 90 dB for 1 W or even 100 dB (especially for some large-coned woofers). I.E., An '84 dB' source "speaker" would require a 400-watt amplifier to produce the same audio energy as a '90 dB' source being driven by a 100-watt amplifier, or a '100 dB' source being driven by a 9.92 watt amplifier. This does not mean a bigger speaker can produce more sound with less overall power. Just that a larger speaker can typically handle more initial power and so requires less amplification to achieve the same high level of output. This means using a speaker with a higher dB rating can be more advantageous as very high power amplifiers become impractical.
A better measure of the 'power' of a system is therefore a plot of maximum loudness before clipping of the amplifier and loudspeaker combined, in dB SPL, at the listening position intended, over the audible frequency spectrum. A good system should be capable of generating higher sound levels below 100 Hz before clipping, as the human ear is less sensitive to low frequencies, as indicated by Equal-loudness contours.
An amplifier can be designed with an audio output circuitry capable of generating a certain power level, but with a power supply unable to supply sufficient power for more than a very short time, and with heat sink
ing that will overheat dangerously if full output power is maintained for long. This makes good technical and commercial sense, as the amplifier can handle music with a relatively low mean power, but with brief peaks; a high 'music power' output can be advertised (and delivered), and money saved on the power supply and heat sink. Program sources that are significantly compressed are more likely to cause trouble, as the mean power can be much higher for the same peak power. Circuitry which protects the amplifier and power supply can prevent equipment damage in the case of sustained high power operation.
More sophisticated equipment usually used in a professional context has advanced circuitry which can handle high peak power levels without delivering more average power to the speakers than they and the amplifier can handle safely.
purchasers wishing to select properly-sized amplifiers for their loudspeakers. Chuck McGregor recommended a rule of thumb in which the amplifier's maximum power output rating was twice the loudspeaker's continuous (so-called "RMS") rating, give or take 20%. In his example, a loudspeaker with a continuous power rating of 250 watts would be well-matched by an amplifier with a maximum power output within the range of 400 to 625 watts.
filter to separate the low-level audio signal into the frequency bands to be handled by each speaker. This approach enables complex active filters to be used on the low level signal, without the need to use passive crossovers of high power handling capability but limited rolloff and with large and expensive inductors and capacitors. An additional advantage is that peak power handling is greater if the signal has simultaneous peaks in two different frequency bands. A single amplifier has to handle the peak power when both signal voltages are at their crest; as power is proportional to the square of voltage, the peak power when both signals are at the same peak voltage is proportional to the square of the sum of the voltages. If separate amplifiers are used, each must handle the square of the peak voltage in its own band. For example, if bass and midrange each has a signal corresponding to 10 W of output, a single amplifier capable of handling a 40 W peak would be needed, but a bass and a treble amplifier each capable of handling 10 W would be sufficient. This is relevant when peaks of comparable amplitude occur in different frequency bands, as with wideband percussion and high-amplitude bass notes.
For most audio applications more power is needed at low frequencies. This requires a high-power amplifier for low frequencies (e.g., 200 watts for 20–200 Hz band), lower power amplifier for the midrange (e.g., 50 watts for 200 to 1000 Hz), and even less the high end (e.g. 5 watts for 1000–20000 Hz). Proper design of a bi/tri amplifier system requires a study of driver (speaker) frequency response and sensitivities to determine optimal crossover frequencies and power amplifier powers.
is putting an end to this with Federal Trade Commission (FTC) Rule 46 CFR 432 (1974), affecting Power Output Claims for Amplifiers Utilized in Home Entertainment Products.
In response to a Federal Trade Commission order, the Consumer Electronics Association
has established a clear and concise measure of audio power for consumer electronics. They have posted an FTC approved product marking template on their web site and the full standard is available for a fee.
Many believe this will resolve much of the ambiguity and confusion in amplifier ratings.
There will be ratings for speaker and powered speaker system too. This specification only applies to audio amplifiers. A UE counterpart is expected and all equipment sold in the US and Europe will be identically tested and rated.
