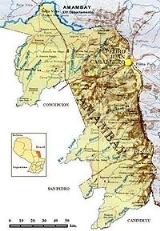
Amambay Department
Encyclopedia
Amambay is a department
in Paraguay
. The capital is Pedro Juan Caballero
.
The name comes from the way is called a part of the Caaguazú Cordillera, “Amambay Cordillera”. Amambay is the name of a fern, typical of the forest in the region.
Once finished the War against the Triple Alliance
, the great extension of land passed to the hands of foreign business men that dedicated to the exploit of yerba and wood.
Pedro Juan Caballero
was found in 1893, and Bella Vista
, in 1902. The department Amambay, as such, was created in 1945 as the No. 10 department of the country. After some limit reorganization was declared as the No. 13 department, with the limits and surface that has nowadays.
The population in the area was consolidated with the establishment of rural colonies dedicated to the agriculture and livestock industry.
Pedro Juan Caballero, the capital of the department, is still known by its old name, Punta Porá, used by the traveling merchants that transported yerba from Matto Grosso to Concepción
.
The limits are:
To the North: Brazil
, from which is separated by the Apa River and Amambay Cordillera.
To the South: Canindeyú Department
To the East: Brazil, from which is separated by the Amambay Cordillera
To the West: Concepción
and San Pedro Departments
Amambay is the highest of Paraguayan territories, it reaches 300 to 400 meters, and the Punta Porá Hill reaches even 700 meters. The Amambay Cordillera serves as the natural limit with Brazil and from it parts the Serranía Cerro Corá, Tacurupytá, Guasú, Alambique, Tuna and Tangaró.
Some isolated hills are: Tranquerita, Tacuara, Verón Cué and Cuatiá.
 The Apa River delimits the territory to the North, just as the Estrella Stream does with Brazil. The Aquidabán River and the streams Tapiracuai, Aquidabán-mi, Cabayu and Guazú are also in Amambay.
The Apa River delimits the territory to the North, just as the Estrella Stream does with Brazil. The Aquidabán River and the streams Tapiracuai, Aquidabán-mi, Cabayu and Guazú are also in Amambay.
The West of the department is bordered by the Ypané River and others such as Tutytí, Aguaray Verde, Puente de la Tabla Puendy and Ypané-mi.
The richness of the region in forestalls resources cause the department to be an area highly affected by the process of deforestation and exploit of wood. Some species of plants are now in danger of extinguish, those are: palm tree, karanday, array, Amambay fern, trébol, yvyra paje, kai kygua and cedar.
In addition, there are some animal species that are in danger too: agua’a sayju, jacaré ita and guasuti.
The protected areas are:
Cerro Corá National Park
: created by decree No. 20.698 on February 11 1976, with a surface of 12.038 hectares. It is located in Pedro Juan Caballero’s district.
The ecosystem has a great variety of fauna and flora.
In Cerro Corá, on the banks of Aquidabán Nigui River, took place an historic event, the death of Marshall Francisco Solano López. In the National Park, there is a monument to him.
In Cerro Guasú, Yasuká Verá, there are caverns and rests of human artifacts of archeological importance that date from 2.500 to 3.800 years ago.
Tapé Tuyá is a road the remaining Paraguayan army took in the campaign of 1896-1870. The area was inhabited by colonies of natives of the Tupí Guaraní Faimily, the Paí Tavyterá and Ava Guaraní. There is a hill in there that was considered to be a holy place by the Ava Guaraní. They thought it was the center of the earth, where the world was created and were born the first man and the first woman.
In Pedro Juan Caballero, the beaches in the banks of Aquidabán River are places of great beauty and attract many visitors, just as do the commercial centers in the city.
The beaches in Bella Vista
are much visited by the tourists.
In the country’s economy, the department ranks sixth place in breeding cattle and produces 2% of the national production of cotton.
The Agricola production of the region is: garlic
, cotton
, rice
, beans, banana
, sweet potato
, coffee
, sweet cane, onion
, sunflower
, lemon
, corn
, tangerine
, manioc, peanut
, mint, sour and sweet orange
, potato, pineapple
, grapefruit
, soy, tobacco
, sorghum
, tartago, tomato
, yerba mate
and carrot
.
