
Anthropogenic
Encyclopedia
Human impact on the environment or anthropogenic impact on the environment includes impacts on biophysical environments
, biodiversity and other resources. The term anthropogenic designates an effect or object resulting from human activity. The term was first used in the technical sense by Russian geologist A. P. Pavlov, and was first used in English by British ecologist Arthur Tansley
in reference to human influences on climax
plant communities. The atmospheric scientist Paul Crutzen introduced the term "anthropocene
" in the mid-1970s. The term is sometimes used in the context of pollution
emissions that are produced as a result of human activities but applies broadly to all major human impacts on the environment.
varies based on the wide variety of agricultural practices employed around the world.
 The environmental impact of fishing can be divided into issues that involve the availability of fish to be caught, such as overfishing
The environmental impact of fishing can be divided into issues that involve the availability of fish to be caught, such as overfishing
, sustainable fisheries
, and fisheries management
; and issues that involve the impact of fishing on other elements of the environment, such as by-catch
.
These conservation issues are part of marine conservation
, and are addressed in fisheries science
programs. There is a growing gap between how many fish are available to be caught and humanity’s desire to catch them, a problem that gets worse as the world population
grows.
Similar to other environmental issue
s, there can be conflict between the fishermen who depend on fishing for their livelihoods and fishery scientists who realise that if future fish populations are to be sustainable
then some fisheries must reduce or even close.
The journal Science
published a four-year study in November 2006, which predicted that, at prevailing trends, the world would run out of wild-caught seafood
in 2048. The scientists stated that the decline was a result of overfishing
, pollution
and other environmental factors that were reducing the population of fisheries at the same time as their ecosystems were being degraded. Yet again the analysis has met criticism as being fundamentally flawed, and many fishery management officials, industry representatives and scientists challenge the findings, although the debate continues. Many countries, such as Tonga
, the United States
, Australia
and New Zealand
, and international management bodies have taken steps to appropriately manage marine resources.
and water
as a result of irrigation
and the ensuing effects on natural and social conditions at the tail-end and downstream of the irrigation scheme.
The impacts stem from the changed hydrological conditions
owing to the installation and operation of the scheme.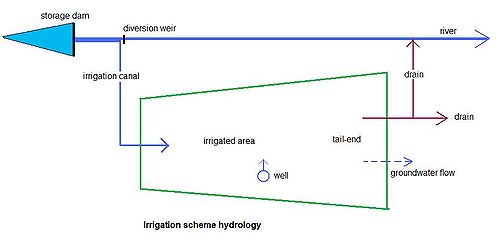 An irrigation scheme often draws water from the river and distributes it over the irrigated area. As a hydrological result it is found that:
An irrigation scheme often draws water from the river and distributes it over the irrigated area. As a hydrological result it is found that:
These may be called direct effects.
The effects thereof on soil and water quality
are indirect and complex, Water logging
and soil salination
are part of these, whereas the subsequent impacts on natural, ecological
and socio-enonomic conditions is very intricate.
Irrigation can also be done extracting groundwater by (tube)wells
. As a hydrological result it is found that the level of the water descends. The effects may be water mining, land/soil subsidence
, and, along the coast, saltwater intrusion
.
Irrigation projects can have large benefits, but the negative side effects are often overlooked
worldwide, and modern practices of raising animals for food contributes on a "massive scale" to air and water pollution
, land degradation, climate change
, and loss of biodiversity
. The initiative concluded that "the livestock sector emerges as one of the top two or three most significant contributors to the most serious environmental problems, at every scale from local to global." In 2006 FAO estimated that meat industry contributes 18% of all emissions of greenhouse gasses. This figure was challenged in 2009 by two World-Watch researchers who estimated a 51% minimum, however this paper has not been peer reviewed.
Animals fed on grain need more water than grain crops. In tracking food animal production from the feed through to the dinner table, the inefficiencies of meat, milk
and egg
production range from a 4:1 energy input to protein output ratio up to 54:1. The result is that producing animal-based food is typically much less efficient than the harvesting of grains, vegetables, legumes, seeds and fruits for direct human consumption.
Relatedly, the production and consumption of meat and other animal products is associated with the
clearing of rainforests, resource depletion, air and water pollution, land and economic inefficiency, species extinction, and other environmental harms.
The author of the influential 2006 Stern Review on climate change has stated "people will need to turn vegetarian if the world is to conquer climate change". This is due to emissions of methane (which is 23 times more potent of a greenhouse gas versus carbon dioxide) from cows and pigs via flatulence
and eructation.
 Palm oil
Palm oil
, produced from the oil palm
, is a basic source of income for many farmers in Southeast Asia
, Central
and West Africa
, and Central America
. It is locally used as a cooking oil, exported for use in many commercial food and personal care products and is converted into biofuel. It produces up to 10 times more oil per unit area as soyabeans, rapeseed
or sunflower
s. Oil palms produce 38% of vegetable oil output on 5% of the world’s vegetable-oil farmland. Palm oil is under increasing scrutiny in relation to its effects on the environment
.
and consumption
is diverse. In recent years there has been a trend towards the increased commercialization of various renewable energy sources
.
In the real world of consumption of fossil fuel resources which lead to global warming
and climate change however little change is being made in many parts of the world. Chinese oil demand for instance, is projected to grow nearly 20% in the next six years, and that country already imports over half of the 8 million barrels a day it uses. If the peak oil
theory proves out, more explorations of viable alternative energy sources, could be more friendly to the environment.
Rapidly advancing technologies can achieve a transition of energy generation, water and waste management, and food production towards better environmental and energy usage practices using methods of systems ecology
and industrial ecology
.
(EPA) to issue a plan to alleviate toxic pollution from coal-fired power plants. After delay and litigation, the EPA now has a court-imposed deadline of March 16, 2011, to issue its report.
at power plants that convert some other kind of energy into electrical power. Each such system has advantages and disadvantages, but many of them pose environmental concerns.
results from the nuclear fuel cycle
, operation, and the lingering effects of the Chernobyl disaster
.
 The environmental impact of the oil shale industry includes the consideration of issues such as land use
The environmental impact of the oil shale industry includes the consideration of issues such as land use
, waste management
, and water
and air pollution
caused by the extraction and processing
of oil shale
. Surface mining
of oil shale deposits
causes the usual environmental impacts of open-pit mining
. In addition, the combustion
and thermal processing generate waste material, which must be disposed of, and harmful atmospheric emissions, including carbon dioxide
, a major greenhouse gas
. Experimental in-situ conversion processes and carbon capture and storage
technologies may reduce some of these concerns in future, but may raise others, such as the pollution of groundwater.
is often negative because it is toxic to almost all forms of life. The possibility of climate change
exists. Petroleum, commonly referred to as oil, is closely linked to virtually all aspects of present society, especially for transportation and heating for both homes and for commercial activities.
 The environmental impact of reservoirs is coming under ever increasing scrutiny as the world demand for water and energy increases and the number and size of reservoirs increases.
The environmental impact of reservoirs is coming under ever increasing scrutiny as the world demand for water and energy increases and the number and size of reservoirs increases.
Dam
s and the reservoir
s can be used to supply drinking water
, generate hydroelectric power, increasing the water supply for irrigation
, provide recreational opportunities and to improve certain aspects of the environment. However, adverse environmental and sociological impacts have also been identified during and after many reservoir constructions. Whether reservoir projects are ultimately beneficial or detrimental—to both the environment and surrounding human populations— has been debated since the 1960s and probably long before that. In 1960 the construction of Llyn Celyn
and the flooding of Capel Celyn
provoked political uproar which continues to this day. More recently, the construction of Three Gorges Dam
and other similar projects throughout Asia
, Africa
and Latin America
have generated considerable environmental and political debate.
 Compared to the environmental impact of traditional energy sources, the environmental impact of wind power is relatively minor. Wind power
Compared to the environmental impact of traditional energy sources, the environmental impact of wind power is relatively minor. Wind power
consumes no fuel, and emits no air pollution
, unlike fossil fuel power sources. The energy consumed to manufacture and transport the materials used to build a wind power plant is equal to the new energy produced by the plant within a few months. While a wind farm may cover a large area of land, many land uses such as agriculture are compatible, with only small areas of turbine foundations and infrastructure made unavailable for use.
There are reports of bird and bat mortality at wind turbines, as there are around other artificial structures. The scale of the ecological impact may or may not be significant, depending on specific circumstances. Prevention and mitigation of wildlife fatalities, and protection of peat bogs, affect the siting and operation of wind turbines.