On May 3, 1974, the Amplifier Rule CFR 16 Part 432 was instated by the Federal Trade Commission
(FTC) requiring audio power and distortion ratings for home entertainment equipment to be measured in a defined manner with power stated in RMS terms. This rule was amended in 1998 to cover self-powered speakers such as are commonly used with personal computers (see examples below).
This regulation did not cover automobile entertainment systems, which consequently still suffer from power ratings confusion. However, a new Approved American National Standard ANSI/CEA-2006-B which includes testing & measurement methods for mobile audio amplifiers is being slowly phased into the market by many manufacturers.
, German Institute for Standardization) describes in DIN 45xxx several standards for measuring audio power. The DIN-standards (DIN-norms) are in common use in Europe.
60268-2 defines power amplifier specifications including power output.
Electric power
Electric power is the rate at which electric energy is transferred by an electric circuit. The SI unit of power is the watt.-Circuits:Electric power, like mechanical power, is represented by the letter P in electrical equations...
transferred from an audio amplifier
Audio amplifier
An audio amplifier is an electronic amplifier that amplifies low-power audio signals to a level suitable for driving loudspeakers and is the final stage in a typical audio playback chain.The preceding stages in such a chain are low power audio amplifiers which perform tasks like pre-amplification,...
to a loudspeaker
Loudspeaker
A loudspeaker is an electroacoustic transducer that produces sound in response to an electrical audio signal input. Non-electrical loudspeakers were developed as accessories to telephone systems, but electronic amplification by vacuum tube made loudspeakers more generally useful...
, measured in watt
Watt
The watt is a derived unit of power in the International System of Units , named after the Scottish engineer James Watt . The unit, defined as one joule per second, measures the rate of energy conversion.-Definition:...
s. The electrical power delivered to the loudspeaker, together with its sensitivity
Sensitivity (electronics)
The sensitivity of an electronic device, such as a communications system receiver, or detection device, such as a PIN diode, is the minimum magnitude of input signal required to produce a specified output signal having a specified signal-to-noise ratio, or other specified criteria.Sensitivity is...
, determines the sound power level generated (with the rest being converted to heat).
Amplifiers are limited in the electrical energy they can amplify, while loudspeakers are limited in the electrical energy they can convert to sound energy without distorting the audio signal or destroying themselves. These power rating
Power rating
In electrical and electronic engineering, the power rating of a device is a guideline set by the manufacturer as a maximum power to be used with that device. This limit is usually set somewhat lower than the level where the device will be damaged, to allow a margin of safety.The power rating can...
s are important to consumers finding compatible products and comparing competitors.
Power handling
In audio electronics, there are several methods of measuring power output (for such things as amplifiers) and power handling capacity (for such things as loudspeakers). The question has engineering, regulatory (consumer protection and advertising), and psychoacoustical aspects and is, in a serious sense, much more complex than may be imagined.Amplifiers are valued in part by their power output capacity. And in the interest of being able to advertise a higher power output number, manufacturers in the US (and elsewhere) began to take advantage of the highly variable nature of most audio signals (especially musical sources) and to cite the peak output (quite brief and rarely sustainable for long) as the amplifier power. There being no standards, imaginative approaches came to be so common that the US Federal Trade Commission
Federal Trade Commission
The Federal Trade Commission is an independent agency of the United States government, established in 1914 by the Federal Trade Commission Act...
intervened in the market and required all amplifier manufacturers to use an engineering based measure (root-mean square) in addition to any other value they might cite.
Amplifiers, being electronic devices, have power limitations deriving from both their electrical and mechanical properties. All amplifiers produce heat as a byproduct of their operation, and if that heat is generated too fast, temperatures will rise high enough to damage components. In addition, for any given electrical load, higher power means higher voltage and current delivered, and either may exceed the capacity of one or more amplifier components.
There are no similar loudspeaker power handling measurement methods in the US; the problem is much harder as many loudspeaker systems have very different power handling capacities at different frequencies (eg, tweeters which handle high frequency signals are physically small and easily damaged, while woofers which handle low frequency signals are larger and more robust) in addition to the previously cited great variation in the power levels inherent in musical signals presented to a loudspeaker.
