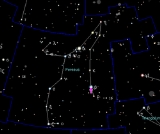
Algol
Encyclopedia
Algol known colloquially as the Demon Star, is a bright star
in the constellation
Perseus
. It is one of the best known eclipsing binaries, the first such star to be discovered, and also one of the first (non-nova
) variable star
s to be discovered. Algol is actually a three-star system (Beta Persei A, B, and C) in which the large and bright primary Beta Persei A is regularly eclipsed by the dimmer Beta Persei B. Thus, Algol's magnitude
is usually near-constant at 2.1, but regularly dips to 3.4 every two days, 20 hours and 49 minutes during the roughly 10-hour long partial eclipses. There is also a secondary eclipse when the brighter star occults
the fainter secondary. This secondary eclipse can only be detected photoelectrically. Algol gives its name to its class of eclipsing variable, known as Algol variable
s.
, but the periodic nature of its brightness variations was not recognized until more than a century later by the British amateur astronomer John Goodricke
(who also proposed a mechanism for the star's variability). In May 1783 he presented his findings to the Royal Society
, suggesting that the periodic variability was caused by a dark body passing in front of the star (or else that the star itself has a darker region that is periodically turned toward the Earth.) For his report he was awarded the Copley Medal
.
In 1881, the Harvard astronomer Edward Charles Pickering
presented evidence that Algol was actually an eclipsing binary. This was confirmed a few years later, in 1889, when the Potsdam astronomer Hermann Carl Vogel
found periodic doppler shifts in the spectrum of Algol, inferring variations in the radial velocity
of this binary system. Thus Algol became one of the first known spectroscopic binaries.
Despite many claims in the modern literature that its ancient association with a demon-like creature (Gorgon
in the Greek tradition, ghoul
in the Arabic tradition) strongly suggests that its variability was known long before the 17th century, there is no conclusive evidence for this.
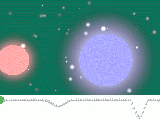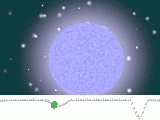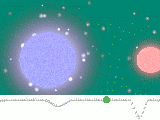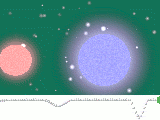 Algol A and Algol B are an eclipsing binary, because their orbital plane
Algol A and Algol B are an eclipsing binary, because their orbital plane
coincidentally contains the Earth
's line of sight
. To be more precise, however, Algol is a triple-star system: the eclipsing binary pair is separated by only 0.062 AU
, while the third star in the system (Algol C) is at an average distance of 2.69 AU from the pair and the mutual orbital period
is 681 days (1.86 years). The total mass of the system is about 5.8 solar masses, and the mass ratios of A, B and C are about 4.5 : 1 : 2.
Studies of Algol led to the Algol paradox
in the theory of stellar evolution
: although components of a binary star form at the same time, and massive stars evolve much faster than the less massive ones, it was observed that the more massive component Algol A is still in the main sequence
, while the less massive Algol B is a subgiant star
at a later evolutionary stage. The paradox can be solved by mass transfer
: when the more massive star became a subgiant, it filled its Roche lobe
, and most of the mass was transferred to the other star, which is still in the main sequence. In some binaries similar to Algol, a gas flow can be seen.
This system also exhibits variable activity in the form of x-ray
and radio
flares. The former is thought to be caused by the magnetic fields of the AB components interacting with the mass transfer. The radio emissions may be created by magnetic cycles similar to sunspots, but, as the magnetic fields around these stars are up to ten times stronger than that of the Sun
, these radio flares are more powerful and longer lasting.
Algol is 92.8 light years from Earth; however, about 7.3 million years ago it passed within 9.8 light years and its apparent magnitude
was approximately −2.5, considerably brighter than Sirius
is today. Because the total mass of the system is 5.8 solar masses, and despite the fairly large distance at closest approach, this may have been enough to perturb the solar system
's Oort cloud
slightly and to increase the number of comet
s entering the inner solar system. However, the actual increase in net cratering rate is believed to have been quite small.
رأس الغول ra's al-ghūl : head (ra's) of the ogre (al-ghūl) (see "ghoul
"). The English name Demon Star is a direct translation.