There are conflicting reports about the effects of noise on people who live very close to a wind turbine.
s is diverse. In recent years, measures have been taken to reduce these effects.
's environmental impact can be split into two aspects: the potential for nanotechnological innovations to help improve the environment, and the possibly novel type of pollution that nanotechnological materials might cause if released into the environment. As nanotechnology is an emerging field, there is great debate regarding to what extent industrial and commercial use of nanomaterials
will affect organisms and ecosystems.
materials and processes can have harmful effects on the environment
, including those from the use of lead
and other additives. Measures can be taken to reduce environmental impact, including accurately estimating paint quantities so that wastage is minimized, use of paints, coatings, painting accessories and techniques that are environmentally preferred. The United States Environmental Protection Agency
guidelines and Green Star
ratings are some of the standards that can be applied.
and the highly mechanised harvesting of wood, paper has become a cheap commodity. This has led to a high level of consumption and waste. With the rise in environmental awareness due to the lobbying by environmental organization
s and with increased government regulation there is now a trend towards sustainability
in the pulp and paper industry
.
s is often greater than what is intended by those who use them. Over 98% of sprayed insecticides and 95% of herbicides reach a destination other than their target species, including nontarget species, air, water, bottom sediments, and food. Pesticide contaminates land and water when it escapes from production sites and storage tanks, when it runs off from fields, when it is discarded, when it is sprayed aerially, and when it is sprayed into water to kill algae.
The amount of pesticide that migrates from the intended application area is influenced by the particular chemical's properties: its propensity for binding to soil, its vapor pressure
, its water solubility
, and its resistance to being broken down over time. Factors in the soil, such as its texture, its ability to retain water, and the amount of organic matter contained in it, also affect the amount of pesticide that will leave the area. Some pesticides contribute to global warming
and the depletion of the ozone layer
.
reasons and the products used by agribusiness
to boost growth or health of livestock. PPCPs have been detected in water bodies throughout the world. The effects of these chemicals on humans and the environment are not yet known, but to date there is no scientific evidence that they have an impact on human health.
 The environmental impact of mining includes erosion
The environmental impact of mining includes erosion
, formation of sinkhole
s, loss of biodiversity
, and contamination of soil, groundwater
and surface water
by chemicals from mining processes. In some cases, additional forest logging is done in the vicinity of mines to increase the available room for the storage of the created debris and soil. Besides creating environmental damage, the contamination resulting from leakage of chemicals also affect the health of the local population. Mining companies in some countries are required to follow environmental and rehabilitation codes, ensuring the area mined is returned to close to its original state. Some mining methods may have significant environmental and public health effects.
 The environmental impact of transport
The environmental impact of transport
is significant because it is a major user of energy, and burns most of the world's petroleum
. This creates air pollution
, including nitrous oxide
s and particulates, and is a significant contributor to global warming
through emission of carbon dioxide
, for which transport is the fastest-growing emission sector. By subsector, road transport is the largest contributor to global warming.
Environmental regulations in developed countries have reduced the individual vehicles emission; however, this has been offset by an increase in the number of vehicles, and more use of each vehicle. Some pathways to reduced the carbon emissions of road vehicles considerably have been studied. Energy use and emissions vary largely between modes, causing environmentalists
to call for a transition from air and road to rail and human-powered transport, and increase transport electrification and energy efficiency
.
Other environmental impacts of transport systems include traffic congestion
and automobile-oriented urban sprawl
, which can consume natural habitat and agricultural lands. By reducing transportation emissions globally, it is predicted that there will be significant positive effects on Earth's air quality, acid rain
, smog
and climate change.
The health impact of transport emissions is also of concern. A recent survey of the studies on the effect of traffic emissions on pregnancy outcomes has linked exposure to emissions to adverse effects on gestational duration and possibly also intrauterine growth.
s emit noise
, particulates, and gases which contribute to climate change
and global dimming
. Despite emission reductions from automobiles and more fuel-efficient and less polluting turbofan
and turboprop
engines, the rapid growth of air travel
in recent years contributes to an increase in total pollution attributable to aviation
. In the EU
, greenhouse gas
emissions from aviation increased by 87% between 1990 and 2006. Among other factors leading to this phenomenon are the increasing number of hypermobile travellers
and social factors that are making air travel commonplace, such as frequent flyer programs.
There is an ongoing debate about possible taxation of air travel and the inclusion of aviation in an emissions trading
scheme, with a view to ensuring that the total external costs of aviation are taken into account.
, habitat destruction
/disturbance and local air quality; and the wider effects including climate change
from vehicle emissions. The design, construction and management of roads, parking
and other related facilities as well as the design and regulation of vehicle
s can change the impacts to varying degrees.
includes greenhouse gas
emissions and oil pollution. Carbon dioxide
emissions from shipping is currently estimated at 4 to 5% of the global total, and estimated by the International Maritime Organisation (IMO) to rise by up to 72% by 2020 if no action is taken.
The First Intersessional Meeting of the IMO Working Group on Greenhouse Gas Emissions from Ships took place in Oslo
, Norway
on 23–27 June 2008. It was tasked with developing the technical basis for the reduction mechanisms that may form part of a future IMO regime to control greenhouse gas emissions from international shipping, and a draft of the actual reduction mechanisms themselves, for further consideration by IMO’s Marine Environment Protection Committee (MEPC).
 As well as the cost to human life and society, there is a significant environmental impact of war. Scorched earth
As well as the cost to human life and society, there is a significant environmental impact of war. Scorched earth
methods during, or after war have been in use for much of recorded history but with modern technology
war can cause a far greater devastation on the environment
. Unexploded ordnance
can render land unusable for further use or make access across it dangerous or fatal.
. Though most experts agree that human beings have accelerated the rate of species extinction, the exact degree of this impact is unknown, perhaps 100 to 1000 times the normal background rate of extinction. Some authors have postulated that without human interference the biodiversity of this planet would continue to grow at an exponential rate.
s are dying around the world. In particular, coral mining, pollution
(organic and non-organic), overfishing
, blast fishing
and the digging of canal
s and access into islands and bays are serious threats to these ecosystems. Coral reefs also face high dangers from pollution, diseases, destructive fishing practices and warming oceans. In order to find answers for these problems, researchers study the various factors that impact reefs. The list of factors is long, including the ocean's role as a carbon dioxide sink
, atmospheric changes, ultraviolet light, ocean acidification
, biological virus
, impacts of dust storms carrying agents to far flung reefs, pollutants, algal bloom
s and others. Reefs are threatened well beyond coastal areas.
General estimates show approximately 10% world's coral reefs are already dead. It is estimated that about 60% of the world's reefs are at risk due to destructive, human-related activities. The threat to the health of reefs is particularly strong in Southeast Asia
, where 80% of reefs are endangered
.
(N) inputs to the environment currently exceed inputs from natural N fixation. As a consequence of anthropogenic inputs, the global nitrogen cycle
(Fig. 1) has been significantly altered over the past century. Global atmospheric nitrous oxide
(N2O) mole fractions have increased from a pre-industrial value of ~270 nmol/mol to ~319 nmol/mol in 2005. Human activities account for over one-third of N2O emissions, most of which are due to the agricultural sector.
Environment (biophysical)
The biophysical environment is the combined modeling of the physical environment and the biological life forms within the environment, and includes all variables, parameters as well as conditions and modes inside the Earth's biosphere. The biophysical environment can be divided into two categories:...
, biodiversity and other resources. The term anthropogenic designates an effect or object resulting from human activity. The term was first used in the technical sense by Russian geologist A. P. Pavlov, and was first used in English by British ecologist Arthur Tansley
Arthur Tansley
Sir Arthur George Tansley FRS was an English botanist who was a pioneer in the science of ecology. He obtained his degree in Biological Science in 1896, with specialization in botany and zoology. From the start, he was much influenced by the Danish plant ecologist Eugenius Warming. He championed...
in reference to human influences on climax
Climax community
In ecology, a climax community, or climatic climax community, is a biological community of plants and animals which, through the process of ecological succession — the development of vegetation in an area over time — has reached a steady state. This equilibrium occurs because the climax community...
plant communities. The atmospheric scientist Paul Crutzen introduced the term "anthropocene
Anthropocene
The Anthropocene is a recent and informal geologic chronological term that serves to mark the evidence and extent of human activities that have had a significant global impact on the Earth's ecosystems...