The people also dedicate to the breeding of several animals, such as cow, horse, sheep, goat, and some birds too, chicken, guinea, turkey, goose and duck.
The most important industries are: food, dairy, mills, yerba industries and sawmills. In Itapopó there is a very modern ceramic industry.
Every year, in October, is organized the Expo Amambay of industry, commerce and services.

The department has paved and pebbled routes. The International Route that communicates Pedro Juan Caballero – Capitán Bado
with Brazil is much used for business purposes.
The airport “Dr. Augusto R. Fuster” in Pedro Juan Caballero, offers regular flies to Asunción.
Amambay’s radio stations are: in AM, La Voz del Amambay and Mcal. López. In FM, Pantanal, amambay, Cerro Corá, Frontera, Capitán Bado and Sin Frontera. There are also, television stations and a telephonic central.
There are 23.921 housings in the department, 16.174 in the urban area and 7.747 in the rural area. The percentage of which count with basic facilities are the following:
Electrical power: 56,3%
Running water: 21%
Trash recollection: 37,7%
Department (subnational entity)
Department is the name given to the administrative and political subdivisions of many countries.As a territorial unit, "department" was first used by the French Revolutionary governments, apparently to emphasize that each territory was simply an administrative sub-division of the united sovereign...
in Paraguay
Paraguay
Paraguay , officially the Republic of Paraguay , is a landlocked country in South America. It is bordered by Argentina to the south and southwest, Brazil to the east and northeast, and Bolivia to the northwest. Paraguay lies on both banks of the Paraguay River, which runs through the center of the...
. The capital is Pedro Juan Caballero
Pedro Juan Caballero, Paraguay
Pedro Juan Caballero is a city in Paraguay, located in Amambay Department of which it is the capital. The city lies on the border with the Brazilian city of Ponta Porã in the state of Mato Grosso do Sul and is known as a centre for cheap electronic and consumer goods, and also as a centre for drug...
.
The name comes from the way is called a part of the Caaguazú Cordillera, “Amambay Cordillera”. Amambay is the name of a fern, typical of the forest in the region.
Districts
The department is divided in 3 districts:- Bella VistaBella Vista, AmambayBella Vista is a border town in northeast of Paraguay, bordering the Brazilian town of Bela Vista, Mato Grosso do Sul. Both towns are divided by the Apa River, only connected by a borderbridge. Small town in beautiful northern region of Amambay...
- Capitán BadoCapitán BadoCapitán Bado is a town in the Amambay department of Paraguay.- Sources :* – World-Gazetteer.com...
- Pedro Juan CaballeroPedro Juan Caballero, ParaguayPedro Juan Caballero is a city in Paraguay, located in Amambay Department of which it is the capital. The city lies on the border with the Brazilian city of Ponta Porã in the state of Mato Grosso do Sul and is known as a centre for cheap electronic and consumer goods, and also as a centre for drug...
History
For a long time, the land was occupied by the natives of the region and suffered the attacks of the Bandeirantes that were looking for the Guaraníes, who were able to find refuge in the jungle of the area.Once finished the War against the Triple Alliance
War of the Triple Alliance
The Paraguayan War , also known as War of the Triple Alliance , was a military conflict in South America fought from 1864 to 1870 between Paraguay and the Triple Alliance of Argentina, Brazil, and Uruguay...
, the great extension of land passed to the hands of foreign business men that dedicated to the exploit of yerba and wood.
Pedro Juan Caballero
Pedro Juan Caballero (politician)
Pedro Juan Caballero was a leading figure of Paraguayan independence. He was born in Tobatí a town located in a region called Department Cordillera, Paraguay. Even though he was 6 years younger than Fulgencio Yegros and 20 than Dr...
was found in 1893, and Bella Vista
Bella Vista, Amambay
Bella Vista is a border town in northeast of Paraguay, bordering the Brazilian town of Bela Vista, Mato Grosso do Sul. Both towns are divided by the Apa River, only connected by a borderbridge. Small town in beautiful northern region of Amambay...