In Hebrew folklore it was known as Rōsh ha Sāṭān 'Satan's Head', via Edmund Chilmead
, who called it 'Divels head' or Rosch hassatan. A Latin
term from the 16th century was Caput Larvae 'Spectre's Head'. It was also linked with Lilith
. Hipparchus
and Pliny
made this a separate, though connected, constellation.
It is known as 大陵五 (the Fifth Star of the Mausoleum) in Chinese astronomy
, and also bore the grim name Tseih She (叠尸 - die2 shi1 in Modern Pinyin), meaning 'piled up corpses'.
, Algol is referred to as "the Gorgon
of Perseus
" and associated with death by decapitation: a theme which mirrors the myth of the hero Perseus
’ victory over the snake-headed Gorgon
Medusa
. Astrologically
, Algol is considered the most unfortunate
star in the sky., and was listed as one of the 15 Behenian stars. Historically, the star has received a strong association with bloody violence across a wide variety of cultures.
Star
A star is a massive, luminous sphere of plasma held together by gravity. At the end of its lifetime, a star can also contain a proportion of degenerate matter. The nearest star to Earth is the Sun, which is the source of most of the energy on Earth...
in the constellation
Constellation
In modern astronomy, a constellation is an internationally defined area of the celestial sphere. These areas are grouped around asterisms, patterns formed by prominent stars within apparent proximity to one another on Earth's night sky....
Perseus
Perseus (constellation)
Perseus is a constellation in the northern sky, named after the Greek hero Perseus. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union...
. It is one of the best known eclipsing binaries, the first such star to be discovered, and also one of the first (non-nova
Nova
A nova is a cataclysmic nuclear explosion in a star caused by the accretion of hydrogen on to the surface of a white dwarf star, which ignites and starts nuclear fusion in a runaway manner...
) variable star
Variable star
A star is classified as variable if its apparent magnitude as seen from Earth changes over time, whether the changes are due to variations in the star's actual luminosity, or to variations in the amount of the star's light that is blocked from reaching Earth...
s to be discovered. Algol is actually a three-star system (Beta Persei A, B, and C) in which the large and bright primary Beta Persei A is regularly eclipsed by the dimmer Beta Persei B. Thus, Algol's magnitude
Apparent magnitude
The apparent magnitude of a celestial body is a measure of its brightness as seen by an observer on Earth, adjusted to the value it would have in the absence of the atmosphere...
is usually near-constant at 2.1, but regularly dips to 3.4 every two days, 20 hours and 49 minutes during the roughly 10-hour long partial eclipses. There is also a secondary eclipse when the brighter star occults
Occultation
An occultation is an event that occurs when one object is hidden by another object that passes between it and the observer. The word is used in astronomy . It can also refer to any situation wherein an object in the foreground blocks from view an object in the background...
the fainter secondary. This secondary eclipse can only be detected photoelectrically. Algol gives its name to its class of eclipsing variable, known as Algol variable
Algol variable
Algol variables or Algol-type binaries are a class of eclipsing binary stars where the orbital plane of the stars are coincident with the line of sight from Earth. When the cooler component passes in front of the hotter one, part of the latter's light is blocked, and the total brightness of the...
s.
Observation history
The variability of Algol was first recorded in 1667 by Geminiano MontanariGeminiano Montanari
thumb|150px|Geminiano Montanari.Geminiano Montanari was an Italian astronomer, lens-maker, and proponent of the experimental approach to science....
, but the periodic nature of its brightness variations was not recognized until more than a century later by the British amateur astronomer John Goodricke
John Goodricke
John Goodricke FRS was an eminent and profoundly deaf amateur astronomer. He is best known for his observations of the variable star Algol in 1782.- Life and work :...
(who also proposed a mechanism for the star's variability). In May 1783 he presented his findings to the Royal Society
Royal Society
The Royal Society of London for Improving Natural Knowledge, known simply as the Royal Society, is a learned society for science, and is possibly the oldest such society in existence. Founded in November 1660, it was granted a Royal Charter by King Charles II as the "Royal Society of London"...
, suggesting that the periodic variability was caused by a dark body passing in front of the star (or else that the star itself has a darker region that is periodically turned toward the Earth.) For his report he was awarded the Copley Medal
Copley Medal
The Copley Medal is an award given by the Royal Society of London for "outstanding achievements in research in any branch of science, and alternates between the physical sciences and the biological sciences"...
.