" in the mid-1970s. The term is sometimes used in the context of pollution
Pollution
Pollution is the introduction of contaminants into a natural environment that causes instability, disorder, harm or discomfort to the ecosystem i.e. physical systems or living organisms. Pollution can take the form of chemical substances or energy, such as noise, heat or light...
emissions that are produced as a result of human activities but applies broadly to all major human impacts on the environment.
Agriculture
The environmental impact of agricultureAgriculture
Agriculture is the cultivation of animals, plants, fungi and other life forms for food, fiber, and other products used to sustain life. Agriculture was the key implement in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that nurtured the...
varies based on the wide variety of agricultural practices employed around the world.
Fishing

Overfishing
Overfishing occurs when fishing activities reduce fish stocks below an acceptable level. This can occur in any body of water from a pond to the oceans....
, sustainable fisheries
Sustainable fisheries
Sustainability in fisheries combines theoretical disciplines, such as the population dynamics of fisheries, with practical strategies, such as avoiding overfishing through techniques such as individual fishing quotas, curtailing destructive and illegal fishing practices by lobbying for appropriate...
, and fisheries management
Fisheries management
Fisheries management draws on fisheries science in order to find ways to protect fishery resources so sustainable exploitation is possible. Modern fisheries management is often referred to as a governmental system of appropriate management rules based on defined objectives and a mix of management...
; and issues that involve the impact of fishing on other elements of the environment, such as by-catch
By-catch
The term “bycatch” is usually used for fish caught unintentionally in a fishery while intending to catch other fish. It may however also indicate untargeted catch in other forms of animal harvesting or collecting...
.
These conservation issues are part of marine conservation
Marine conservation
Marine conservation, also known as marine resources conservation, is the protection and preservation of ecosystems in oceans and seas. Marine conservation focuses on limiting human-caused damage to marine ecosystems, and on restoring damaged marine ecosystems...
, and are addressed in fisheries science
Fisheries science
Fisheries science is the academic discipline of managing and understanding fisheries. It is a multidisciplinary science, which draws on the disciplines of oceanography, marine biology, marine conservation, ecology, population dynamics, economics and management to attempt to provide an integrated...
programs. There is a growing gap between how many fish are available to be caught and humanity’s desire to catch them, a problem that gets worse as the world population
World population
The world population is the total number of living humans on the planet Earth. As of today, it is estimated to be billion by the United States Census Bureau...
grows.
Similar to other environmental issue
Environmental issue
Environmental issues are negative aspects of human activity on the biophysical environment. Environmentalism, a social and environmental movement that started in the 1960s, addresses environmental issues through advocacy, education and activism.-Types:...
s, there can be conflict between the fishermen who depend on fishing for their livelihoods and fishery scientists who realise that if future fish populations are to be sustainable
Sustainability
Sustainability is the capacity to endure. For humans, sustainability is the long-term maintenance of well being, which has environmental, economic, and social dimensions, and encompasses the concept of union, an interdependent relationship and mutual responsible position with all living and non...
then some fisheries must reduce or even close.
The journal Science
Science (journal)
Science is the academic journal of the American Association for the Advancement of Science and is one of the world's top scientific journals....
published a four-year study in November 2006, which predicted that, at prevailing trends, the world would run out of wild-caught seafood
Seafood
Seafood is any form of marine life regarded as food by humans. Seafoods include fish, molluscs , crustaceans , echinoderms . Edible sea plants, such as some seaweeds and microalgae, are also seafood, and are widely eaten around the world, especially in Asia...
in 2048. The scientists stated that the decline was a result of overfishing
Overfishing
Overfishing occurs when fishing activities reduce fish stocks below an acceptable level. This can occur in any body of water from a pond to the oceans....
, pollution
Pollution
Pollution is the introduction of contaminants into a natural environment that causes instability, disorder, harm or discomfort to the ecosystem i.e. physical systems or living organisms. Pollution can take the form of chemical substances or energy, such as noise, heat or light...
and other environmental factors that were reducing the population of fisheries at the same time as their ecosystems were being degraded. Yet again the analysis has met criticism as being fundamentally flawed, and many fishery management officials, industry representatives and scientists challenge the findings, although the debate continues. Many countries, such as Tonga
Tonga
Tonga, officially the Kingdom of Tonga , is a state and an archipelago in the South Pacific Ocean, comprising 176 islands scattered over of ocean in the South Pacific...
, the United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
, Australia
Australia
Australia , officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country in the Southern Hemisphere comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands in the Indian and Pacific Oceans. It is the world's sixth-largest country by total area...
and New Zealand
New Zealand
New Zealand is an island country in the south-western Pacific Ocean comprising two main landmasses and numerous smaller islands. The country is situated some east of Australia across the Tasman Sea, and roughly south of the Pacific island nations of New Caledonia, Fiji, and Tonga...
, and international management bodies have taken steps to appropriately manage marine resources.
Irrigation
The environmental impact of irrigation includes the changes in quantity and quality of soilSoil
Soil is a natural body consisting of layers of mineral constituents of variable thicknesses, which differ from the parent materials in their morphological, physical, chemical, and mineralogical characteristics...
and water
Water
Water is a chemical substance with the chemical formula H2O. A water molecule contains one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms connected by covalent bonds. Water is a liquid at ambient conditions, but it often co-exists on Earth with its solid state, ice, and gaseous state . Water also exists in a...
as a result of irrigation
Irrigation
Irrigation may be defined as the science of artificial application of water to the land or soil. It is used to assist in the growing of agricultural crops, maintenance of landscapes, and revegetation of disturbed soils in dry areas and during periods of inadequate rainfall...
and the ensuing effects on natural and social conditions at the tail-end and downstream of the irrigation scheme.
The impacts stem from the changed hydrological conditions
Hydrology
Hydrology is the study of the movement, distribution, and quality of water on Earth and other planets, including the hydrologic cycle, water resources and environmental watershed sustainability...
owing to the installation and operation of the scheme.

- the downstream river dischargeDischargeDischarge in the context to expel or to "let go" may refer to:* A military discharge, issued when a member of the armed forces is released from service* Termination of employment, the end of an employee's duration with an employer...
is reduced - the evaporationEvaporationEvaporation is a type of vaporization of a liquid that occurs only on the surface of a liquid. The other type of vaporization is boiling, which, instead, occurs on the entire mass of the liquid....
in the scheme is increased - the groundwater rechargeRechargeGroundwater recharge or deep drainage or deep percolation is a hydrologic process where water moves downward from surface water to groundwater. This process usually occurs in the vadose zone below plant roots and is often expressed as a flux to the water table surface...
in the scheme is increased - the level of the water table rises
- the drainageDrainageDrainage is the natural or artificial removal of surface and sub-surface water from an area. Many agricultural soils need drainage to improve production or to manage water supplies.-Early history:...
flow is increased
These may be called direct effects.
The effects thereof on soil and water quality
Water quality
Water quality is the physical, chemical and biological characteristics of water. It is a measure of the condition of water relative to the requirements of one or more biotic species and or to any human need or purpose. It is most frequently used by reference to a set of standards against which...
are indirect and complex, Water logging
Waterlogging
Waterlogging or water logging may refer to:* Waterlogging , saturation of the soil by groundwater sufficient to prevent or hinder agriculture...
and soil salination
Soil salination
Soil salinity is the salt content in the soil.- Causes of soil salinity :Salt-affected soils are caused by excess accumulation of salts, typically most pronounced at the soil surface. Salts can be transported to the soil surface by capillary transport from a salt laden water table and then...
are part of these, whereas the subsequent impacts on natural, ecological
Ecology
Ecology is the scientific study of the relations that living organisms have with respect to each other and their natural environment. Variables of interest to ecologists include the composition, distribution, amount , number, and changing states of organisms within and among ecosystems...
and socio-enonomic conditions is very intricate.
Irrigation can also be done extracting groundwater by (tube)wells
Water well
A water well is an excavation or structure created in the ground by digging, driving, boring or drilling to access groundwater in underground aquifers. The well water is drawn by an electric submersible pump, a trash pump, a vertical turbine pump, a handpump or a mechanical pump...
. As a hydrological result it is found that the level of the water descends. The effects may be water mining, land/soil subsidence
Groundwater-related subsidence
Groundwater-related subsidence is the subsidence of land resulting from groundwater extraction, and a major problem in the developing world as major metropolises swell without adequate regulation and enforcement, as well as a being a common problem in the developed world...
, and, along the coast, saltwater intrusion
Saltwater intrusion
Saltwater intrusion is the movement of saline water into freshwater aquifers. Most often, it is caused by ground-water pumping from coastal wells, or from construction of navigation channels or oil field canals. The channels and canals provide conduits for salt water to be brought into fresh...
