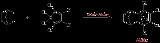
Aldrin
Encyclopedia
Aldrin is an organochlorine insecticide
that was widely used until the 1970s, when it was banned in most countries. It is a colourless solid. Before the ban, it was heavily used as a pesticide to treat seed and soil. Aldrin and related "cyclodiene" pesticides became notorious as persistent organic pollutant
s.
with norbornadiene
in a Diels-Alder reaction
to give the adduct.
Aldrin is named after the German chemist Kurt Alder
, one of the coinventors of this kind of reaction. An estimated 270 million kilograms of aldrin and related cyclodiene pesticides were produced between 1946 and 1976.
In soil, on plant surfaces, or in the digestive tracts of insects, aldrin oxidizes to the epoxide
dieldrin
, which is more strongly insecticidal
. In the U.S., aldrin was cancelled in 1974. The substance is banned from use for plant protection by the EU.
Insecticide
An insecticide is a pesticide used against insects. They include ovicides and larvicides used against the eggs and larvae of insects respectively. Insecticides are used in agriculture, medicine, industry and the household. The use of insecticides is believed to be one of the major factors behind...
that was widely used until the 1970s, when it was banned in most countries. It is a colourless solid. Before the ban, it was heavily used as a pesticide to treat seed and soil. Aldrin and related "cyclodiene" pesticides became notorious as persistent organic pollutant
Persistent organic pollutant
thumb|right|275px|State parties to the Stockholm Convention on Persistent Organic PollutantsPersistent organic pollutants are organic compounds that are resistant to environmental degradation through chemical, biological, and photolytic processes...
s.
Production
Aldrin is produced by combining hexachlorocyclopentadieneHexachlorocyclopentadiene
Hexachlorocyclopentadiene is an organochlorine compound that is a precursor to several pesticides. This colourless liquid is an inexpensive reactive diene. Many of its derivatives proved to be highly controversial, as studies showed them to be persistent organic pollutants. Collectively, the...
with norbornadiene
Norbornadiene
Norbornadiene is an organic compound. This bicyclic hydrocarbon is the most stable diolefin derived from the norbornane and norbornene. Norbornadiene is primarily of interest as a ligand in homogeneous catalysis, but it has been heavily studied due to its high reactivity and distinctive...
in a Diels-Alder reaction
Diels-Alder reaction
The Diels–Alder reaction is an organic chemical reaction between a conjugated diene and a substituted alkene, commonly termed the dienophile, to form a substituted cyclohexene system. The reaction can proceed even if some of the atoms in the newly formed ring are not carbon...
to give the adduct.

Aldrin is named after the German chemist Kurt Alder
Kurt Alder
Kurt Alder was a German chemist and Nobel laureate.-Biography:Alder was born in the industrial area of Königshütte, Silesia , where he received his early schooling...
, one of the coinventors of this kind of reaction. An estimated 270 million kilograms of aldrin and related cyclodiene pesticides were produced between 1946 and 1976.
In soil, on plant surfaces, or in the digestive tracts of insects, aldrin oxidizes to the epoxide
Epoxide
An epoxide is a cyclic ether with three ring atoms. This ring approximately defines an equilateral triangle, which makes it highly strained. The strained ring makes epoxides more reactive than other ethers. Simple epoxides are named from the parent compound ethylene oxide or oxirane, such as in...
dieldrin
Dieldrin
Dieldrin is a chlorinated hydrocarbon originally produced in 1948 by J. Hyman & Co, Denver, as an insecticide. Dieldrin is closely related to aldrin, which reacts further to form dieldrin. Aldrin is not toxic to insects; it is oxidized in the insect to form dieldrin which is the active compound...
, which is more strongly insecticidal
Environmental impact and regulation
Like related polychlorinated pesticides, aldrin is highly lipophilic. Its solubility in water is only 0.027 mg/L, which exacerbates its persistence in the environment. It was banned by the Stockholm Convention on Persistent Organic PollutantsStockholm Convention on Persistent Organic Pollutants
Stockholm Convention on Persistent Organic Pollutants is an international environmental treaty, signed in 2001 and effective from May 2004, that aims to eliminate or restrict the production and use of persistent organic pollutants .- History :...
. In the U.S., aldrin was cancelled in 1974. The substance is banned from use for plant protection by the EU.