For loudspeakers, there is also a thermal and a mechanical aspect to maximum power handling. Not all energy delivered to a loudspeaker is emitted as sound. In fact, most is converted to heat, and that heat must not rise too high or damage will follow. High level signals over a prolonged period can cause thermal damage, some of which will be immediately obvious, but much will have the effect of reducing longevity or performance margin. In addition, loudspeaker components have mechanical limits which can be exceeded by even a very brief power peak; an example is the most common sort of loudspeaker driver, which cannot move in or out
Excursion (audio)
Excursion is defined as how far the cone of a speaker linearly travels from its resting position. In general lower frequency drivers or subwoofers are designed to move more air and have more excursion than those of higher frequency...
more than some limit without mechanical damage.
Power calculations

Alternating current
In alternating current the movement of electric charge periodically reverses direction. In direct current , the flow of electric charge is only in one direction....
waveform varies over time, AC power
AC power
Power in an electric circuit is the rate of flow of energy past a given point of the circuit. In alternating current circuits, energy storage elements such as inductance and capacitance may result in periodic reversals of the direction of energy flow...
, which includes audio power, is typically measured as an average over time. It is based on this formula:
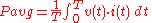
For a purely resistive load, a simpler equation can be used, based on the root mean square
Root mean square
In mathematics, the root mean square , also known as the quadratic mean, is a statistical measure of the magnitude of a varying quantity. It is especially useful when variates are positive and negative, e.g., sinusoids...
(RMS) values of the voltage and current waveforms:

In the case of a steady sinusoidal tone (not music) into a purely resistive load, this can be calculated from the peak amplitude of the voltage
Voltage
Voltage, otherwise known as electrical potential difference or electric tension is the difference in electric potential between two points — or the difference in electric potential energy per unit charge between two points...
waveform (which is easier to measure with an oscilloscope
Oscilloscope
An oscilloscope is a type of electronic test instrument that allows observation of constantly varying signal voltages, usually as a two-dimensional graph of one or more electrical potential differences using the vertical or 'Y' axis, plotted as a function of time,...
) and the load's resistance:

Though a speaker is not purely resistive, these equations are often used to approximate power measurements for such a system.
Example
An ideal (100% efficient) push-pull amplifier with a 12-volt supply can drive a sinusoidal signal with a peak amplitude of 6 V. When connected to an 8 ohm loudspeaker this would deliver:
Thus the output of an inexpensive car audio amplifier is limited by the voltage of the alternator. In most actual car systems, the amplifiers are connected in a bridge-tied load
Bridge-tied load
A bridge-tied load , also known as bridged transformerless and bridged mono, is an output configuration for audio amplifiers, a form of impedance bridging used mainly in professional audio applications. The two channels of a stereo amplifier are fed the same monaural audio signal, with one...
configuration, and speaker impedances are no higher than 4 Ω. High-power car amplifiers use a DC-to-DC converter to generate a higher supply voltage.
Continuous power
Continuous power ratings are a staple of performance specifications for audio amplifiers and, sometimes, loudspeakers. Continuous power is sometimes incorrectly referred to as RMS power and is derived from Root mean squareRoot mean square
In mathematics, the root mean square , also known as the quadratic mean, is a statistical measure of the magnitude of a varying quantity. It is especially useful when variates are positive and negative, e.g., sinusoids...
(RMS), a method for measuring AC voltage or current.
In its 1974 Amplifier Rule meant to combat the unrealistic power claims made by many hi-fi amplifier manufacturers, the FTC
FTC
FTC may refer to:- Organizations :* Federal Trade Commission, a US agency for consumer protection* Ferencvárosi TC, a Hungarian sports club* Financial Training Center Limited, a training institution in Tanzania...
prescribed continuous power measurements performed with sine wave signals on advertising and specification citations for amplifiers sold in the US. Typically, an amplifier's power specifications are calculated by measuring its RMS output voltage, with a continuous sine wave signal, at the onset of clipping—defined arbitrarily as a stated percentage of total harmonic distortion (THD)—into specified load resistances. Typical loads used are 8 and 4 ohms per channel; many amplifiers used in professional audio are also specified at 2 ohms.