.
Irrigation projects can have large benefits, but the negative side effects are often overlooked
Meat production
The environmental impact of meat production includes pollution and the use of resources such as fossil fuels, water, and land. According to a 2006 report by the Livestock, Environment And Development Initiative, the livestock industry is one of the largest contributors to environmental degradationEnvironmental degradation
Environmental degradation is the deterioration of the environment through depletion of resources such as air, water and soil; the destruction of ecosystems and the extinction of wildlife...
worldwide, and modern practices of raising animals for food contributes on a "massive scale" to air and water pollution
Pollution
Pollution is the introduction of contaminants into a natural environment that causes instability, disorder, harm or discomfort to the ecosystem i.e. physical systems or living organisms. Pollution can take the form of chemical substances or energy, such as noise, heat or light...
, land degradation, climate change
Climate change
Climate change is a significant and lasting change in the statistical distribution of weather patterns over periods ranging from decades to millions of years. It may be a change in average weather conditions or the distribution of events around that average...
, and loss of biodiversity
Biodiversity
Biodiversity is the degree of variation of life forms within a given ecosystem, biome, or an entire planet. Biodiversity is a measure of the health of ecosystems. Biodiversity is in part a function of climate. In terrestrial habitats, tropical regions are typically rich whereas polar regions...
. The initiative concluded that "the livestock sector emerges as one of the top two or three most significant contributors to the most serious environmental problems, at every scale from local to global." In 2006 FAO estimated that meat industry contributes 18% of all emissions of greenhouse gasses. This figure was challenged in 2009 by two World-Watch researchers who estimated a 51% minimum, however this paper has not been peer reviewed.
Animals fed on grain need more water than grain crops. In tracking food animal production from the feed through to the dinner table, the inefficiencies of meat, milk
Milk
Milk is a white liquid produced by the mammary glands of mammals. It is the primary source of nutrition for young mammals before they are able to digest other types of food. Early-lactation milk contains colostrum, which carries the mother's antibodies to the baby and can reduce the risk of many...
and egg
Egg (food)
Eggs are laid by females of many different species, including birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish, and have probably been eaten by mankind for millennia. Bird and reptile eggs consist of a protective eggshell, albumen , and vitellus , contained within various thin membranes...
production range from a 4:1 energy input to protein output ratio up to 54:1. The result is that producing animal-based food is typically much less efficient than the harvesting of grains, vegetables, legumes, seeds and fruits for direct human consumption.
Relatedly, the production and consumption of meat and other animal products is associated with the
clearing of rainforests, resource depletion, air and water pollution, land and economic inefficiency, species extinction, and other environmental harms.
The author of the influential 2006 Stern Review on climate change has stated "people will need to turn vegetarian if the world is to conquer climate change". This is due to emissions of methane (which is 23 times more potent of a greenhouse gas versus carbon dioxide) from cows and pigs via flatulence
Flatulence
Flatulence is the expulsion through the rectum of a mixture of gases that are byproducts of the digestion process of mammals and other animals. The medical term for the mixture of gases is flatus, informally known as a fart, or simply gas...
and eructation.
Palm oil

Palm oil
Palm oil, coconut oil and palm kernel oil are edible plant oils derived from the fruits of palm trees. Palm oil is extracted from the pulp of the fruit of the oil palm Elaeis guineensis; palm kernel oil is derived from the kernel of the oil palm and coconut oil is derived from the kernel of the...
, produced from the oil palm
Oil palm
The oil palms comprise two species of the Arecaceae, or palm family. They are used in commercial agriculture in the production of palm oil. The African Oil Palm Elaeis guineensis is native to West Africa, occurring between Angola and Gambia, while the American Oil Palm Elaeis oleifera is native to...
, is a basic source of income for many farmers in Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia, South-East Asia, South East Asia or Southeastern Asia is a subregion of Asia, consisting of the countries that are geographically south of China, east of India, west of New Guinea and north of Australia. The region lies on the intersection of geological plates, with heavy seismic...
, Central
Central Africa
Central Africa is a core region of the African continent which includes Burundi, the Central African Republic, Chad, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, and Rwanda....
and West Africa
West Africa
West Africa or Western Africa is the westernmost region of the African continent. Geopolitically, the UN definition of Western Africa includes the following 16 countries and an area of approximately 5 million square km:-Flags of West Africa:...
, and Central America
Central America
Central America is the central geographic region of the Americas. It is the southernmost, isthmian portion of the North American continent, which connects with South America on the southeast. When considered part of the unified continental model, it is considered a subcontinent...
. It is locally used as a cooking oil, exported for use in many commercial food and personal care products and is converted into biofuel. It produces up to 10 times more oil per unit area as soyabeans, rapeseed
Rapeseed
Rapeseed , also known as rape, oilseed rape, rapa, rappi, rapaseed is a bright yellow flowering member of the family Brassicaceae...
or sunflower
Sunflower
Sunflower is an annual plant native to the Americas. It possesses a large inflorescence . The sunflower got its name from its huge, fiery blooms, whose shape and image is often used to depict the sun. The sunflower has a rough, hairy stem, broad, coarsely toothed, rough leaves and circular heads...
s. Oil palms produce 38% of vegetable oil output on 5% of the world’s vegetable-oil farmland. Palm oil is under increasing scrutiny in relation to its effects on the environment
Environment (biophysical)
The biophysical environment is the combined modeling of the physical environment and the biological life forms within the environment, and includes all variables, parameters as well as conditions and modes inside the Earth's biosphere. The biophysical environment can be divided into two categories:...
.
Energy industry
The environmental impact of energy harvestingEnergy harvesting
Energy harvesting is the process by which energy is derived from external sources , captured, and stored for small, wireless autonomous devices, like those used in wearable electronics and wireless sensor networks.Energy harvesters...
and consumption
Energy consumption
Energy consumption is the consumption of energy or power. It is covered in the following articles and categories:* World energy consumption* Domestic energy consumption* Fuel efficiency in transportation* Electric energy consumption* Electricity generation...
is diverse. In recent years there has been a trend towards the increased commercialization of various renewable energy sources
Renewable energy commercialization
Renewable energy commercialization involves the deployment of three generations of renewable energy technologies dating back more than 100 years. First-generation technologies, which are already mature and economically competitive, include biomass, hydroelectricity, geothermal power and heat...
.
In the real world of consumption of fossil fuel resources which lead to global warming
Global warming
Global warming refers to the rising average temperature of Earth's atmosphere and oceans and its projected continuation. In the last 100 years, Earth's average surface temperature increased by about with about two thirds of the increase occurring over just the last three decades...
and climate change however little change is being made in many parts of the world. Chinese oil demand for instance, is projected to grow nearly 20% in the next six years, and that country already imports over half of the 8 million barrels a day it uses. If the peak oil
Peak oil
Peak oil is the point in time when the maximum rate of global petroleum extraction is reached, after which the rate of production enters terminal decline. This concept is based on the observed production rates of individual oil wells, projected reserves and the combined production rate of a field...
theory proves out, more explorations of viable alternative energy sources, could be more friendly to the environment.
Rapidly advancing technologies can achieve a transition of energy generation, water and waste management, and food production towards better environmental and energy usage practices using methods of systems ecology
Systems ecology
Systems ecology is an interdisciplinary field of ecology, taking a holistic approach to the study of ecological systems, especially ecosystems. Systems ecology can be seen as an application of general systems theory to ecology. Central to the systems ecology approach is the idea that an ecosystem...
and industrial ecology
Industrial ecology
Industrial Ecology is the study of material and energy flows through industrial systems. The global industrial economy can be modeled as a network of industrial processes that extract resources from the Earth and transform those resources into commodities which can be bought and sold to meet the...
.
Biodiesel
The environmental impact of biodiesel is diverse.Coal mining and burning
The environmental impact of coal mining and burning is diverse. Legislation passed by the U.S. Congress in 1990 required the United States Environmental Protection AgencyUnited States Environmental Protection Agency
The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency is an agency of the federal government of the United States charged with protecting human health and the environment, by writing and enforcing regulations based on laws passed by Congress...
(EPA) to issue a plan to alleviate toxic pollution from coal-fired power plants. After delay and litigation, the EPA now has a court-imposed deadline of March 16, 2011, to issue its report.
