
Air Quality Index
Encyclopedia

Air quality index values are divided into ranges, and each range is assigned a descriptor and a color code. Standardized public health advisories are associated with each AQI range. An agency might also encourage members of the public to take public transportation or work from home when AQI levels are high.
Limitations of the AQI
Most air contaminants do not have an associated AQI. Many countries monitor ground-level ozone, particulates, sulfur dioxideSulfur dioxide
Sulfur dioxide is the chemical compound with the formula . It is released by volcanoes and in various industrial processes. Since coal and petroleum often contain sulfur compounds, their combustion generates sulfur dioxide unless the sulfur compounds are removed before burning the fuel...
, carbon monoxide
Carbon monoxide
Carbon monoxide , also called carbonous oxide, is a colorless, odorless, and tasteless gas that is slightly lighter than air. It is highly toxic to humans and animals in higher quantities, although it is also produced in normal animal metabolism in low quantities, and is thought to have some normal...
and nitrogen dioxide
Nitrogen dioxide
Nitrogen dioxide is the chemical compound with the formula it is one of several nitrogen oxides. is an intermediate in the industrial synthesis of nitric acid, millions of tons of which are produced each year. This reddish-brown toxic gas has a characteristic sharp, biting odor and is a prominent...
and calculate air quality indices for these pollutants.
Causes of poor air quality
The AQI can worsen (go up) due to lack of dilution of air emissions by fresh air. Stagnant air, often caused by an anticycloneAnticyclone
An anticyclone is a weather phenomenon defined by the United States' National Weather Service's glossary as "[a] large-scale circulation of winds around a central region of high atmospheric pressure, clockwise in the Northern Hemisphere, counterclockwise in the Southern Hemisphere"...
or temperature inversion, or other lack of wind
Wind
Wind is the flow of gases on a large scale. On Earth, wind consists of the bulk movement of air. In outer space, solar wind is the movement of gases or charged particles from the sun through space, while planetary wind is the outgassing of light chemical elements from a planet's atmosphere into space...
s lets air pollution
Air pollution
Air pollution is the introduction of chemicals, particulate matter, or biological materials that cause harm or discomfort to humans or other living organisms, or cause damage to the natural environment or built environment, into the atmosphere....
remain in a local area.
Canada
Air quality in Canada has been reported for many years with provincial Air Quality Indices (AQIs). Significantly, AQI values reflect air quality management objectives, which are based on the lowest achievable emissions rate, and not exclusively concern for human health. The Air Quality Health IndexAir Quality Health Index
The Air Quality Health Index or is a scale designed to help understand the impact of air quality on health. It is a health protection tool used to make decisions to reduce short-term exposure to air pollution by adjusting activity levels during increased levels of air pollution...
or (AQHI) is a scale designed to help understand the impact of air quality on health.
It is a health protection tool used to make decisions to reduce short-term exposure to air pollution by adjusting activity levels during increased levels of air pollution. The Air Quality Health Index also provides advice on how to improve air quality by proposing behavioral change to reduce the environmental footprint. This index pays particular attention to people who are sensitive to air pollution. It provides them with advice on how to protect their health during air quality levels associated with low, moderate, high and very high health risks.
The Air Quality Health Index provides a number from 1 to 10+ to indicate the level of health risk associated with local air quality. On occasion, when the amount of air pollution is abnormally high, the number may exceed 10. The AQHI provides a local air quality current value as well as a local air quality maximums forecast for today, tonight, and tomorrow, and provides associated health advice.
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | + |
| Risk: | Low (1-3) | Moderate (4-6) | High (7-10) | Very high (above 10) |
| Health Risk | Air Quality Health Index | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| API | 0 - 25 | Low | None expected. |
|---|---|---|---|
| 26 - 50 | Medium | None expected for the general population. | |
| 51 - 100 | High | Acute health effects are not expected but chronic effects may be observed if one is persistently exposed to such levels. | |
| 100 - 200 | Very High | People with existing heart or respiratory illnesses may notice mild aggravation of their health conditions. Generally healthy individuals may also notice some discomfort. | |
| 201 - 500 | Severe | People with existing heart or respiratory illnesses may experience significant aggravation of their symptoms. There may also be widespread symptoms in the healthy population (e.g. eye irritation, wheezing, coughing, phlegm and sore throats). |
Mainland China
China's Ministry of Environmental Protection (MEPMinistry of Environmental Protection of the People's Republic of China
The Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People's Republic of China , formerly State Environmental Protection Administration , is a cabinet-level ministry in the executive branch of the Chinese Government . It replaced the SEPA during the March 2008 National People's Congress sessions in...