Continuous power measurements do not actually describe the highly varied signals found in audio equipment but are widely regarded as a reasonable way of describing an amplifier's maximum output capability. Most amplifiers are capable of higher power if driven further into clipping, with corresponding increases in harmonic distortion, so the continuous power output rating cited for an amplifier should be understood to be the maximum power (at or below a particular acceptable amount of harmonic distortion) in the frequency band of interest. For audio equipment, this is nearly always the nominal frequency range of human hearing, 20Hz to 20 kHz. Other electronic equipment is intended to handle other frequency bands.
In loudspeakers, thermal capacities of the voice coils and magnet structures largely determine continuous power handling ratings. However, at the lower end of a loudspeaker's usable frequency range, its power handling might necessarily be derated because of mechanical excursion limits. For example, a subwoofer
Subwoofer
A subwoofer is a woofer, or a complete loudspeaker, which is dedicated to the reproduction of low-pitched audio frequencies known as the "bass". The typical frequency range for a subwoofer is about 20–200 Hz for consumer products, below 100 Hz for professional live sound, and below...
rated at 100 watts
Watt
The watt is a derived unit of power in the International System of Units , named after the Scottish engineer James Watt . The unit, defined as one joule per second, measures the rate of energy conversion.-Definition:...
may be able to handle 100 watts of power at 80 hertz
Hertz
The hertz is the SI unit of frequency defined as the number of cycles per second of a periodic phenomenon. One of its most common uses is the description of the sine wave, particularly those used in radio and audio applications....
, but at 25 hertz it might not be able to handle nearly as much power since such frequencies would, for some drivers in some enclosures, force the driver beyond its mechanical limits much before reaching 100 watts from the amplifier. The continuous ("RMS") value is also referred to as the nominal value, there being a regulatory requirement to use it.
Peak power
Peak power is the maximum level of work or energy output that is measured during an observation period. See also: Power-PhysicsPower (physics)
In physics, power is the rate at which energy is transferred, used, or transformed. For example, the rate at which a light bulb transforms electrical energy into heat and light is measured in watts—the more wattage, the more power, or equivalently the more electrical energy is used per unit...
Exercise physiologists measure peak power in their evaluation of human energy-generating capacities. Peak power also refers to the time of day when there is the most demand for electricity, requiring more power from the electrical grid. Some plans for creating a more energy-efficient infrastructure call for power plants which are only online during peak times. Peak power here refers to the maximum amount of power an electronic component can possibly handle for an instant without damage. Because of the highly dynamic nature of many audio signals (eg, music, which accounts for an alternative name, music power) there is some sense in attempting to characterize the ability of equipment to handle quickly changing power levels. But, how small an instant is a matter of some variation from observer to observer and so a peak power rating is necessarily more than a little indeterminate.
It always produces a higher value than the continuous ("RMS") figure, however, and so has been tempting to use in advertising. Generally, whatever the definition of instant used, distortion is also higher for an instant. For instance, an amplifier (especially a surround sound
Surround sound
Surround sound encompasses a range of techniques such as for enriching the sound reproduction quality of an audio source with audio channels reproduced via additional, discrete speakers. Surround sound is characterized by a listener location or sweet spot where the audio effects work best, and...
receiver), may be rated at 1,000 watts peak power, but the harmonic distortion level might be 10 percent under those conditions. Peak power is also referred to as max power or PMPO (Peak Music Power Output).
Peak power is a common way to rate the power handling electronics, especially loudspeaker
Loudspeaker
A loudspeaker is an electroacoustic transducer that produces sound in response to an electrical audio signal input. Non-electrical loudspeakers were developed as accessories to telephone systems, but electronic amplification by vacuum tube made loudspeakers more generally useful...
s and amplifiers. It is a very impractical and exaggerated rating used by manufacturers to make their products seem much more powerful than they actually are. Peak power refers to the maximum amount of power something can handle before damage. In speakers, the peak power rating (also referred to as "max power" or Peak Music Power Output (PMPO), is often five or six times greater than the continuous ("RMS") rating.
