
Antarctic
Encyclopedia



Region
Region is most commonly found as a term used in terrestrial and astrophysics sciences also an area, notably among the different sub-disciplines of geography, studied by regional geographers. Regions consist of subregions that contain clusters of like areas that are distinctive by their uniformity...
around the Earth
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun, and the densest and fifth-largest of the eight planets in the Solar System. It is also the largest of the Solar System's four terrestrial planets...
's South Pole
South Pole
The South Pole, also known as the Geographic South Pole or Terrestrial South Pole, is one of the two points where the Earth's axis of rotation intersects its surface. It is the southernmost point on the surface of the Earth and lies on the opposite side of the Earth from the North Pole...
, opposite the Arctic
Arctic
The Arctic is a region located at the northern-most part of the Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean and parts of Canada, Russia, Greenland, the United States, Norway, Sweden, Finland, and Iceland. The Arctic region consists of a vast, ice-covered ocean, surrounded by treeless permafrost...
region around the North Pole
North Pole
The North Pole, also known as the Geographic North Pole or Terrestrial North Pole, is, subject to the caveats explained below, defined as the point in the northern hemisphere where the Earth's axis of rotation meets its surface...
. The Antarctic comprises the continent
Continent
A continent is one of several very large landmasses on Earth. They are generally identified by convention rather than any strict criteria, with seven regions commonly regarded as continents—they are : Asia, Africa, North America, South America, Antarctica, Europe, and Australia.Plate tectonics is...
of Antarctica and the ice shelves
Ice shelf
An ice shelf is a thick, floating platform of ice that forms where a glacier or ice sheet flows down to a coastline and onto the ocean surface. Ice shelves are only found in Antarctica, Greenland and Canada. The boundary between the floating ice shelf and the grounded ice that feeds it is called...
, waters and island
Island
An island or isle is any piece of sub-continental land that is surrounded by water. Very small islands such as emergent land features on atolls can be called islets, cays or keys. An island in a river or lake may be called an eyot , or holm...
territories in the Southern Ocean
Southern Ocean
The Southern Ocean comprises the southernmost waters of the World Ocean, generally taken to be south of 60°S latitude and encircling Antarctica. It is usually regarded as the fourth-largest of the five principal oceanic divisions...
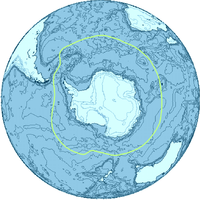
situated south of the Antarctic Convergence
Antarctic Convergence
The Antarctic Convergence is a curve continuously encircling Antarctica where cold, northward-flowing Antarctic waters meet the relatively warmer waters of the subantarctic. Antarctic waters predominantly sink beneath subantarctic waters, while associated zones of mixing and upwelling create a zone...
. The region covers some 20% of the Southern Hemisphere
Southern Hemisphere
The Southern Hemisphere is the part of Earth that lies south of the equator. The word hemisphere literally means 'half ball' or "half sphere"...
, of which 5.5% (14 million km2) is the surface area of the continent itself.
Geography
The maritime part of the region constitutes the area of application of the international Convention for the Conservation of Antarctic Marine Living ResourcesConvention for the Conservation of Antarctic Marine Living Resources
The Convention on the Conservation of Antarctic Marine Living Resources, also Commission on the Conservation of Antarctic Marine Living Resources, and CCAMLR, is part of the Antarctic Treaty System...
(CCAMLR), where for technical reasons the Convention uses an approximation of the Convergence line by means of a line joining specified points along parallels of latitude
Circle of latitude
A circle of latitude, on the Earth, is an imaginary east-west circle connecting all locations that share a given latitude...
and meridians of longitude
Meridian (geography)
A meridian is an imaginary line on the Earth's surface from the North Pole to the South Pole that connects all locations along it with a given longitude. The position of a point along the meridian is given by its latitude. Each meridian is perpendicular to all circles of latitude...