Electricity generation
The environmental impact of electricity generation is significant because modern society uses large amounts of electrical power. This power is normally generatedElectricity generation
Electricity generation is the process of generating electric energy from other forms of energy.The fundamental principles of electricity generation were discovered during the 1820s and early 1830s by the British scientist Michael Faraday...
at power plants that convert some other kind of energy into electrical power. Each such system has advantages and disadvantages, but many of them pose environmental concerns.
Nuclear power
The environmental impact of nuclear powerNuclear power
Nuclear power is the use of sustained nuclear fission to generate heat and electricity. Nuclear power plants provide about 6% of the world's energy and 13–14% of the world's electricity, with the U.S., France, and Japan together accounting for about 50% of nuclear generated electricity...
results from the nuclear fuel cycle
Nuclear fuel cycle
The nuclear fuel cycle, also called nuclear fuel chain, is the progression of nuclear fuel through a series of differing stages. It consists of steps in the front end, which are the preparation of the fuel, steps in the service period in which the fuel is used during reactor operation, and steps in...
, operation, and the lingering effects of the Chernobyl disaster
Chernobyl disaster
The Chernobyl disaster was a nuclear accident that occurred on 26 April 1986 at the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant in Ukraine , which was under the direct jurisdiction of the central authorities in Moscow...
.
Oil shale industry

Land use
Land use is the human use of land. Land use involves the management and modification of natural environment or wilderness into built environment such as fields, pastures, and settlements. It has also been defined as "the arrangements, activities and inputs people undertake in a certain land cover...
, waste management
Waste management
Waste management is the collection, transport, processing or disposal,managing and monitoring of waste materials. The term usually relates to materials produced by human activity, and the process is generally undertaken to reduce their effect on health, the environment or aesthetics...
, and water
Water pollution
Water pollution is the contamination of water bodies . Water pollution occurs when pollutants are discharged directly or indirectly into water bodies without adequate treatment to remove harmful compounds....
and air pollution
Air pollution
Air pollution is the introduction of chemicals, particulate matter, or biological materials that cause harm or discomfort to humans or other living organisms, or cause damage to the natural environment or built environment, into the atmosphere....
caused by the extraction and processing
Oil shale industry
Oil shale industry is an industry of mining and processing of oil shale—a fine-grained sedimentary rock, containing significant amounts of kerogen , from which liquid hydrocarbons can be manufactured. The industry has developed in Brazil, China, Estonia and to some extent in Germany, Israel and...
of oil shale
Oil shale
Oil shale, an organic-rich fine-grained sedimentary rock, contains significant amounts of kerogen from which liquid hydrocarbons called shale oil can be produced...
. Surface mining
Surface mining
Surface mining , is a type of mining in which soil and rock overlying the mineral deposit are removed...
of oil shale deposits
Oil shale reserves
Oil shale reserves refers to oil shale resources that are recoverable under given economic restraints and technological abilities. Oil shale deposits range from small presently non-economic occurrences to large presently commercially exploitable reserves...
causes the usual environmental impacts of open-pit mining
Open-pit mining
Open-pit mining or opencast mining refers to a method of extracting rock or minerals from the earth by their removal from an open pit or borrow....
. In addition, the combustion
Combustion
Combustion or burning is the sequence of exothermic chemical reactions between a fuel and an oxidant accompanied by the production of heat and conversion of chemical species. The release of heat can result in the production of light in the form of either glowing or a flame...
and thermal processing generate waste material, which must be disposed of, and harmful atmospheric emissions, including carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a naturally occurring chemical compound composed of two oxygen atoms covalently bonded to a single carbon atom...
, a major greenhouse gas
Greenhouse gas
A greenhouse gas is a gas in an atmosphere that absorbs and emits radiation within the thermal infrared range. This process is the fundamental cause of the greenhouse effect. The primary greenhouse gases in the Earth's atmosphere are water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, and ozone...
. Experimental in-situ conversion processes and carbon capture and storage
Carbon capture and storage
Carbon capture and storage , alternatively referred to as carbon capture and sequestration, is a technology to prevent large quantities of from being released into the atmosphere from the use of fossil fuel in power generation and other industries. It is often regarded as a means of mitigating...
technologies may reduce some of these concerns in future, but may raise others, such as the pollution of groundwater.
Petroleum
The environmental impact of petroleumPetroleum
Petroleum or crude oil is a naturally occurring, flammable liquid consisting of a complex mixture of hydrocarbons of various molecular weights and other liquid organic compounds, that are found in geologic formations beneath the Earth's surface. Petroleum is recovered mostly through oil drilling...
is often negative because it is toxic to almost all forms of life. The possibility of climate change
Climate change
Climate change is a significant and lasting change in the statistical distribution of weather patterns over periods ranging from decades to millions of years. It may be a change in average weather conditions or the distribution of events around that average...
exists. Petroleum, commonly referred to as oil, is closely linked to virtually all aspects of present society, especially for transportation and heating for both homes and for commercial activities.
Reservoirs

Dam
Dam
A dam is a barrier that impounds water or underground streams. Dams generally serve the primary purpose of retaining water, while other structures such as floodgates or levees are used to manage or prevent water flow into specific land regions. Hydropower and pumped-storage hydroelectricity are...
s and the reservoir
Reservoir
A reservoir , artificial lake or dam is used to store water.Reservoirs may be created in river valleys by the construction of a dam or may be built by excavation in the ground or by conventional construction techniques such as brickwork or cast concrete.The term reservoir may also be used to...
s can be used to supply drinking water
Drinking water
Drinking water or potable water is water pure enough to be consumed or used with low risk of immediate or long term harm. In most developed countries, the water supplied to households, commerce and industry is all of drinking water standard, even though only a very small proportion is actually...
, generate hydroelectric power, increasing the water supply for irrigation
Irrigation
Irrigation may be defined as the science of artificial application of water to the land or soil. It is used to assist in the growing of agricultural crops, maintenance of landscapes, and revegetation of disturbed soils in dry areas and during periods of inadequate rainfall...
, provide recreational opportunities and to improve certain aspects of the environment. However, adverse environmental and sociological impacts have also been identified during and after many reservoir constructions. Whether reservoir projects are ultimately beneficial or detrimental—to both the environment and surrounding human populations— has been debated since the 1960s and probably long before that. In 1960 the construction of Llyn Celyn
Llyn Celyn
Llyn Celyn is a large reservoir constructed between 1960 and 1965 in the valley of the River Tryweryn in Gwynedd, North Wales. It measures roughly 2½ miles long by a mile wide, and has a maximum depth of...
and the flooding of Capel Celyn
Capel Celyn
Capel Celyn was a rural community to the north west of Bala in Gwynedd, north Wales, in the Afon Tryweryn valley. The village and other parts of the valley were flooded to create a reservoir, Llyn Celyn, in order to supply Liverpool and The Wirral with water for industry...
provoked political uproar which continues to this day. More recently, the construction of Three Gorges Dam
Three Gorges Dam
The Three Gorges Dam is a hydroelectric dam that spans the Yangtze River by the town of Sandouping, located in the Yiling District of Yichang, in Hubei province, China...
and other similar projects throughout Asia
Asia
Asia is the world's largest and most populous continent, located primarily in the eastern and northern hemispheres. It covers 8.7% of the Earth's total surface area and with approximately 3.879 billion people, it hosts 60% of the world's current human population...
, Africa
Africa
Africa is the world's second largest and second most populous continent, after Asia. At about 30.2 million km² including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of the Earth's total surface area and 20.4% of the total land area...
and Latin America
Latin America
Latin America is a region of the Americas where Romance languages – particularly Spanish and Portuguese, and variably French – are primarily spoken. Latin America has an area of approximately 21,069,500 km² , almost 3.9% of the Earth's surface or 14.1% of its land surface area...
have generated considerable environmental and political debate.
Wind power

Wind power
Wind power is the conversion of wind energy into a useful form of energy, such as using wind turbines to make electricity, windmills for mechanical power, windpumps for water pumping or drainage, or sails to propel ships....
consumes no fuel, and emits no air pollution
Air pollution
Air pollution is the introduction of chemicals, particulate matter, or biological materials that cause harm or discomfort to humans or other living organisms, or cause damage to the natural environment or built environment, into the atmosphere....
, unlike fossil fuel power sources. The energy consumed to manufacture and transport the materials used to build a wind power plant is equal to the new energy produced by the plant within a few months. While a wind farm may cover a large area of land, many land uses such as agriculture are compatible, with only small areas of turbine foundations and infrastructure made unavailable for use.