Ambiguity: Among amplifiers, the peak power rating is fairly ambiguous as it varies depending on "acceptable" maximum harmonic distortion. For example, the peak power output rating of surround sound
Surround sound
Surround sound encompasses a range of techniques such as for enriching the sound reproduction quality of an audio source with audio channels reproduced via additional, discrete speakers. Surround sound is characterized by a listener location or sweet spot where the audio effects work best, and...
receivers is often taken at 10 percent THD
THD
THD may refer to:* That Handsome Devil, an American alternative rock band* Total harmonic distortion, a measure of the distortion of an audio signal* Total Hi Def , an optical disc format* Th.D. or D.Th...
. The highest generally acceptable level of total harmonic distortion
Total harmonic distortion
The total harmonic distortion, or THD, of a signal is a measurement of the harmonic distortion present and is defined as the ratio of the sum of the powers of all harmonic components to the power of the fundamental frequency...
is considered to be 0.1%. Hence, two max power output ratings are sometimes provided, one at 0.1% THD, and another at 10% THD.
Total system power
Total system power is a term often used in audio electronicsAudio engineering
An audio engineer, also called audio technician, audio technologist or sound technician, is a specialist in a skilled trade that deals with the use of machinery and equipment for the recording, mixing and reproduction of sounds. The field draws on many artistic and vocational areas, including...
to rate the power of an audio system. Total system power refers to the total power consumption
Energy consumption
Energy consumption is the consumption of energy or power. It is covered in the following articles and categories:* World energy consumption* Domestic energy consumption* Fuel efficiency in transportation* Electric energy consumption* Electricity generation...
of the unit, rather than the power handling of the speakers
Loudspeaker
A loudspeaker is an electroacoustic transducer that produces sound in response to an electrical audio signal input. Non-electrical loudspeakers were developed as accessories to telephone systems, but electronic amplification by vacuum tube made loudspeakers more generally useful...
or the power output of the amplifier
Amplifier
Generally, an amplifier or simply amp, is a device for increasing the power of a signal.In popular use, the term usually describes an electronic amplifier, in which the input "signal" is usually a voltage or a current. In audio applications, amplifiers drive the loudspeakers used in PA systems to...
. This can be viewed as a somewhat deceptive marketing
Marketing
Marketing is the process used to determine what products or services may be of interest to customers, and the strategy to use in sales, communications and business development. It generates the strategy that underlies sales techniques, business communication, and business developments...
ploy, as the total power consumption of the unit will of course be greater than any of its other power ratings, except for, perhaps, the peak power of the amplifier, which is essentially an exaggerated value anyway. Shelf stereo
Shelf stereo
thumb|right|200px|A Magnavox 2.0 shelf stereoThe term shelf stereo refers to any home stereo system that is physically suitable for placement on a shelf or other similar location. Shelf stereo systems are becoming more popular as their capabilities increase while size decreases. The price of shelf...
s and surround sound
Surround sound
Surround sound encompasses a range of techniques such as for enriching the sound reproduction quality of an audio source with audio channels reproduced via additional, discrete speakers. Surround sound is characterized by a listener location or sweet spot where the audio effects work best, and...
receivers are often rated using total system power.
One way to use total system power to get a more accurate estimate of power is to consider the amplifier class which would give an educated guess of the power output by considering the efficiency of the class. For example, class AB amplifiers are around 25 or 50% efficiency while Class D amps are much higher; around 80% or more efficiency. A very exceptional efficiency for a specific Class D amp, the ROHM
Rohm
ROHM Semiconductor is a Japanese electronic parts supplier based in Kyoto, Japan. ROHM was incorporated as Toyo Electronics Industry Corporation by Kenichiro Sato on September 17, 1958. The name was officially changed to Rohm in 1981 and then changed again to "ROHM Semiconductor" in January of...
BD5421efs, operates at 90% efficiency.
In some cases, an audio device may be measured by the total system power of all its loudspeakers by adding all their peak power ratings. Many home theater in a box
Home theater in a box
A "home theater in a box" is an integrated home theater package which "bundles" together a combination DVD player/ multi-channel amplifier , speaker wires, connection cables, a remote control, a set of five or more surround sound speakers and a low-frequency...
systems are rated this way. Often low-end home theater systems' power ratings are taken at a high level of harmonic distortion as well; as high as 10%, which would be noticeable.