. The implementation of the Convention is managed through an international Commission headquartered in Hobart
Hobart
Hobart is the state capital and most populous city of the Australian island state of Tasmania. Founded in 1804 as a penal colony,Hobart is Australia's second oldest capital city after Sydney. In 2009, the city had a greater area population of approximately 212,019. A resident of Hobart is known as...
, Australia
Australia
Australia , officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country in the Southern Hemisphere comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands in the Indian and Pacific Oceans. It is the world's sixth-largest country by total area...
by an efficient system of annual fishing
Fishing
Fishing is the activity of trying to catch wild fish. Fish are normally caught in the wild. Techniques for catching fish include hand gathering, spearing, netting, angling and trapping....
quotas, licenses and international inspectors on the fishing vessels, as well as satellite
Satellite
In the context of spaceflight, a satellite is an object which has been placed into orbit by human endeavour. Such objects are sometimes called artificial satellites to distinguish them from natural satellites such as the Moon....
surveillance.
Most of the Antarctic region is situated south of 60°S latitude parallel, and is governed in accordance with the international legal regime of the Antarctic Treaty System
Antarctic Treaty System
The Antarctic Treaty and related agreements, collectively called the Antarctic Treaty System or ATS, regulate international relations with respect to Antarctica, Earth's only continent without a native human population. For the purposes of the treaty system, Antarctica is defined as all of the land...
. The Treaty area covers the continent itself and its immediately adjacent islands, as well as the archipelago
Archipelago
An archipelago , sometimes called an island group, is a chain or cluster of islands. The word archipelago is derived from the Greek ἄρχι- – arkhi- and πέλαγος – pélagos through the Italian arcipelago...
s of the South Orkney Islands
South Orkney Islands
The South Orkney Islands are a group of islands in the Southern Ocean, about north-east of the tip of the Antarctic Peninsula. They have a total area of about ....
, South Shetland Islands
South Shetland Islands
The South Shetland Islands are a group of Antarctic islands, lying about north of the Antarctic Peninsula, with a total area of . By the Antarctic Treaty of 1959, the Islands' sovereignty is neither recognized nor disputed by the signatories and they are free for use by any signatory for...
, Peter I Island
Peter I Island
Peter I Island is an uninhabited volcanic island in the Bellingshausen Sea, from Antarctica. It is claimed as a dependency of Norway, and along with Queen Maud Land and Bouvet Island comprises one of the three Norwegian dependent territories in the Antarctic and sub-Antarctic. Peter I Island is ...
, Scott Island
Scott Island
Scott Island is a small uninhabited island of volcanic origin in the Ross Sea, Southern Ocean, northeast of Cape Adare, the northeastern extremity of Victoria Land, Antarctica. It is long north-south, and between and wide, reaching a height of and covering an area of...
and Balleny Islands
Balleny Islands
The Balleny Islands are a series of uninhabited islands in the Southern Ocean extending from 66°15' to 67°35'S and 162°30' to 165°00'E. The group extends for about in a northwest-southeast direction. The islands are heavily glaciated and are of volcanic origin. Glaciers project from their slopes...
.
The islands situated between 60°S latitude parallel to the south and the Antarctic Convergence
Antarctic Convergence
The Antarctic Convergence is a curve continuously encircling Antarctica where cold, northward-flowing Antarctic waters meet the relatively warmer waters of the subantarctic. Antarctic waters predominantly sink beneath subantarctic waters, while associated zones of mixing and upwelling create a zone...
to the north, and their respective 200 nautical miles (370.4 km) Exclusive Economic Zone
Exclusive Economic Zone
Under the law of the sea, an exclusive economic zone is a seazone over which a state has special rights over the exploration and use of marine resources, including production of energy from water and wind. It stretches from the seaward edge of the state's territorial sea out to 200 nautical...
s fall under the national jurisdiction
Jurisdiction
Jurisdiction is the practical authority granted to a formally constituted legal body or to a political leader to deal with and make pronouncements on legal matters and, by implication, to administer justice within a defined area of responsibility...
of the countries that possess them: South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands
South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands
South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands is a British overseas territory and overseas territory of the European Union in the southern Atlantic Ocean. It is a remote and inhospitable collection of islands, consisting of South Georgia and a chain of smaller islands, known as the South Sandwich...