In 1881, the Harvard astronomer Edward Charles Pickering
Edward Charles Pickering
Edward Charles Pickering was an American astronomer and physicist, brother of William Henry Pickering.Along with Carl Vogel, Pickering discovered the first spectroscopic binary stars. He wrote Elements of Physical Manipulations .Pickering attended Boston Latin School, and received his B.S. from...
presented evidence that Algol was actually an eclipsing binary. This was confirmed a few years later, in 1889, when the Potsdam astronomer Hermann Carl Vogel
Hermann Carl Vogel
Hermann Carl Vogel was a German astronomer. He was born in Leipzig, Kingdom of Saxony.Vogel pioneered the use of the spectroscope in astronomy...
found periodic doppler shifts in the spectrum of Algol, inferring variations in the radial velocity
Radial velocity
Radial velocity is the velocity of an object in the direction of the line of sight . In astronomy, radial velocity most commonly refers to the spectroscopic radial velocity...
of this binary system. Thus Algol became one of the first known spectroscopic binaries.
Despite many claims in the modern literature that its ancient association with a demon-like creature (Gorgon
Gorgon
In Greek mythology, the Gorgon was a terrifying female creature. The name derives from the Greek word gorgós, which means "dreadful." While descriptions of Gorgons vary across Greek literature, the term commonly refers to any of three sisters who had hair of living, venomous snakes, and a...
in the Greek tradition, ghoul
Ghoul
A ghoul is a folkloric monster associated with graveyards and consuming human flesh, often classified as undead. The oldest surviving literature that mention ghouls is likely One Thousand and One Nights...
in the Arabic tradition) strongly suggests that its variability was known long before the 17th century, there is no conclusive evidence for this.
System

Orbital plane (astronomy)
All of the planets, comets, and asteroids in the solar system are in orbit around the Sun. All of those orbits line up with each other making a semi-flat disk called the orbital plane. The orbital plane of an object orbiting another is the geometrical plane in which the orbit is embedded...
coincidentally contains the Earth
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun, and the densest and fifth-largest of the eight planets in the Solar System. It is also the largest of the Solar System's four terrestrial planets...
's line of sight
Line-of-sight propagation
Line-of-sight propagation refers to electro-magnetic radiation or acoustic wave propagation. Electromagnetic transmission includes light emissions traveling in a straight line...
. To be more precise, however, Algol is a triple-star system: the eclipsing binary pair is separated by only 0.062 AU
Astronomical unit
An astronomical unit is a unit of length equal to about or approximately the mean Earth–Sun distance....
, while the third star in the system (Algol C) is at an average distance of 2.69 AU from the pair and the mutual orbital period
Orbital period
The orbital period is the time taken for a given object to make one complete orbit about another object.When mentioned without further qualification in astronomy this refers to the sidereal period of an astronomical object, which is calculated with respect to the stars.There are several kinds of...
is 681 days (1.86 years). The total mass of the system is about 5.8 solar masses, and the mass ratios of A, B and C are about 4.5 : 1 : 2.
| Components | Semimajor axis | Ellipticity Orbital eccentricity The orbital eccentricity of an astronomical body is the amount by which its orbit deviates from a perfect circle, where 0 is perfectly circular, and 1.0 is a parabola, and no longer a closed orbit... |
Period Orbital period The orbital period is the time taken for a given object to make one complete orbit about another object.When mentioned without further qualification in astronomy this refers to the sidereal period of an astronomical object, which is calculated with respect to the stars.There are several kinds of... |
Inclination Inclination Inclination in general is the angle between a reference plane and another plane or axis of direction.-Orbits:The inclination is one of the six orbital parameters describing the shape and orientation of a celestial orbit... |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A—B | 0.00218″ | 0.00 | 2.87 days | 97.69° |
| (AB)—C | 0.09461″ | 0.225 | 680.05 days | 83.98° |
Studies of Algol led to the Algol paradox
Algol paradox
In stellar astronomy, the Algol paradox is an apparently paradoxical situation when elements of a binary star seem to evolve in discord with the established theories of stellar evolution...
in the theory of stellar evolution
Stellar evolution
Stellar evolution is the process by which a star undergoes a sequence of radical changes during its lifetime. Depending on the mass of the star, this lifetime ranges from only a few million years to trillions of years .Stellar evolution is not studied by observing the life of a single...