Sine wave power
The term sine power is used in the specification and measurement of audio power. A meaningful and reliable measure of the maximum powerPower (physics)
In physics, power is the rate at which energy is transferred, used, or transformed. For example, the rate at which a light bulb transforms electrical energy into heat and light is measured in watts—the more wattage, the more power, or equivalently the more electrical energy is used per unit...
output of an audio amplifier – or the power
Power (physics)
In physics, power is the rate at which energy is transferred, used, or transformed. For example, the rate at which a light bulb transforms electrical energy into heat and light is measured in watts—the more wattage, the more power, or equivalently the more electrical energy is used per unit...
handling of a loudspeaker – is continuous average sine wave
Sine wave
The sine wave or sinusoid is a mathematical function that describes a smooth repetitive oscillation. It occurs often in pure mathematics, as well as physics, signal processing, electrical engineering and many other fields...
power. The peak power of a sine wave of RMS value X is √2*X; conversely, the RMS value of a sine wave of peak X is (1/√2)*X. For a resistive load, the average power is the product of the RMS current and RMS voltage.
Harmonic distortion increases with power output; the maximum continuous power output of an amplifier is always stated at a given percentage of distortion, say 1% THD+N at 1 kHz. Considerably more power can be delivered if distortion is allowed to increase; some manufacturers quote maximum power at a higher distortion, like 10%, making their equipment appear more powerful than if measured at an acceptable distortion level.
In the US on May 3, 1974, the Amplifier Rule CFR 16 Part 432 (39 FR 15387) was instated by the Federal Trade Commission
Federal Trade Commission
The Federal Trade Commission is an independent agency of the United States government, established in 1914 by the Federal Trade Commission Act...
(FTC) requiring audio power and distortion ratings for home entertainment equipment to be measured in a defined manner with power stated in RMS terms. (See more in the section Standards at the end of this article). The erroneous term "watts RMS" is actually used in CE regulations.
PMPO
Peak Music Power Output (PMPO), sometimes misused in advertising as Peak momentary performance output, is a much more dubious figure of meritFigure of merit
A figure of merit is a quantity used to characterize the performance of a device, system or method, relative to its alternatives. In engineering, figures of merit are often defined for particular materials or devices in order to determine their relative utility for an application...
, of interest more to advertising copy-writers than to consumers. The term PMPO has never been defined in any standard, but it is often taken to be the sum of some sort of peak power for each amplifier in a system. Different manufacturers use different definitions, so that the ratio of PMPO to continuous power output varies widely; it is not possible to convert from one to the other. Most amplifiers can sustain their PMPO for only a very short time, if at all; loudspeakers are not designed to withstand their stated PMPO for anything but a momentary peak without serious damage.
Power and loudness in the real world
Perceived "loudnessLoudness
Loudness is the quality of a sound that is primarily a psychological correlate of physical strength . More formally, it is defined as "that attribute of auditory sensation in terms of which sounds can be ordered on a scale extending from quiet to loud."Loudness, a subjective measure, is often...
" varies logarithmically
Logarithmic scale
A logarithmic scale is a scale of measurement using the logarithm of a physical quantity instead of the quantity itself.A simple example is a chart whose vertical axis increments are labeled 1, 10, 100, 1000, instead of 1, 2, 3, 4...
with output power (other inversely proportionate factors are; frequency, number and material of objects through which the sound waves must travel, as well as distance between source and receiver) a given change in output power produces a much smaller change in perceived loudness. Consequently it is useful and accurate to express perceived loudness in the logarithmic decibel
Decibel
The decibel is a logarithmic unit that indicates the ratio of a physical quantity relative to a specified or implied reference level. A ratio in decibels is ten times the logarithm to base 10 of the ratio of two power quantities...
(dB) scale.