There are reports of bird and bat mortality at wind turbines, as there are around other artificial structures. The scale of the ecological impact may or may not be significant, depending on specific circumstances. Prevention and mitigation of wildlife fatalities, and protection of peat bogs, affect the siting and operation of wind turbines.
There are conflicting reports about the effects of noise on people who live very close to a wind turbine.
Cleaning agents
The environmental impact of cleaning agentCleaning agent
Cleaning agents are substances, usually liquids, that are used to remove dirt, including dust, stains, bad smells, and clutter on surfaces. Purposes of cleaning agents include health, beauty, absence of offensive odor, avoidance of shame, and avoidance of spreading of dirt and contaminants to...
s is diverse. In recent years, measures have been taken to reduce these effects.
Nanotechnology
NanotechnologyNanotechnology
Nanotechnology is the study of manipulating matter on an atomic and molecular scale. Generally, nanotechnology deals with developing materials, devices, or other structures possessing at least one dimension sized from 1 to 100 nanometres...
's environmental impact can be split into two aspects: the potential for nanotechnological innovations to help improve the environment, and the possibly novel type of pollution that nanotechnological materials might cause if released into the environment. As nanotechnology is an emerging field, there is great debate regarding to what extent industrial and commercial use of nanomaterials
Nanomaterials
Nanomaterials is a field that takes a materials science-based approach to nanotechnology. It studies materials with morphological features on the nanoscale, and especially those that have special properties stemming from their nanoscale dimensions...
will affect organisms and ecosystems.
Paint
The environmental impact of paint is diverse. Traditional paintingPainting
Painting is the practice of applying paint, pigment, color or other medium to a surface . The application of the medium is commonly applied to the base with a brush but other objects can be used. In art, the term painting describes both the act and the result of the action. However, painting is...
materials and processes can have harmful effects on the environment
Environment (biophysical)
The biophysical environment is the combined modeling of the physical environment and the biological life forms within the environment, and includes all variables, parameters as well as conditions and modes inside the Earth's biosphere. The biophysical environment can be divided into two categories:...
, including those from the use of lead
Lead
Lead is a main-group element in the carbon group with the symbol Pb and atomic number 82. Lead is a soft, malleable poor metal. It is also counted as one of the heavy metals. Metallic lead has a bluish-white color after being freshly cut, but it soon tarnishes to a dull grayish color when exposed...
and other additives. Measures can be taken to reduce environmental impact, including accurately estimating paint quantities so that wastage is minimized, use of paints, coatings, painting accessories and techniques that are environmentally preferred. The United States Environmental Protection Agency
United States Environmental Protection Agency
The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency is an agency of the federal government of the United States charged with protecting human health and the environment, by writing and enforcing regulations based on laws passed by Congress...
guidelines and Green Star
Green Star (Australia)
Green Star is a voluntary environmental rating system for buildings in Australia. It was launched in 2003 by the Green Building Council of Australia....
ratings are some of the standards that can be applied.
Paper
The environmental impact of paper is significant, which has led to changes in industry and behaviour at both business and personal levels. With the use of modern technology such as the printing pressPrinting press
A printing press is a device for applying pressure to an inked surface resting upon a print medium , thereby transferring the ink...
and the highly mechanised harvesting of wood, paper has become a cheap commodity. This has led to a high level of consumption and waste. With the rise in environmental awareness due to the lobbying by environmental organization
Environmental organization
An environmental organization is an organization that seeks to protect, analyze or monitor the environment against misuse or degradation or lobby for these goals....
s and with increased government regulation there is now a trend towards sustainability
Sustainability
Sustainability is the capacity to endure. For humans, sustainability is the long-term maintenance of well being, which has environmental, economic, and social dimensions, and encompasses the concept of union, an interdependent relationship and mutual responsible position with all living and non...
in the pulp and paper industry
Pulp and paper industry
The global pulp and paper industry is dominated by North American , northern European and East Asian countries...
.
Pesticides
The environmental impact of pesticidePesticide
Pesticides are substances or mixture of substances intended for preventing, destroying, repelling or mitigating any pest.A pesticide may be a chemical unicycle, biological agent , antimicrobial, disinfectant or device used against any pest...
s is often greater than what is intended by those who use them. Over 98% of sprayed insecticides and 95% of herbicides reach a destination other than their target species, including nontarget species, air, water, bottom sediments, and food. Pesticide contaminates land and water when it escapes from production sites and storage tanks, when it runs off from fields, when it is discarded, when it is sprayed aerially, and when it is sprayed into water to kill algae.
The amount of pesticide that migrates from the intended application area is influenced by the particular chemical's properties: its propensity for binding to soil, its vapor pressure
Vapor pressure
Vapor pressure or equilibrium vapor pressure is the pressure of a vapor in thermodynamic equilibrium with its condensed phases in a closed system. All liquids have a tendency to evaporate, and some solids can sublimate into a gaseous form...
, its water solubility
Solubility
Solubility is the property of a solid, liquid, or gaseous chemical substance called solute to dissolve in a solid, liquid, or gaseous solvent to form a homogeneous solution of the solute in the solvent. The solubility of a substance fundamentally depends on the used solvent as well as on...
, and its resistance to being broken down over time. Factors in the soil, such as its texture, its ability to retain water, and the amount of organic matter contained in it, also affect the amount of pesticide that will leave the area. Some pesticides contribute to global warming
Global warming
Global warming refers to the rising average temperature of Earth's atmosphere and oceans and its projected continuation. In the last 100 years, Earth's average surface temperature increased by about with about two thirds of the increase occurring over just the last three decades...
and the depletion of the ozone layer
Ozone layer
The ozone layer is a layer in Earth's atmosphere which contains relatively high concentrations of ozone . This layer absorbs 97–99% of the Sun's high frequency ultraviolet light, which is potentially damaging to the life forms on Earth...
.
Pharmaceuticals and personal care products
The environmental impact of pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs) is largely speculative. PPCPs are substances used by individuals for personal health or cosmeticCosmetics
Cosmetics are substances used to enhance the appearance or odor of the human body. Cosmetics include skin-care creams, lotions, powders, perfumes, lipsticks, fingernail and toe nail polish, eye and facial makeup, towelettes, permanent waves, colored contact lenses, hair colors, hair sprays and...
reasons and the products used by agribusiness
Agribusiness
In agriculture, agribusiness is a generic term for the various businesses involved in food production, including farming and contract farming, seed supply, agrichemicals, farm machinery, wholesale and distribution, processing, marketing, and retail sales....
to boost growth or health of livestock. PPCPs have been detected in water bodies throughout the world. The effects of these chemicals on humans and the environment are not yet known, but to date there is no scientific evidence that they have an impact on human health.
Mining

Erosion
Erosion is when materials are removed from the surface and changed into something else. It only works by hydraulic actions and transport of solids in the natural environment, and leads to the deposition of these materials elsewhere...
, formation of sinkhole
Sinkhole
A sinkhole, also known as a sink, shake hole, swallow hole, swallet, doline or cenote, is a natural depression or hole in the Earth's surface caused by karst processes — the chemical dissolution of carbonate rocks or suffosion processes for example in sandstone...
s, loss of biodiversity
Biodiversity
Biodiversity is the degree of variation of life forms within a given ecosystem, biome, or an entire planet. Biodiversity is a measure of the health of ecosystems. Biodiversity is in part a function of climate. In terrestrial habitats, tropical regions are typically rich whereas polar regions...
, and contamination of soil, groundwater
Groundwater
Groundwater is water located beneath the ground surface in soil pore spaces and in the fractures of rock formations. A unit of rock or an unconsolidated deposit is called an aquifer when it can yield a usable quantity of water. The depth at which soil pore spaces or fractures and voids in rock...
and surface water
Surface water
Surface water is water collecting on the ground or in a stream, river, lake, wetland, or ocean; it is related to water collecting as groundwater or atmospheric water....
by chemicals from mining processes. In some cases, additional forest logging is done in the vicinity of mines to increase the available room for the storage of the created debris and soil. Besides creating environmental damage, the contamination resulting from leakage of chemicals also affect the health of the local population. Mining companies in some countries are required to follow environmental and rehabilitation codes, ensuring the area mined is returned to close to its original state. Some mining methods may have significant environmental and public health effects.
