
Asperity
Encyclopedia
Materials science
Materials science is an interdisciplinary field applying the properties of matter to various areas of science and engineering. This scientific field investigates the relationship between the structure of materials at atomic or molecular scales and their macroscopic properties. It incorporates...
, asperity, defined as "unevenness of surface, roughness, ruggedness" (OED
Oxford English Dictionary
The Oxford English Dictionary , published by the Oxford University Press, is the self-styled premier dictionary of the English language. Two fully bound print editions of the OED have been published under its current name, in 1928 and 1989. The first edition was published in twelve volumes , and...
, from the Latin asper — "rough"), has implications (for example) in physics
Physics
Physics is a natural science that involves the study of matter and its motion through spacetime, along with related concepts such as energy and force. More broadly, it is the general analysis of nature, conducted in order to understand how the universe behaves.Physics is one of the oldest academic...
and seismology
Seismology
Seismology is the scientific study of earthquakes and the propagation of elastic waves through the Earth or through other planet-like bodies. The field also includes studies of earthquake effects, such as tsunamis as well as diverse seismic sources such as volcanic, tectonic, oceanic,...
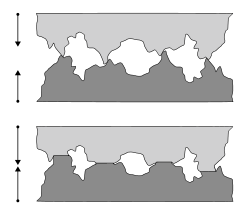
. Smooth surfaces, even those polished to a mirror finish, are not truly smooth on an atomic scale. They are rough, with sharp, rough or rugged projections, termed "asperities".
When two macroscopically smooth surfaces come into contact, initially they only touch at a few of these asperity points. These cover only a very small portion of the surface area. Friction
Friction
Friction is the force resisting the relative motion of solid surfaces, fluid layers, and/or material elements sliding against each other. There are several types of friction:...
and wear
Wear
In materials science, wear is erosion or sideways displacement of material from its "derivative" and original position on a solid surface performed by the action of another surface....
originate at these points and thus understanding their behavior becomes important when studying materials in contact. When the surfaces are subjected to a compressive load, the asperities plastically deform, increasing the contact area between the two surfaces until the contact area is sufficient to support the load.
The Archard equation
Archard equation
The Archard wear equation is a simple model used to describe sliding wear and is based around the theory of asperity contact. The Archard equation was developed later than the Reye's hypothesis, though both came to the same physical conclusions, that the volume of the removed debris due to wear is...
provides a simplified model of asperity deformation when materials in contact are subject to a force.