An increase/decrease of 3 dB corresponds to a doubling/halving of power. The sensitivity of loudspeakers,rather than merely the often-quoted power-handling capacity, is important. Many high quality domestic speakers have a sensitivity of 84 dB for 1 W at 1 meter, but professional speakers can have a figure of 90 dB for 1 W or even 100 dB (especially for some large-coned woofers). I.E., An '84 dB' source "speaker" would require a 400-watt amplifier to produce the same audio energy as a '90 dB' source being driven by a 100-watt amplifier, or a '100 dB' source being driven by a 9.92 watt amplifier. This does not mean a bigger speaker can produce more sound with less overall power. Just that a larger speaker can typically handle more initial power and so requires less amplification to achieve the same high level of output. This means using a speaker with a higher dB rating can be more advantageous as very high power amplifiers become impractical.
A better measure of the 'power' of a system is therefore a plot of maximum loudness before clipping of the amplifier and loudspeaker combined, in dB SPL, at the listening position intended, over the audible frequency spectrum. A good system should be capable of generating higher sound levels below 100 Hz before clipping, as the human ear is less sensitive to low frequencies, as indicated by Equal-loudness contours.
'Music power' — the real issues
The term "Music Power" has been used in relation to both amplifiers and loudspeakers with some validity. When live music is recorded without amplitude compression or limiting, the resulting signal contains brief peaks of very much higher amplitude (20 dB or more) than the mean, and since power is proportional to the square of signal voltage their reproduction would require an amplifier capable of providing brief peaks of power around a hundred times greater than the average level. Thus the ideal 100-watt audio system would need to be capable of handling brief peaks of 10,000 watts in order to avoid clipping (see Programme levels). Most loudspeakers are in fact capable of withstanding peaks of several times their continuous rating (though not a hundred times), since thermal inertia prevents the voice coils from burning out on short bursts. It is therefore acceptable, and desirable, to drive a loudspeaker from a power amplifier with a higher continuous rating several times the steady power that the speaker can withstand, but only if care is taken not to overheat it; this is difficult, especially on modern recordings which tend to be heavily compressed and so can be played at high levels without the obvious distortion that would result from an uncompressed recording when the amplifier started clipping.An amplifier can be designed with an audio output circuitry capable of generating a certain power level, but with a power supply unable to supply sufficient power for more than a very short time, and with heat sink
Heat sink
A heat sink is a term for a component or assembly that transfers heat generated within a solid material to a fluid medium, such as air or a liquid. Examples of heat sinks are the heat exchangers used in refrigeration and air conditioning systems and the radiator in a car...
ing that will overheat dangerously if full output power is maintained for long. This makes good technical and commercial sense, as the amplifier can handle music with a relatively low mean power, but with brief peaks; a high 'music power' output can be advertised (and delivered), and money saved on the power supply and heat sink. Program sources that are significantly compressed are more likely to cause trouble, as the mean power can be much higher for the same peak power. Circuitry which protects the amplifier and power supply can prevent equipment damage in the case of sustained high power operation.
More sophisticated equipment usually used in a professional context has advanced circuitry which can handle high peak power levels without delivering more average power to the speakers than they and the amplifier can handle safely.
Matching amplifier to loudspeaker
Charles "Chuck" McGregor, while serving as senior technologist for Eastern Acoustic Works, wrote a guideline for professional audioProfessional audio
Professional audio, also 'pro audio', refers to both an activity and a type of audio equipment. Typically it encompasses the production or reproduction of sound for an audience, by individuals who do such work as an occupation like live event support, using sound reinforcement systems designed for...
purchasers wishing to select properly-sized amplifiers for their loudspeakers. Chuck McGregor recommended a rule of thumb in which the amplifier's maximum power output rating was twice the loudspeaker's continuous (so-called "RMS") rating, give or take 20%. In his example, a loudspeaker with a continuous power rating of 250 watts would be well-matched by an amplifier with a maximum power output within the range of 400 to 625 watts.