Transport

Transport
Transport or transportation is the movement of people, cattle, animals and goods from one location to another. Modes of transport include air, rail, road, water, cable, pipeline, and space. The field can be divided into infrastructure, vehicles, and operations...
is significant because it is a major user of energy, and burns most of the world's petroleum
Petroleum
Petroleum or crude oil is a naturally occurring, flammable liquid consisting of a complex mixture of hydrocarbons of various molecular weights and other liquid organic compounds, that are found in geologic formations beneath the Earth's surface. Petroleum is recovered mostly through oil drilling...
. This creates air pollution
Air pollution
Air pollution is the introduction of chemicals, particulate matter, or biological materials that cause harm or discomfort to humans or other living organisms, or cause damage to the natural environment or built environment, into the atmosphere....
, including nitrous oxide
Nitrous oxide
Nitrous oxide, commonly known as laughing gas or sweet air, is a chemical compound with the formula . It is an oxide of nitrogen. At room temperature, it is a colorless non-flammable gas, with a slightly sweet odor and taste. It is used in surgery and dentistry for its anesthetic and analgesic...
s and particulates, and is a significant contributor to global warming
Global warming
Global warming refers to the rising average temperature of Earth's atmosphere and oceans and its projected continuation. In the last 100 years, Earth's average surface temperature increased by about with about two thirds of the increase occurring over just the last three decades...
through emission of carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a naturally occurring chemical compound composed of two oxygen atoms covalently bonded to a single carbon atom...
, for which transport is the fastest-growing emission sector. By subsector, road transport is the largest contributor to global warming.
Environmental regulations in developed countries have reduced the individual vehicles emission; however, this has been offset by an increase in the number of vehicles, and more use of each vehicle. Some pathways to reduced the carbon emissions of road vehicles considerably have been studied. Energy use and emissions vary largely between modes, causing environmentalists
Environmentalism
Environmentalism is a broad philosophy, ideology and social movement regarding concerns for environmental conservation and improvement of the health of the environment, particularly as the measure for this health seeks to incorporate the concerns of non-human elements...
to call for a transition from air and road to rail and human-powered transport, and increase transport electrification and energy efficiency
Efficient energy use
Efficient energy use, sometimes simply called energy efficiency, is the goal of efforts to reduce the amount of energy required to provide products and services. For example, insulating a home allows a building to use less heating and cooling energy to achieve and maintain a comfortable temperature...
.
Other environmental impacts of transport systems include traffic congestion
Traffic congestion
Traffic congestion is a condition on road networks that occurs as use increases, and is characterized by slower speeds, longer trip times, and increased vehicular queueing. The most common example is the physical use of roads by vehicles. When traffic demand is great enough that the interaction...
and automobile-oriented urban sprawl
Urban sprawl
Urban sprawl, also known as suburban sprawl, is a multifaceted concept, which includes the spreading outwards of a city and its suburbs to its outskirts to low-density and auto-dependent development on rural land, high segregation of uses Urban sprawl, also known as suburban sprawl, is a...
, which can consume natural habitat and agricultural lands. By reducing transportation emissions globally, it is predicted that there will be significant positive effects on Earth's air quality, acid rain
Acid rain
Acid rain is a rain or any other form of precipitation that is unusually acidic, meaning that it possesses elevated levels of hydrogen ions . It can have harmful effects on plants, aquatic animals, and infrastructure. Acid rain is caused by emissions of carbon dioxide, sulfur dioxide and nitrogen...
, smog
Smog
Smog is a type of air pollution; the word "smog" is a portmanteau of smoke and fog. Modern smog is a type of air pollution derived from vehicular emission from internal combustion engines and industrial fumes that react in the atmosphere with sunlight to form secondary pollutants that also combine...
and climate change.
The health impact of transport emissions is also of concern. A recent survey of the studies on the effect of traffic emissions on pregnancy outcomes has linked exposure to emissions to adverse effects on gestational duration and possibly also intrauterine growth.
Aviation
The environmental impact of aviation occurs because aircraft engineAircraft engine
An aircraft engine is the component of the propulsion system for an aircraft that generates mechanical power. Aircraft engines are almost always either lightweight piston engines or gas turbines...
s emit noise
Noise pollution
Noise pollution is excessive, displeasing human, animal or machine-created environmental noise that disrupts the activity or balance of human or animal life...
, particulates, and gases which contribute to climate change
Climate change
Climate change is a significant and lasting change in the statistical distribution of weather patterns over periods ranging from decades to millions of years. It may be a change in average weather conditions or the distribution of events around that average...
and global dimming
Global dimming
Global dimming is the gradual reduction in the amount of global direct irradiance at the Earth's surface that was observed for several decades after the start of systematic measurements in the 1950s. The effect varies by location, but worldwide it has been estimated to be of the order of a 4%...
. Despite emission reductions from automobiles and more fuel-efficient and less polluting turbofan
Turbofan
The turbofan is a type of airbreathing jet engine that is widely used for aircraft propulsion. A turbofan combines two types of engines, the turbo portion which is a conventional gas turbine engine, and the fan, a propeller-like ducted fan...
and turboprop
Turboprop
A turboprop engine is a type of turbine engine which drives an aircraft propeller using a reduction gear.The gas turbine is designed specifically for this application, with almost all of its output being used to drive the propeller...
engines, the rapid growth of air travel
Air travel
Air travel is a form of travel in vehicles such as airplanes, helicopters, hot air balloons, blimps, gliders, hang gliding, parachuting or anything else that can sustain flight.-Domestic and international flights:...
in recent years contributes to an increase in total pollution attributable to aviation
Aviation
Aviation is the design, development, production, operation, and use of aircraft, especially heavier-than-air aircraft. Aviation is derived from avis, the Latin word for bird.-History:...
. In the EU
European Union
The European Union is an economic and political union of 27 independent member states which are located primarily in Europe. The EU traces its origins from the European Coal and Steel Community and the European Economic Community , formed by six countries in 1958...
, greenhouse gas
Greenhouse gas
A greenhouse gas is a gas in an atmosphere that absorbs and emits radiation within the thermal infrared range. This process is the fundamental cause of the greenhouse effect. The primary greenhouse gases in the Earth's atmosphere are water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, and ozone...
emissions from aviation increased by 87% between 1990 and 2006. Among other factors leading to this phenomenon are the increasing number of hypermobile travellers
Hypermobility (travel)
The term hypermobility in regard to travelers arose around 1980 and is a concept that has increased in useage since the early 1990s: Damette ; Hepworth and Ducatel ; Whitelegg ; Lowe ; van der Stoep ; Shields ; Cox ; Adams ; Khisty and Zeitler ; Gössling et al. ; and Mander & Randles...
and social factors that are making air travel commonplace, such as frequent flyer programs.
There is an ongoing debate about possible taxation of air travel and the inclusion of aviation in an emissions trading
Emissions trading
Emissions trading is a market-based approach used to control pollution by providing economic incentives for achieving reductions in the emissions of pollutants....
scheme, with a view to ensuring that the total external costs of aviation are taken into account.
Roads
The environmental impact of roads includes the local effects of highways (public roads) such as on noise, water pollutionWater pollution
Water pollution is the contamination of water bodies . Water pollution occurs when pollutants are discharged directly or indirectly into water bodies without adequate treatment to remove harmful compounds....
, habitat destruction
Habitat destruction
Habitat destruction is the process in which natural habitat is rendered functionally unable to support the species present. In this process, the organisms that previously used the site are displaced or destroyed, reducing biodiversity. Habitat destruction by human activity mainly for the purpose of...
/disturbance and local air quality; and the wider effects including climate change
Climate change
Climate change is a significant and lasting change in the statistical distribution of weather patterns over periods ranging from decades to millions of years. It may be a change in average weather conditions or the distribution of events around that average...
from vehicle emissions. The design, construction and management of roads, parking
Parking
Parking is the act of stopping a vehicle and leaving it unoccupied for more than a brief time. Parking on one or both sides of a road is commonly permitted, though often with restrictions...
and other related facilities as well as the design and regulation of vehicle
Vehicle
A vehicle is a device that is designed or used to transport people or cargo. Most often vehicles are manufactured, such as bicycles, cars, motorcycles, trains, ships, boats, and aircraft....
s can change the impacts to varying degrees.
Shipping
The environmental impact of shippingShipping
Shipping has multiple meanings. It can be a physical process of transporting commodities and merchandise goods and cargo, by land, air, and sea. It also can describe the movement of objects by ship.Land or "ground" shipping can be by train or by truck...
includes greenhouse gas
Greenhouse gas
A greenhouse gas is a gas in an atmosphere that absorbs and emits radiation within the thermal infrared range. This process is the fundamental cause of the greenhouse effect. The primary greenhouse gases in the Earth's atmosphere are water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, and ozone...
emissions and oil pollution. Carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a naturally occurring chemical compound composed of two oxygen atoms covalently bonded to a single carbon atom...
emissions from shipping is currently estimated at 4 to 5% of the global total, and estimated by the International Maritime Organisation (IMO) to rise by up to 72% by 2020 if no action is taken.