) is responsible for measuring the level of air pollution in China. As of 28 August 2008, MEP monitors daily pollution level in 86 of its major cities. The API level is based on the level of 5 atmospheric pollutants, namely sulfur dioxide
Sulfur dioxide
Sulfur dioxide is the chemical compound with the formula . It is released by volcanoes and in various industrial processes. Since coal and petroleum often contain sulfur compounds, their combustion generates sulfur dioxide unless the sulfur compounds are removed before burning the fuel...
(SO2), nitrogen dioxide
Nitrogen dioxide
Nitrogen dioxide is the chemical compound with the formula it is one of several nitrogen oxides. is an intermediate in the industrial synthesis of nitric acid, millions of tons of which are produced each year. This reddish-brown toxic gas has a characteristic sharp, biting odor and is a prominent...
(NO2), suspended particulates (PM10), carbon monoxide
Carbon monoxide
Carbon monoxide , also called carbonous oxide, is a colorless, odorless, and tasteless gas that is slightly lighter than air. It is highly toxic to humans and animals in higher quantities, although it is also produced in normal animal metabolism in low quantities, and is thought to have some normal...
(CO), and ozone
Ozone
Ozone , or trioxygen, is a triatomic molecule, consisting of three oxygen atoms. It is an allotrope of oxygen that is much less stable than the diatomic allotrope...
(O3) measured at the monitoring stations throughout each city.
API Mechanics
An individual score is assigned to the level of each pollutant and the final API is the highest of those 5 scores. The pollutants can be measured quite differently. SO2, NO2 and PM10 concentration are measured as average per day. CO and O3 are more harmful and are measured as average per hour. The final API value is calculated per day.
The scale for each pollutant is non-linear, as is the final API score. Thus an API of 100 does not mean twice the pollution of API at 50, nor does it mean twice as harmful. While an API of 50 from day 1 to 182 and API of 100 from day 183 to 365 does provide an annual average of 75, it does not mean the pollution is acceptable even if the benchmark of 100 is deemed safe. This is because the benchmark is a 24 hour target. The annual average must match against the annual target. It is entirely possible to have safe air every day of the year but still fail the annual pollution benchmark.
API and Health Implications (Daily Targets)
| API | 0 - 50 | Excellent | No health implications |
|---|---|---|---|
| 51 -100 | Good | No health implications | |
| 101-150 | Slightly Polluted | Slight irrations may occur, individuals with breathing or heart problems should reduce outdoor exercise. | |
| 151-200 | Lightly Polluted | Slight irrations may occur, individuals with breathing or heart problems should reduce outdoor exercise. | |
| 201-250 | Moderately Polluted | Healthy people will be noticeably affected. People with breathing or heart problems will experience reduced endurance in activities. These individuals and elders should remain indoors and restrict activities. | |
| 251-300 | Heavily Polluted | Healthy people will be noticeably affected. People with breathing or heart problems will experience reduced endurance in activities. These individuals and elders should remain indoors and restrict activities. | |
| 300+ | Severely Polluted | Healthy people will experience reduced endurance in activities. There may be strong irritations and symptoms and may trigger other illnesses. Elders and the sick should remain indoors and avoid exercise. Healthy individuals should avoid out door activities. |
Mexico
The air quality in MexicoMexico
The United Mexican States , commonly known as Mexico , is a federal constitutional republic in North America. It is bordered on the north by the United States; on the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; on the southeast by Guatemala, Belize, and the Caribbean Sea; and on the east by the Gulf of...
is reported in IMECAs. The IMECA is calculated using the measurements of average times of the chemicals ozone
Ozone
Ozone , or trioxygen, is a triatomic molecule, consisting of three oxygen atoms. It is an allotrope of oxygen that is much less stable than the diatomic allotrope...