: although components of a binary star form at the same time, and massive stars evolve much faster than the less massive ones, it was observed that the more massive component Algol A is still in the main sequence
Main sequence
The main sequence is a continuous and distinctive band of stars that appears on plots of stellar color versus brightness. These color-magnitude plots are known as Hertzsprung–Russell diagrams after their co-developers, Ejnar Hertzsprung and Henry Norris Russell...
, while the less massive Algol B is a subgiant star
Subgiant star
A subgiant star is a star that is slightly brighter than a normal main-sequence star of the same spectral class, but not as bright as true giant stars...
at a later evolutionary stage. The paradox can be solved by mass transfer
Mass transfer
Mass transfer is the net movement of mass from one location, usually meaning a stream, phase, fraction or component, to another. Mass transfer occurs in many processes, such as absorption, evaporation, adsorption, drying, precipitation, membrane filtration, and distillation. Mass transfer is used...
: when the more massive star became a subgiant, it filled its Roche lobe
Roche lobe
The Roche lobe is the region of space around a star in a binary system within which orbiting material is gravitationally bound to that star. If the star expands past its Roche lobe, then the material can escape the gravitational pull of the star. If the star is in a binary system then the material...
, and most of the mass was transferred to the other star, which is still in the main sequence. In some binaries similar to Algol, a gas flow can be seen.
This system also exhibits variable activity in the form of x-ray
X-ray
X-radiation is a form of electromagnetic radiation. X-rays have a wavelength in the range of 0.01 to 10 nanometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range 30 petahertz to 30 exahertz and energies in the range 120 eV to 120 keV. They are shorter in wavelength than UV rays and longer than gamma...
and radio
Radio
Radio is the transmission of signals through free space by modulation of electromagnetic waves with frequencies below those of visible light. Electromagnetic radiation travels by means of oscillating electromagnetic fields that pass through the air and the vacuum of space...
flares. The former is thought to be caused by the magnetic fields of the AB components interacting with the mass transfer. The radio emissions may be created by magnetic cycles similar to sunspots, but, as the magnetic fields around these stars are up to ten times stronger than that of the Sun
Sun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is almost perfectly spherical and consists of hot plasma interwoven with magnetic fields...
, these radio flares are more powerful and longer lasting.
Algol is 92.8 light years from Earth; however, about 7.3 million years ago it passed within 9.8 light years and its apparent magnitude
Apparent magnitude
The apparent magnitude of a celestial body is a measure of its brightness as seen by an observer on Earth, adjusted to the value it would have in the absence of the atmosphere...
was approximately −2.5, considerably brighter than Sirius
Sirius
Sirius is the brightest star in the night sky. With a visual apparent magnitude of −1.46, it is almost twice as bright as Canopus, the next brightest star. The name "Sirius" is derived from the Ancient Greek: Seirios . The star has the Bayer designation Alpha Canis Majoris...
is today. Because the total mass of the system is 5.8 solar masses, and despite the fairly large distance at closest approach, this may have been enough to perturb the solar system
Solar System
The Solar System consists of the Sun and the astronomical objects gravitationally bound in orbit around it, all of which formed from the collapse of a giant molecular cloud approximately 4.6 billion years ago. The vast majority of the system's mass is in the Sun...
's Oort cloud
Oort cloud
The Oort cloud , or the Öpik–Oort cloud , is a hypothesized spherical cloud of comets which may lie roughly 50,000 AU, or nearly a light-year, from the Sun. This places the cloud at nearly a quarter of the distance to Proxima Centauri, the nearest star to the Sun...
slightly and to increase the number of comet
Comet
A comet is an icy small Solar System body that, when close enough to the Sun, displays a visible coma and sometimes also a tail. These phenomena are both due to the effects of solar radiation and the solar wind upon the nucleus of the comet...
s entering the inner solar system. However, the actual increase in net cratering rate is believed to have been quite small.
Etymology
The name Algol derives from ArabicArabic language
Arabic is a name applied to the descendants of the Classical Arabic language of the 6th century AD, used most prominently in the Quran, the Islamic Holy Book...
رأس الغول ra's al-ghūl : head (ra's) of the ogre (al-ghūl) (see "ghoul
Ghoul
A ghoul is a folkloric monster associated with graveyards and consuming human flesh, often classified as undead. The oldest surviving literature that mention ghouls is likely One Thousand and One Nights...