(United Kingdom
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
; also an EU Overseas territory), Bouvet Island
Bouvet Island
Bouvet Island is an uninhabited Antarctic volcanic island in the South Atlantic Ocean, 2,525 km south-southwest of South Africa. It is a dependent territory of Norway and, lying north of 60°S latitude, is not subject to the Antarctic Treaty. The centre of the island is an ice-filled crater of an...
(Norway
Norway
Norway , officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic unitary constitutional monarchy whose territory comprises the western portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula, Jan Mayen, and the Arctic archipelago of Svalbard and Bouvet Island. Norway has a total area of and a population of about 4.9 million...
), and Heard and McDonald Islands
Heard Island and McDonald Islands
The Heard Island and McDonald Islands are an Australian external territory and volcanic group of barren Antarctic islands, about two-thirds of the way from Madagascar to Antarctica. The group's overall size is in area and it has of coastline...
(Australia
Australia
Australia , officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country in the Southern Hemisphere comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands in the Indian and Pacific Oceans. It is the world's sixth-largest country by total area...
).
Kerguelen Islands
Kerguelen Islands
The Kerguelen Islands , also known as the Desolation Islands, are a group of islands in the southern Indian Ocean constituting the emerged part of the otherwise submerged Kerguelen Plateau. The islands, along with Adélie Land, the Crozet Islands and the Amsterdam and Saint Paul Islands are part of...
(France
France
The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
; also an EU Overseas territory) are situated in the Antarctic Convergence area, while the Falkland Islands
Falkland Islands
The Falkland Islands are an archipelago in the South Atlantic Ocean, located about from the coast of mainland South America. The archipelago consists of East Falkland, West Falkland and 776 lesser islands. The capital, Stanley, is on East Falkland...
, Isla de los Estados
Isla de los Estados
Isla de los Estados is an Argentine island that lies off the eastern extremity of the Argentine portion of Tierra del Fuego, from which it is separated by the Le Maire Strait...
, Hornos Island
Hornos Island
Hornos Island is a Chilean island at the southern tip of South America. The island is mostly known for being the location of Cape Horn. It is generally considered South America's southernmost island, but the Diego Ramírez Islands are farther south...
with Cape Horn
Cape Horn
Cape Horn is the southernmost headland of the Tierra del Fuego archipelago of southern Chile, and is located on the small Hornos Island...
, Diego Ramírez Islands
Diego Ramírez Islands
The Diego Ramírez Islands are a small group of lesser islands located in the southernmost extreme of Chile about south-west of Cape Horn and south-south-east of Ildefonso Islands, stretching north-south . Their land area is little more than...
, Campbell Island
Campbell Island, New Zealand
Campbell Island is a remote, subantarctic island of New Zealand and the main island of the Campbell Island group. It covers of the group's , and is surrounded by numerous stacks, rocks and islets like Dent Island, Folly Island , Isle de Jeanette Marie, and Jacquemart Island, the latter being the...
, Macquarie Island
Macquarie Island
Macquarie Island lies in the southwest corner of the Pacific Ocean, about half-way between New Zealand and Antarctica, at 54°30S, 158°57E. Politically, it has formed part of the Australian state of Tasmania since 1900 and became a Tasmanian State Reserve in 1978. In 1997 it became a world heritage...
