
Ascocarp
Encyclopedia

Sporocarp (fungi)
In fungi, the sporocarp is a multicellular structure on which spore-producing structures, such as basidia or asci, are borne...
) of an ascomycete fungus. It consists of very tightly interwoven hypha
Hypha
A hypha is a long, branching filamentous structure of a fungus, and also of unrelated Actinobacteria. In most fungi, hyphae are the main mode of vegetative growth, and are collectively called a mycelium; yeasts are unicellular fungi that do not grow as hyphae.-Structure:A hypha consists of one or...
e and may contain millions of asci
Ascus
An ascus is the sexual spore-bearing cell produced in ascomycete fungi. On average, asci normally contain eight ascospores, produced by a meiotic cell division followed, in most species, by a mitotic cell division. However, asci in some genera or species can number one , two, four, or multiples...
, each of which typically contains eight ascospores. Ascocarps are most commonly bowl-shaped, but may take on a number of other forms.
Classification of ascocarps
The ascocarp is classified according to its placement (in ways not fundamental to the basic taxonomy). It is called epigeous if it grows above ground, as with the morelMorel
Morchella, the true morels, is a genus of edible mushrooms closely related to anatomically simpler cup fungi. These distinctive mushrooms appear honeycomb-like in that the upper portion is composed of a network of ridges with pits between them....
s, whilst underground ascocarps, such as truffles are hypogeous.
The form of the hymenium
Hymenium
The hymenium is the tissue layer on the hymenophore of a fungal fruiting body where the cells develop into basidia or asci, which produce spores. In some species all of the cells of the hymenium develop into basidia or asci, while in others some cells develop into sterile cells called cystidia or...
is divided into the following types (which are important for classification). Apothecia can be relatively large and fleshy, whereas the others are microscopic — about the size of flecks of ground pepper.
- Apothecium: This is wide; open saucer-shaped or cup shaped fruit body. It is sessile, fleshy . Structure of Apothecium chiefly consist of 3 parts namely hymenium (upper concave surface), hypothecium and excipulum. The asci are present in the hymenium layer. The asci are freely exposed at maturity. Example –members of Dictyomycetes.
Here the fertile layer is free, so that many spores can be dispersed simultaneously. The morel
Morel
Morchella, the true morels, is a genus of edible mushrooms closely related to anatomically simpler cup fungi. These distinctive mushrooms appear honeycomb-like in that the upper portion is composed of a network of ridges with pits between them....
, Morchella, an edible ascocarp, not a mushroom, favored by gourmets, is a mass of apothecia fused together in a single large structure or cap. The genera Helvella
Helvella
Helvella is a genus of ascomycete fungus of the Helvellaceae family. The mushrooms, commonly known as elfin saddles, are identified by their irregularly shaped caps, fluted stems, and fuzzy undersurfaces. They are found in North America and in Europe. Well known species include the whitish H....
and Gyromitra
Gyromitra
Gyromitra is a genus of ascomycete mushrooms found in the northern hemisphere. The most famous member is the controversial false morel ...
are similar.
 |
 |
- Cleistothecium:
A cleistothecium is a globose, completely closed fruit body with no special opening to the outside. The fruit wall which is called peredium may simple consist of loosely interwoven hyphae or pseudoparechyma. It may be covered with hyphal outgrowth called appendages. The asci inside the ascocarps are found usually scattered i.e. as in Eurotium or arising in tufts from the basal region of ascocarps as in Erysiphe. The asci are globose, pear shaped and released by irregular disintegration of the wall of cleistothecium. Example –Gymnoascus (some authors called gymnothecium), Eurotium (imperfect state –Aspergillus).
In this case the ascocarp is round with the hymenium enclosed, so the spores do not automatically get released, and fungi with cleistothecia have had to develop new strategies to disseminate their spores. The truffles, for instance, have solved this problem by attracting animals such as wild boar
Boar
Wild boar, also wild pig, is a species of the pig genus Sus, part of the biological family Suidae. The species includes many subspecies. It is the wild ancestor of the domestic pig, an animal with which it freely hybridises...
s, which break open the tasty ascocarps and spread the spores over a wide area. Cleistothecia are found mostly in fungi that have little room available for their ascocarps, for instance those that live under tree bark, or underground like truffles. Also, the dermatophyte
Dermatophyte
Dermatophytes are a common label for a group of three types of fungus that commonly causes skin disease in animals and humans. These anamorphic genera are: Microsporum, Epidermophyton and Trichophyton. There are about 40 species in these three genera...
Arthroderma forms cleistothecia.
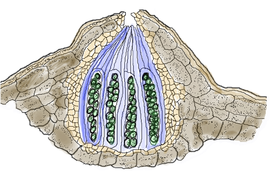
- Perithecium: This is a flask shaped structures opening by a pore or ostiole (short papilla opening by a circular pore) through which the ascospores escape. The oistolar canal may be lined by a hair like structures called periphyses. The unitunicate asci are usually cylindrical in shape borne in a stipe (stalk), released from a pore, developed from inner wall of perithecium and arise from a basal plectenchyma-centrum. Example - members of Sphaeriales, Hypocreales. Perithecia are also found in XylariaXylariaXylaria is a genus of ascomycetous fungi commonly found growing on dead wood. The name comes from the Greek xýlon meaning wood .Two of the common species of the genus are Xylaria hypoxylon and Xylaria polymorpha....
(Dead Man’s Fingers, Candle Snuff) and NectriaNectriaThis article is about a genus of fungi. For the echinoderm genus, see Nectria .Nectria is a genus of Ascomycete fungi. They are most often encountered as saprophytes on decaying wood but some species can also occur as parasites of trees, especially fruit trees and a number of other hardwood trees...
.
- Pseudothecium: this is similar to a peritheciu, but the asci are not regularly organised into a hymenium and they are bitunicate, having a double wall that expands when it takes up water and shoots the enclosed spores out suddenly to disperse them. Example species are Apple scabApple scabApple scab is a disease to Malus trees, such as apple trees, caused by the ascomycete fungus Venturia inaequalis. The disease manifests as dull black or grey-brown lesions on the surface of tree leaves, buds or fruits. Lesions may also appear less frequently on the woody tissues of the tree. Fruits...
(Venturia inaequalis) and the horse chestnut disease Guignardia aesculi.