"). The English name Demon Star is a direct translation.
In Hebrew folklore it was known as Rōsh ha Sāṭān 'Satan's Head', via Edmund Chilmead
Edmund Chilmead
Edmund Chilmead was an English writer and translator, who produced both scholarly works and hack writing. He is also known as a musician.He studied at Magdalen College, Oxford, where he graduated M.A. in 1631...
, who called it 'Divels head' or Rosch hassatan. A Latin
Latin
Latin is an Italic language originally spoken in Latium and Ancient Rome. It, along with most European languages, is a descendant of the ancient Proto-Indo-European language. Although it is considered a dead language, a number of scholars and members of the Christian clergy speak it fluently, and...
term from the 16th century was Caput Larvae 'Spectre's Head'. It was also linked with Lilith
Lilith
Lilith is a character in Jewish mythology, found earliest in the Babylonian Talmud, who is generally thought to be related to a class of female demons Līlīṯu in Mesopotamian texts. However, Lowell K. Handy notes, "Very little information has been found relating to the Akkadian and Babylonian view...
. Hipparchus
Hipparchus
Hipparchus, the common Latinization of the Greek Hipparkhos, can mean:* Hipparchus, the ancient Greek astronomer** Hipparchic cycle, an astronomical cycle he created** Hipparchus , a lunar crater named in his honour...
and Pliny
Pliny the Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus , better known as Pliny the Elder, was a Roman author, naturalist, and natural philosopher, as well as naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and personal friend of the emperor Vespasian...
made this a separate, though connected, constellation.
It is known as 大陵五 (the Fifth Star of the Mausoleum) in Chinese astronomy
Chinese astronomy
Astronomy in China has a very long history, with historians considering that "they [the Chinese] were the most persistent and accurate observers of celestial phenomena anywhere in the world before the Arabs."...
, and also bore the grim name Tseih She (叠尸 - die2 shi1 in Modern Pinyin), meaning 'piled up corpses'.
Cultural significance
In the Tetrabiblos, the 2nd century astrological text of the Alexandrian astronomer PtolemyPtolemy
Claudius Ptolemy , was a Roman citizen of Egypt who wrote in Greek. He was a mathematician, astronomer, geographer, astrologer, and poet of a single epigram in the Greek Anthology. He lived in Egypt under Roman rule, and is believed to have been born in the town of Ptolemais Hermiou in the...
, Algol is referred to as "the Gorgon
Gorgon
In Greek mythology, the Gorgon was a terrifying female creature. The name derives from the Greek word gorgós, which means "dreadful." While descriptions of Gorgons vary across Greek literature, the term commonly refers to any of three sisters who had hair of living, venomous snakes, and a...
of Perseus
Perseus (constellation)
Perseus is a constellation in the northern sky, named after the Greek hero Perseus. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union...
" and associated with death by decapitation: a theme which mirrors the myth of the hero Perseus
Perseus
Perseus ,Perseos and Perseas are not used in English. the legendary founder of Mycenae and of the Perseid dynasty of Danaans there, was the first of the mythic heroes of Greek mythology whose exploits in defeating various archaic monsters provided the founding myths of the Twelve Olympians...
’ victory over the snake-headed Gorgon
Gorgon
In Greek mythology, the Gorgon was a terrifying female creature. The name derives from the Greek word gorgós, which means "dreadful." While descriptions of Gorgons vary across Greek literature, the term commonly refers to any of three sisters who had hair of living, venomous snakes, and a...
Medusa
Medusa
In Greek mythology Medusa , " guardian, protectress") was a Gorgon, a chthonic monster, and a daughter of Phorcys and Ceto. The author Hyginus, interposes a generation and gives Medusa another chthonic pair as parents. Gazing directly upon her would turn onlookers to stone...
. Astrologically
Astrology
Astrology consists of a number of belief systems which hold that there is a relationship between astronomical phenomena and events in the human world...
, Algol is considered the most unfortunate
Luck
Luck or fortuity is good fortune which occurs beyond one's control, without regard to one's will, intention, or desired result. There are at least two senses people usually mean when they use the term, the prescriptive sense and the descriptive sense...
star in the sky., and was listed as one of the 15 Behenian stars. Historically, the star has received a strong association with bloody violence across a wide variety of cultures.