(O3), sulphur dioxide (SO2), nitrogen dioxide
Nitrogen dioxide
Nitrogen dioxide is the chemical compound with the formula it is one of several nitrogen oxides. is an intermediate in the industrial synthesis of nitric acid, millions of tons of which are produced each year. This reddish-brown toxic gas has a characteristic sharp, biting odor and is a prominent...
(NO2), carbon monoxide
Carbon monoxide
Carbon monoxide , also called carbonous oxide, is a colorless, odorless, and tasteless gas that is slightly lighter than air. It is highly toxic to humans and animals in higher quantities, although it is also produced in normal animal metabolism in low quantities, and is thought to have some normal...
(CO) and particles lower than 10 micrometers (PM10).
Singapore
SingaporeSingapore
Singapore , officially the Republic of Singapore, is a Southeast Asian city-state off the southern tip of the Malay Peninsula, north of the equator. An island country made up of 63 islands, it is separated from Malaysia by the Straits of Johor to its north and from Indonesia's Riau Islands by the...
uses the Pollutant Standards Index
Pollutant Standards Index
The Pollutant Standards Index, or PSI, provides a uniform system of measuring pollution levels for the major air pollutants. It is based on a scale devised by the United States Environmental Protection Agency to provide a way for broadcasts and newspapers to report air quality on a daily basis.The...
to report on its air quality.
The PSI chart below is grouped by index values and descriptors, according to the National Environment Agency
National Environment Agency
National Environment Agency formed on 1 July 2002, is a statutory board under the Ministry of the Environment and Water Resources in Singapore. As a statutory board, it gives NEA greater administrative autonomy to be more nimble in the protection of the environment...
.
| PSI | ||
|---|---|---|
| CAI | Description | Health Implications |
| 0-50 | Good | A level that will not impact patients suffering from diseases related to air pollution. |
| 51-100 | Moderate | A level that may have a meager impact on patients in case of chronic exposure. |
| 101-150 | Unhealthy for sensitive groups | A level that may have harmful impacts on patients and members of sensitive groups. |
| 151-250 | Unhealthy | A level that may have harmful impacts on patients and members of sensitive groups (children, aged or weak people), and also cause the general public unpleasant feelings. |
| 251-350 | Very unhealthy | A level that may have a serious impact on patients and members of sensitive groups in case of acute exposure. |
| 351-500 | Hazardous | A level that may need to take emergency measures for patients and members of sensitive groups and have harmful impacts on the general public. |
United Kingdom
AEA TechnologyAEA Technology
AEA Technology plc was formed in 1996 as the privatised offshoot of the United Kingdom Atomic Energy Authority. It is a constituent of the FTSE Fledgling Index. Originally it consisted of divisions with expertise in a wide variety of areas, mostly the products of nuclear-related research...
issue air quality forecasts for the UK on behalf of DEFRA wherein the level of pollution is described either as an index (ranging from 1 to 10) or as a banding (low, moderate, high or very high). These levels are based on the health effects of each pollutant.
| Index | 1 - 3 | Low | Effects are unlikely to be noticed even by individuals who know they are sensitive to air pollutants. |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4 - 6 | Moderate | Mild effects, unlikely to require action, may be noticed amongst sensitive individuals. | |
| 7 - 9 | High | Significant effects may be noticed by sensitive individuals and action to avoid or reduce these effects may be needed (e.g. reducing exposure by spending less time in polluted areas outdoors). Asthmatics will find that their 'reliever' inhaler is likely to reverse the effects on the lung. | |
| 10 | Very High | The effects on sensitive individuals described for 'High' levels of pollution may worsen. |
The forecast is produced for a number of different pollutants and their typical health effects are shown in the following table.
| Pollutant | Health Effects at High Level |
|---|---|
| Nitrogen dioxide Ozone Sulphur dioxide |
These gases irritate the airways of the lungs, increasing the symptoms of those suffering from lung diseases. |
| Particulates |
Fine particles can be carried deep into the lungs where they can cause inflammation and a worsening of heart and lung diseases |
United States
The United States Environmental Protection AgencyUnited States Environmental Protection Agency
The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency is an agency of the federal government of the United States charged with protecting human health and the environment, by writing and enforcing regulations based on laws passed by Congress...
