
Atomic spacing
Encyclopedia
Atomic spacing refers to the distance between the nuclei
of atom
s in a material. This space is extremely large compared to the size of the nucleus, because it is the strength of the bonds which make a material strong. The atomic spacing is usually determined by passing an electromagnetic wave of known frequency
through the material, and using the laws of diffraction
to determine its atomic spacing.
The frequency of an electromagnetic wave can be calculated using the formula:
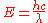
Rearranged to:
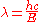
Where λ = Frequency,
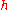 = Planck Constant
= Planck Constant
(6.626068 × 10-34 m2 kg / s)
 = The speed of light
= The speed of light
(299,792,458 m/s)
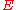 = The energy of a photon
= The energy of a photon
Atomic nucleus
The nucleus is the very dense region consisting of protons and neutrons at the center of an atom. It was discovered in 1911, as a result of Ernest Rutherford's interpretation of the famous 1909 Rutherford experiment performed by Hans Geiger and Ernest Marsden, under the direction of Rutherford. The...
of atom
Atom
The atom is a basic unit of matter that consists of a dense central nucleus surrounded by a cloud of negatively charged electrons. The atomic nucleus contains a mix of positively charged protons and electrically neutral neutrons...
s in a material. This space is extremely large compared to the size of the nucleus, because it is the strength of the bonds which make a material strong. The atomic spacing is usually determined by passing an electromagnetic wave of known frequency
Frequency
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit time. It is also referred to as temporal frequency.The period is the duration of one cycle in a repeating event, so the period is the reciprocal of the frequency...
through the material, and using the laws of diffraction
Diffraction
Diffraction refers to various phenomena which occur when a wave encounters an obstacle. Italian scientist Francesco Maria Grimaldi coined the word "diffraction" and was the first to record accurate observations of the phenomenon in 1665...
to determine its atomic spacing.
The frequency of an electromagnetic wave can be calculated using the formula:
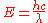
Rearranged to:
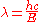
Where λ = Frequency,
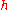 = Planck Constant
= Planck ConstantPlanck constant
The Planck constant , also called Planck's constant, is a physical constant reflecting the sizes of energy quanta in quantum mechanics. It is named after Max Planck, one of the founders of quantum theory, who discovered it in 1899...
(6.626068 × 10-34 m2 kg / s)
 = The speed of light
= The speed of lightSpeed of light
The speed of light in vacuum, usually denoted by c, is a physical constant important in many areas of physics. Its value is 299,792,458 metres per second, a figure that is exact since the length of the metre is defined from this constant and the international standard for time...
(299,792,458 m/s)
 = The energy of a photon
= The energy of a photon