The First Intersessional Meeting of the IMO Working Group on Greenhouse Gas Emissions from Ships took place in Oslo
Oslo
Oslo is a municipality, as well as the capital and most populous city in Norway. As a municipality , it was established on 1 January 1838. Founded around 1048 by King Harald III of Norway, the city was largely destroyed by fire in 1624. The city was moved under the reign of Denmark–Norway's King...
, Norway
Norway
Norway , officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic unitary constitutional monarchy whose territory comprises the western portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula, Jan Mayen, and the Arctic archipelago of Svalbard and Bouvet Island. Norway has a total area of and a population of about 4.9 million...
on 23–27 June 2008. It was tasked with developing the technical basis for the reduction mechanisms that may form part of a future IMO regime to control greenhouse gas emissions from international shipping, and a draft of the actual reduction mechanisms themselves, for further consideration by IMO’s Marine Environment Protection Committee (MEPC).
War

Scorched earth
A scorched earth policy is a military strategy or operational method which involves destroying anything that might be useful to the enemy while advancing through or withdrawing from an area...
methods during, or after war have been in use for much of recorded history but with modern technology
Technology
Technology is the making, usage, and knowledge of tools, machines, techniques, crafts, systems or methods of organization in order to solve a problem or perform a specific function. It can also refer to the collection of such tools, machinery, and procedures. The word technology comes ;...
war can cause a far greater devastation on the environment
Environment (biophysical)
The biophysical environment is the combined modeling of the physical environment and the biological life forms within the environment, and includes all variables, parameters as well as conditions and modes inside the Earth's biosphere. The biophysical environment can be divided into two categories:...
. Unexploded ordnance
Unexploded ordnance
Unexploded ordnance are explosive weapons that did not explode when they were employed and still pose a risk of detonation, potentially many decades after they were used or discarded.While "UXO" is widely and informally used, munitions and explosives of...
can render land unusable for further use or make access across it dangerous or fatal.
Biodiversity
Human impact on biodiversity is significant, humans have caused the extinction of many species including the dodo and perhaps even many of the large megafaunal species during the last ice ageIce age
An ice age or, more precisely, glacial age, is a generic geological period of long-term reduction in the temperature of the Earth's surface and atmosphere, resulting in the presence or expansion of continental ice sheets, polar ice sheets and alpine glaciers...
. Though most experts agree that human beings have accelerated the rate of species extinction, the exact degree of this impact is unknown, perhaps 100 to 1000 times the normal background rate of extinction. Some authors have postulated that without human interference the biodiversity of this planet would continue to grow at an exponential rate.
Coral reefs
Human impact on coral reefs is significant. Coral reefCoral reef
Coral reefs are underwater structures made from calcium carbonate secreted by corals. Coral reefs are colonies of tiny living animals found in marine waters that contain few nutrients. Most coral reefs are built from stony corals, which in turn consist of polyps that cluster in groups. The polyps...
s are dying around the world. In particular, coral mining, pollution
Pollution
Pollution is the introduction of contaminants into a natural environment that causes instability, disorder, harm or discomfort to the ecosystem i.e. physical systems or living organisms. Pollution can take the form of chemical substances or energy, such as noise, heat or light...
(organic and non-organic), overfishing
Overfishing
Overfishing occurs when fishing activities reduce fish stocks below an acceptable level. This can occur in any body of water from a pond to the oceans....
, blast fishing
Blast fishing
Blast fishing or dynamite fishing is the practice of using explosives to stun or kill schools of fish for easy collection. This often illegal practice can be extremely destructive to the surrounding ecosystem, as the explosion often destroys the underlying habitat that supports the fish...
and the digging of canal
Canal
Canals are man-made channels for water. There are two types of canal:#Waterways: navigable transportation canals used for carrying ships and boats shipping goods and conveying people, further subdivided into two kinds:...
s and access into islands and bays are serious threats to these ecosystems. Coral reefs also face high dangers from pollution, diseases, destructive fishing practices and warming oceans. In order to find answers for these problems, researchers study the various factors that impact reefs. The list of factors is long, including the ocean's role as a carbon dioxide sink
Carbon dioxide sink
A carbon sink is a natural or artificial reservoir that accumulates and stores some carbon-containing chemical compound for an indefinite period. The process by which carbon sinks remove carbon dioxide from the atmosphere is known as carbon sequestration...
, atmospheric changes, ultraviolet light, ocean acidification
Ocean acidification
Ocean acidification is the name given to the ongoing decrease in the pH and increase in acidity of the Earth's oceans, caused by the uptake of anthropogenic carbon dioxide from the atmosphere....
, biological virus
Virus
A virus is a small infectious agent that can replicate only inside the living cells of organisms. Viruses infect all types of organisms, from animals and plants to bacteria and archaea...
, impacts of dust storms carrying agents to far flung reefs, pollutants, algal bloom
Algal bloom
An algal bloom is a rapid increase or accumulation in the population of algae in an aquatic system. Algal blooms may occur in freshwater as well as marine environments. Typically, only one or a small number of phytoplankton species are involved, and some blooms may be recognized by discoloration...
s and others. Reefs are threatened well beyond coastal areas.
General estimates show approximately 10% world's coral reefs are already dead. It is estimated that about 60% of the world's reefs are at risk due to destructive, human-related activities. The threat to the health of reefs is particularly strong in Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia, South-East Asia, South East Asia or Southeastern Asia is a subregion of Asia, consisting of the countries that are geographically south of China, east of India, west of New Guinea and north of Australia. The region lies on the intersection of geological plates, with heavy seismic...
, where 80% of reefs are endangered
Endangered species
An endangered species is a population of organisms which is at risk of becoming extinct because it is either few in numbers, or threatened by changing environmental or predation parameters...
.
Nitrogen cycle
Human impact on the nitrogen cycle is diverse. Agricultural and industrial nitrogenNitrogen
Nitrogen is a chemical element that has the symbol N, atomic number of 7 and atomic mass 14.00674 u. Elemental nitrogen is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, and mostly inert diatomic gas at standard conditions, constituting 78.08% by volume of Earth's atmosphere...
(N) inputs to the environment currently exceed inputs from natural N fixation. As a consequence of anthropogenic inputs, the global nitrogen cycle
Nitrogen cycle
The nitrogen cycle is the process by which nitrogen is converted between its various chemical forms. This transformation can be carried out by both biological and non-biological processes. Important processes in the nitrogen cycle include fixation, mineralization, nitrification, and denitrification...
(Fig. 1) has been significantly altered over the past century. Global atmospheric nitrous oxide
Nitrous oxide
Nitrous oxide, commonly known as laughing gas or sweet air, is a chemical compound with the formula . It is an oxide of nitrogen. At room temperature, it is a colorless non-flammable gas, with a slightly sweet odor and taste. It is used in surgery and dentistry for its anesthetic and analgesic...
(N2O) mole fractions have increased from a pre-industrial value of ~270 nmol/mol to ~319 nmol/mol in 2005. Human activities account for over one-third of N2O emissions, most of which are due to the agricultural sector.
See also
- AnthropoceneAnthropoceneThe Anthropocene is a recent and informal geologic chronological term that serves to mark the evidence and extent of human activities that have had a significant global impact on the Earth's ecosystems...
- Attribution of recent climate changeAttribution of recent climate changeAttribution of recent climate change is the effort to scientifically ascertain mechanisms responsible for recent changes observed in the Earth's climate...
- BiomeBiomeBiomes are climatically and geographically defined as similar climatic conditions on the Earth, such as communities of plants, animals, and soil organisms, and are often referred to as ecosystems. Some parts of the earth have more or less the same kind of abiotic and biotic factors spread over a...
- Environmental issueEnvironmental issueEnvironmental issues are negative aspects of human activity on the biophysical environment. Environmentalism, a social and environmental movement that started in the 1960s, addresses environmental issues through advocacy, education and activism.-Types:...
- SustainabilitySustainabilitySustainability is the capacity to endure. For humans, sustainability is the long-term maintenance of well being, which has environmental, economic, and social dimensions, and encompasses the concept of union, an interdependent relationship and mutual responsible position with all living and non...