Power handling in 'active' speakers
Active speakers comprise two or three speakers per channel, each fitted with its own amplifier, and preceded by an electronic crossoverAudio crossover
Audio crossovers are a class of electronic filter used in audio applications. Most individual loudspeaker drivers are incapable of covering the entire audio spectrum from low frequencies to high frequencies with acceptable relative volume and lack of distortion so most hi-fi speaker systems use a...
filter to separate the low-level audio signal into the frequency bands to be handled by each speaker. This approach enables complex active filters to be used on the low level signal, without the need to use passive crossovers of high power handling capability but limited rolloff and with large and expensive inductors and capacitors. An additional advantage is that peak power handling is greater if the signal has simultaneous peaks in two different frequency bands. A single amplifier has to handle the peak power when both signal voltages are at their crest; as power is proportional to the square of voltage, the peak power when both signals are at the same peak voltage is proportional to the square of the sum of the voltages. If separate amplifiers are used, each must handle the square of the peak voltage in its own band. For example, if bass and midrange each has a signal corresponding to 10 W of output, a single amplifier capable of handling a 40 W peak would be needed, but a bass and a treble amplifier each capable of handling 10 W would be sufficient. This is relevant when peaks of comparable amplitude occur in different frequency bands, as with wideband percussion and high-amplitude bass notes.
For most audio applications more power is needed at low frequencies. This requires a high-power amplifier for low frequencies (e.g., 200 watts for 20–200 Hz band), lower power amplifier for the midrange (e.g., 50 watts for 200 to 1000 Hz), and even less the high end (e.g. 5 watts for 1000–20000 Hz). Proper design of a bi/tri amplifier system requires a study of driver (speaker) frequency response and sensitivities to determine optimal crossover frequencies and power amplifier powers.
US
Peak momentary power output and peak music power output are two different measurements with different specifications and should not be used interchangeably. Manufacturers who use different words such as pulse or performance may be reflecting their own non-standard system of measurement, with an unknown meaning. The Federal Trade CommissionFederal Trade Commission
The Federal Trade Commission is an independent agency of the United States government, established in 1914 by the Federal Trade Commission Act...
is putting an end to this with Federal Trade Commission (FTC) Rule 46 CFR 432 (1974), affecting Power Output Claims for Amplifiers Utilized in Home Entertainment Products.
In response to a Federal Trade Commission order, the Consumer Electronics Association
Consumer Electronics Association
The Consumer Electronics Association is a standards and trade organization for the consumer electronics industry in the United States. The Consumer Electronics Association is the preeminent trade association promoting growth in the $173 billion U.S...
has established a clear and concise measure of audio power for consumer electronics. They have posted an FTC approved product marking template on their web site and the full standard is available for a fee.
Many believe this will resolve much of the ambiguity and confusion in amplifier ratings.
There will be ratings for speaker and powered speaker system too. This specification only applies to audio amplifiers. A UE counterpart is expected and all equipment sold in the US and Europe will be identically tested and rated.
On May 3, 1974, the Amplifier Rule CFR 16 Part 432 was instated by the Federal Trade Commission
Federal Trade Commission
The Federal Trade Commission is an independent agency of the United States government, established in 1914 by the Federal Trade Commission Act...
(FTC) requiring audio power and distortion ratings for home entertainment equipment to be measured in a defined manner with power stated in RMS terms. This rule was amended in 1998 to cover self-powered speakers such as are commonly used with personal computers (see examples below).
This regulation did not cover automobile entertainment systems, which consequently still suffer from power ratings confusion. However, a new Approved American National Standard ANSI/CEA-2006-B which includes testing & measurement methods for mobile audio amplifiers is being slowly phased into the market by many manufacturers.
Europe
DIN (Deutsches Institut für NormungDeutsches Institut für Normung
is the German national organization for standardization and is that country's ISO member body. DIN is a Registered German Association headquartered in Berlin...
, German Institute for Standardization) describes in DIN 45xxx several standards for measuring audio power. The DIN-standards (DIN-norms) are in common use in Europe.
International
IECInternational Electrotechnical Commission
The International Electrotechnical Commission is a non-profit, non-governmental international standards organization that prepares and publishes International Standards for all electrical, electronic and related technologies – collectively known as "electrotechnology"...
60268-2 defines power amplifier specifications including power output.
External links
- Amplifier Power Ratings (and How to calculate satisfactory PMPO values) by Rod Elliott
- Understanding amplifier power ratings
- Audio power and the corresponding factors: Subjectivly sensed loudness (volume), objectively measured sound pressure (voltage), and theoretically calculated sound intensity (acoustic power)