, Amsterdam
Île Amsterdam
New Amsterdam, Amsterdam Island, or Île Amsterdam is a French island in the Indian Ocean located at . It is part of the French Southern and Antarctic Lands.- History :...
and Saint Paul
Île Saint-Paul
Île Saint-Paul is an island forming part of the French Southern and Antarctic Lands in the Indian Ocean, with an area of . It is located about southwest of the larger Île Amsterdam, and south of Réunion...
Islands, Crozet Islands
Crozet Islands
The Crozet Islands are a sub-antarctic archipelago of small islands in the southern Indian Ocean. They form one of the five administrative districts of the French Southern and Antarctic Lands.-Geography:...
, Prince Edward Islands
Prince Edward Islands
The Prince Edward Islands are two small islands in the sub-antarctic Indian Ocean that are part of South Africa. The islands, named Marion Island and Prince Edward Island, are located at ....
, and Gough Island
Gough Island
Gough Island , also known historically as Gonçalo Álvares or Diego Alvarez, is a volcanic island in the South Atlantic Ocean. It is a dependency of Tristan da Cunha and part of the British overseas territory of Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha...
and Tristan da Cunha group
Tristan da Cunha
Tristan da Cunha is a remote volcanic group of islands in the south Atlantic Ocean and the main island of that group. It is the most remote inhabited archipelago in the world, lying from the nearest land, South Africa, and from South America...
remain north of the Convergence and thus outside the Antarctic region.
Society
The first Antarctic land discovered was the island of South Georgia, visited by the EnglishKingdom of England
The Kingdom of England was, from 927 to 1707, a sovereign state to the northwest of continental Europe. At its height, the Kingdom of England spanned the southern two-thirds of the island of Great Britain and several smaller outlying islands; what today comprises the legal jurisdiction of England...
merchant Anthony de la Roché
Anthony de la Roché
Anthony de la Roché, born sometime in the 17th century, was an English merchant born in London to a French Huguenot father and an English mother...
in 1675. The first human born in the Antarctic was Solveig Gunbjørg Jacobsen born on 8 October 1913 in Grytviken
Grytviken
Grytviken is the principal settlement in the British territory of South Georgia in the South Atlantic. It was so named in 1902 by the Swedish surveyor Johan Gunnar Andersson who found old English try pots used to render seal oil at the site. It is the best harbour on the island, consisting of a...
, South Georgia.
The Antarctic region had no indigenous population when first discovered, and its present inhabitants comprise a few thousand transient scientific
Science
Science is a systematic enterprise that builds and organizes knowledge in the form of testable explanations and predictions about the universe...
and other personnel working on tours of duty at the several dozen research stations maintained by various countries. However, the region is visited by more than 40,000 tourists annually, the most popular destinations being the Antarctic Peninsula
Antarctic Peninsula
The Antarctic Peninsula is the northernmost part of the mainland of Antarctica. It extends from a line between Cape Adams and a point on the mainland south of Eklund Islands....
area (especially the South Shetland Islands
South Shetland Islands
The South Shetland Islands are a group of Antarctic islands, lying about north of the Antarctic Peninsula, with a total area of . By the Antarctic Treaty of 1959, the Islands' sovereignty is neither recognized nor disputed by the signatories and they are free for use by any signatory for...
) and South Georgia Island.
In December 2009, the growth of tourism
Tourism in Antarctica
Tourism in Antarctica started with sea tourism in the 1960s. Air overflights of Antarctica started in the 1970s with sightseeing flights by airliners from Australia and New Zealand, and were resumed in the 1990s. Private yacht trips started in the late 1960s. The tour season lasts from November to...
, with consequences for both the ecology and the safety of the travellers in its great and remote wilderness, was noted at a conference in New Zealand by experts from signatories to the Antarctic Treaty. The definitive results of the conference would be presented at the Antarctic Treaty states' meeting in Uruguay in May 2010.
See also
- Antarctic CircleAntarctic CircleThe Antarctic Circle is one of the five major circles of latitude that mark maps of the Earth. For 2011, it is the parallel of latitude that runs south of the Equator.-Description:...