, in 1902. The department Amambay, as such, was created in 1945 as the No. 10 department of the country. After some limit reorganization was declared as the No. 13 department, with the limits and surface that has nowadays.
The population in the area was consolidated with the establishment of rural colonies dedicated to the agriculture and livestock industry.
Pedro Juan Caballero, the capital of the department, is still known by its old name, Punta Porá, used by the traveling merchants that transported yerba from Matto Grosso to Concepción
Concepción Department (Paraguay)
Concepción is a department of Paraguay. The capital is the city of Concepción.- History :Throughout history, this department has suffered a great amount of poblational instability, especially in the times of the colony, due to the advance of the Brazilian “bandeirantes” through the east and the...
.
Limits
Amambay is located in the north part of the Oriental Region of Paraguay. The exact geographic location is between the parallels 55º 28’ and 57º 00’ of West longitude and between meridians 22º 05’ and 23º 05’ of South latitude.The limits are:
To the North: Brazil
Brazil
Brazil , officially the Federative Republic of Brazil , is the largest country in South America. It is the world's fifth largest country, both by geographical area and by population with over 192 million people...
, from which is separated by the Apa River and Amambay Cordillera.
To the South: Canindeyú Department
Canindeyú Department
Canindeyú is a department in Paraguay. The capital is the city of Salto del Guairá.-Districts:The department is divided in 11 districts:# Corpus Christi# Curuguaty# General Francisco Caballero Alvarez # Itanará# Katueté# La Paloma...
To the East: Brazil, from which is separated by the Amambay Cordillera
To the West: Concepción
Concepción Department (Paraguay)
Concepción is a department of Paraguay. The capital is the city of Concepción.- History :Throughout history, this department has suffered a great amount of poblational instability, especially in the times of the colony, due to the advance of the Brazilian “bandeirantes” through the east and the...
and San Pedro Departments
Climate
The average temperature is 21°C; it reaches 35°C in summer and drops to -1°C in winter. The rainy months are January, February and March.Orography and soil
In the territory are predominant, from north to south sandstone and rocks.Amambay is the highest of Paraguayan territories, it reaches 300 to 400 meters, and the Punta Porá Hill reaches even 700 meters. The Amambay Cordillera serves as the natural limit with Brazil and from it parts the Serranía Cerro Corá, Tacurupytá, Guasú, Alambique, Tuna and Tangaró.
Some isolated hills are: Tranquerita, Tacuara, Verón Cué and Cuatiá.
Hydrography

The West of the department is bordered by the Ypané River and others such as Tutytí, Aguaray Verde, Puente de la Tabla Puendy and Ypané-mi.
Natural environment
The entire department belongs to the Ecological Region of Amambay.The richness of the region in forestalls resources cause the department to be an area highly affected by the process of deforestation and exploit of wood. Some species of plants are now in danger of extinguish, those are: palm tree, karanday, array, Amambay fern, trébol, yvyra paje, kai kygua and cedar.
In addition, there are some animal species that are in danger too: agua’a sayju, jacaré ita and guasuti.
The protected areas are:
- Estrella Forest: 30.000 hectares.
- Pira’y Forest: 22.500 hectares.
- Guasú Hill: 15.000 hectares.
- Sarambí Hill: 15.000 hectares.
Cerro Corá National Park
Cerro Cora National Park
Cerro Cora National Park, is the biggest protected area in Paraguay. It is located in Amambay Region, close to the border with Brazil. It was established by a decree on February 11, 1976. It is a Natural Reservation, as well as an historical and cultural center...
: created by decree No. 20.698 on February 11 1976, with a surface of 12.038 hectares. It is located in Pedro Juan Caballero’s district.
The ecosystem has a great variety of fauna and flora.