- Antarctic ConvergenceAntarctic ConvergenceThe Antarctic Convergence is a curve continuously encircling Antarctica where cold, northward-flowing Antarctic waters meet the relatively warmer waters of the subantarctic. Antarctic waters predominantly sink beneath subantarctic waters, while associated zones of mixing and upwelling create a zone...
- Antarctica
- Antarctic - Hello Sir Records, North Florida Indie/Instrumental Band
Islands:
- South Georgia and the South Sandwich IslandsSouth Georgia and the South Sandwich IslandsSouth Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands is a British overseas territory and overseas territory of the European Union in the southern Atlantic Ocean. It is a remote and inhospitable collection of islands, consisting of South Georgia and a chain of smaller islands, known as the South Sandwich...
- Bouvet IslandBouvet IslandBouvet Island is an uninhabited Antarctic volcanic island in the South Atlantic Ocean, 2,525 km south-southwest of South Africa. It is a dependent territory of Norway and, lying north of 60°S latitude, is not subject to the Antarctic Treaty. The centre of the island is an ice-filled crater of an...
- Kerguelen IslandsKerguelen IslandsThe Kerguelen Islands , also known as the Desolation Islands, are a group of islands in the southern Indian Ocean constituting the emerged part of the otherwise submerged Kerguelen Plateau. The islands, along with Adélie Land, the Crozet Islands and the Amsterdam and Saint Paul Islands are part of...
- Heard Island and McDonald IslandsHeard Island and McDonald IslandsThe Heard Island and McDonald Islands are an Australian external territory and volcanic group of barren Antarctic islands, about two-thirds of the way from Madagascar to Antarctica. The group's overall size is in area and it has of coastline...
- South Orkney IslandsSouth Orkney IslandsThe South Orkney Islands are a group of islands in the Southern Ocean, about north-east of the tip of the Antarctic Peninsula. They have a total area of about ....
- South Shetland IslandsSouth Shetland IslandsThe South Shetland Islands are a group of Antarctic islands, lying about north of the Antarctic Peninsula, with a total area of . By the Antarctic Treaty of 1959, the Islands' sovereignty is neither recognized nor disputed by the signatories and they are free for use by any signatory for...
- Peter I IslandPeter I IslandPeter I Island is an uninhabited volcanic island in the Bellingshausen Sea, from Antarctica. It is claimed as a dependency of Norway, and along with Queen Maud Land and Bouvet Island comprises one of the three Norwegian dependent territories in the Antarctic and sub-Antarctic. Peter I Island is ...
- Scott IslandScott IslandScott Island is a small uninhabited island of volcanic origin in the Ross Sea, Southern Ocean, northeast of Cape Adare, the northeastern extremity of Victoria Land, Antarctica. It is long north-south, and between and wide, reaching a height of and covering an area of...
- Balleny IslandsBalleny IslandsThe Balleny Islands are a series of uninhabited islands in the Southern Ocean extending from 66°15' to 67°35'S and 162°30' to 165°00'E. The group extends for about in a northwest-southeast direction. The islands are heavily glaciated and are of volcanic origin. Glaciers project from their slopes...
Further reading
- Krupnik, Igor, Michael A. Lang, and Scott E. Miller, eds. Smithsonian at the Poles: Contributions to International Polar Year Science. Washington, D.C.: Smithsonian Institution Scholarly Press, 2009.
This proceedings volume features the research presented at the Smithsonian at the Poles symposium, convened as part of the International Polar Year 2007-2008. Copies of this book are available for free pdf download by clicking on the included link.
External links
- British Services Antarctic Expedition 2012
- Committee for Environmental Protection of Antarctica
- Secretariat of the Antarctic Treaty
- CCAMLR Commission
- Antarctic Heritage Trusts
- International Association of Antarctica Tour Operators
- Map of the Antarctic Convergence
- The South Atlantic and Subantarctic Islands