Tourism
Amambay is a department very favored by nature’s beauty. Amambay Cordillera forms a chain of mountains: Cerro Corá, Tacurý Pytá, Guasú and Alambique. The most important hills are: Cerro Corá, located in the National Park, Acuá, Lorito, Guasú, Muralle and Sarambí.In Cerro Corá, on the banks of Aquidabán Nigui River, took place an historic event, the death of Marshall Francisco Solano López. In the National Park, there is a monument to him.
In Cerro Guasú, Yasuká Verá, there are caverns and rests of human artifacts of archeological importance that date from 2.500 to 3.800 years ago.
Tapé Tuyá is a road the remaining Paraguayan army took in the campaign of 1896-1870. The area was inhabited by colonies of natives of the Tupí Guaraní Faimily, the Paí Tavyterá and Ava Guaraní. There is a hill in there that was considered to be a holy place by the Ava Guaraní. They thought it was the center of the earth, where the world was created and were born the first man and the first woman.
In Pedro Juan Caballero, the beaches in the banks of Aquidabán River are places of great beauty and attract many visitors, just as do the commercial centers in the city.
The beaches in Bella Vista
Bella Vista, Amambay
Bella Vista is a border town in northeast of Paraguay, bordering the Brazilian town of Bela Vista, Mato Grosso do Sul. Both towns are divided by the Apa River, only connected by a borderbridge. Small town in beautiful northern region of Amambay...
are much visited by the tourists.
Economy
It is a territory of intense commerce because of its limitation with Brazil.In the country’s economy, the department ranks sixth place in breeding cattle and produces 2% of the national production of cotton.
The Agricola production of the region is: garlic
Garlic
Allium sativum, commonly known as garlic, is a species in the onion genus, Allium. Its close relatives include the onion, shallot, leek, chive, and rakkyo. Dating back over 6,000 years, garlic is native to central Asia, and has long been a staple in the Mediterranean region, as well as a frequent...
, cotton
Cotton
Cotton is a soft, fluffy staple fiber that grows in a boll, or protective capsule, around the seeds of cotton plants of the genus Gossypium. The fiber is almost pure cellulose. The botanical purpose of cotton fiber is to aid in seed dispersal....
, rice
Rice
Rice is the seed of the monocot plants Oryza sativa or Oryza glaberrima . As a cereal grain, it is the most important staple food for a large part of the world's human population, especially in East Asia, Southeast Asia, South Asia, the Middle East, and the West Indies...
, beans, banana
Banana
Banana is the common name for herbaceous plants of the genus Musa and for the fruit they produce. Bananas come in a variety of sizes and colors when ripe, including yellow, purple, and red....
, sweet potato
Potato
The potato is a starchy, tuberous crop from the perennial Solanum tuberosum of the Solanaceae family . The word potato may refer to the plant itself as well as the edible tuber. In the region of the Andes, there are some other closely related cultivated potato species...
, coffee
Coffee
Coffee is a brewed beverage with a dark,init brooo acidic flavor prepared from the roasted seeds of the coffee plant, colloquially called coffee beans. The beans are found in coffee cherries, which grow on trees cultivated in over 70 countries, primarily in equatorial Latin America, Southeast Asia,...
, sweet cane, onion
Onion
The onion , also known as the bulb onion, common onion and garden onion, is the most widely cultivated species of the genus Allium. The genus Allium also contains a number of other species variously referred to as onions and cultivated for food, such as the Japanese bunching onion The onion...
, sunflower
Sunflower
Sunflower is an annual plant native to the Americas. It possesses a large inflorescence . The sunflower got its name from its huge, fiery blooms, whose shape and image is often used to depict the sun. The sunflower has a rough, hairy stem, broad, coarsely toothed, rough leaves and circular heads...
, lemon
Lemon
The lemon is both a small evergreen tree native to Asia, and the tree's ellipsoidal yellow fruit. The fruit is used for culinary and non-culinary purposes throughout the world – primarily for its juice, though the pulp and rind are also used, mainly in cooking and baking...
, corn
Maize
Maize known in many English-speaking countries as corn or mielie/mealie, is a grain domesticated by indigenous peoples in Mesoamerica in prehistoric times. The leafy stalk produces ears which contain seeds called kernels. Though technically a grain, maize kernels are used in cooking as a vegetable...
, tangerine
Tangerine
__notoc__The tangerine is an orange-colored citrus fruit which is closely related to the Mandarin orange . Taxonomically, it should probably be formally named as a subspecies or variety of Citrus reticulata; further work seems to be required to ascertain its correct scientific name...
, manioc, peanut
Peanut
The peanut, or groundnut , is a species in the legume or "bean" family , so it is not a nut. The peanut was probably first cultivated in the valleys of Peru. It is an annual herbaceous plant growing tall...
, mint, sour and sweet orange
Orange (fruit)
An orange—specifically, the sweet orange—is the citrus Citrus × sinensis and its fruit. It is the most commonly grown tree fruit in the world....
, potato, pineapple
Pineapple
Pineapple is the common name for a tropical plant and its edible fruit, which is actually a multiple fruit consisting of coalesced berries. It was given the name pineapple due to its resemblance to a pine cone. The pineapple is by far the most economically important plant in the Bromeliaceae...
, grapefruit
Grapefruit
The grapefruit , is a subtropical citrus tree known for its sour fruit, an 18th-century hybrid first bred in Barbados. When found, it was named the "forbidden fruit"; it has also been misidentified with the pomelo or shaddock , one of the parents of this hybrid, the other being sweet orange The...
, soy, tobacco
Tobacco
Tobacco is an agricultural product processed from the leaves of plants in the genus Nicotiana. It can be consumed, used as a pesticide and, in the form of nicotine tartrate, used in some medicines...
, sorghum
Sorghum
Sorghum is a genus of numerous species of grasses, one of which is raised for grain and many of which are used as fodder plants either cultivated or as part of pasture. The plants are cultivated in warmer climates worldwide. Species are native to tropical and subtropical regions of all continents...
, tartago, tomato
Tomato
The word "tomato" may refer to the plant or the edible, typically red, fruit which it bears. Originating in South America, the tomato was spread around the world following the Spanish colonization of the Americas, and its many varieties are now widely grown, often in greenhouses in cooler...
, yerba mate
Yerba mate
Maté, yerba maté or erva maté , Ilex paraguariensis, is a species of holly native to subtropical South America in northeastern Argentina, Bolivia, southern Brazil, Uruguay and Paraguay...
and carrot
Carrot
The carrot is a root vegetable, usually orange in colour, though purple, red, white, and yellow varieties exist. It has a crisp texture when fresh...
.
The people also dedicate to the breeding of several animals, such as cow, horse, sheep, goat, and some birds too, chicken, guinea, turkey, goose and duck.
The most important industries are: food, dairy, mills, yerba industries and sawmills. In Itapopó there is a very modern ceramic industry.
Every year, in October, is organized the Expo Amambay of industry, commerce and services.

Communication and services
The most important ways of access to Amambay are Route No. 5 “Gral. Bernardino Caballero” that communicates with Concepción and joins Route No. 3 “Gral. Elizardo Aquino”, which connects with Asunción and Cnel. Oviedo. Route No. 11 “Juana de Lara” reaches to Capitán Bado.The department has paved and pebbled routes. The International Route that communicates Pedro Juan Caballero – Capitán Bado
Capitán Bado
Capitán Bado is a town in the Amambay department of Paraguay.- Sources :* – World-Gazetteer.com...
with Brazil is much used for business purposes.
The airport “Dr. Augusto R. Fuster” in Pedro Juan Caballero, offers regular flies to Asunción.
Amambay’s radio stations are: in AM, La Voz del Amambay and Mcal. López. In FM, Pantanal, amambay, Cerro Corá, Frontera, Capitán Bado and Sin Frontera. There are also, television stations and a telephonic central.
There are 23.921 housings in the department, 16.174 in the urban area and 7.747 in the rural area. The percentage of which count with basic facilities are the following:
Electrical power: 56,3%
Running water: 21%
Trash recollection: 37,7%