(EPA) uses the following AQI:
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
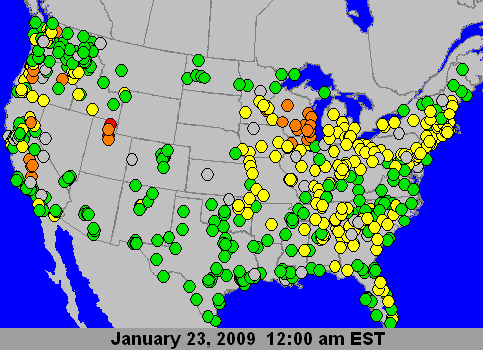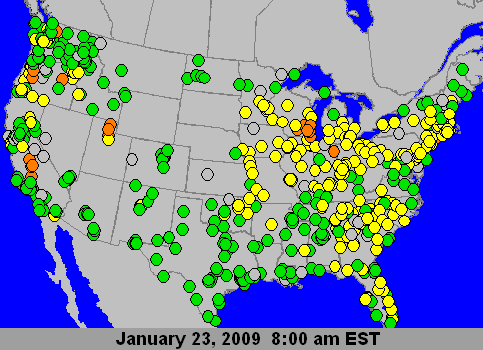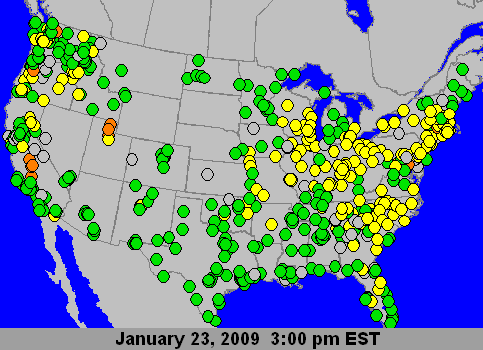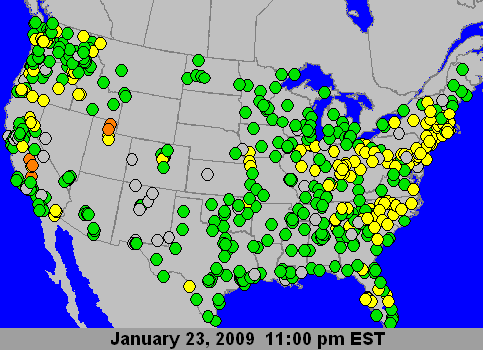 |
PM2.5 24-Hour AQI Loop, Courtesy US EPA
The air quality index is a piecewise linear function of the pollutant concentration.
At the boundary between AQI categories, there is a discontinuous jump of one AQI unit.
To convert from concentration to AQI the equation:

is used, where:
 = the (Air Quality) index,
= the (Air Quality) index, = the pollutant concentration,
= the pollutant concentration, = the concentration breakpoint that is ≤
= the concentration breakpoint that is ≤  ,
, = the concentration breakpoint that is ≥
= the concentration breakpoint that is ≥  ,
, = the index breakpoint corresponding to
= the index breakpoint corresponding to  ,
, = the index breakpoint corresponding to
= the index breakpoint corresponding to  .
.For breakpoints for different pollutants, see:
http://www.epa.gov/airnow/aqi_tech_assistance.pdf.
For example, suppose a monitor records a 24-hour average fine particle (PM2.5) concentration of 12.0 micrograms per cubic meter. EPA's table of breakpoints for PM2.5 is:
 |
 |
 |
 |
Category |
| 0 | 15.4 | 0 | 50 | Good |
| 15.5 | 40.4 | 51 | 100 | Moderate |
| 40.5 | 65.4 | 101 | 150 | Unhealthy for Sensitive Groups |
| 65.5 | 150.4 | 151 | 200 | Unhealthy |
| 150.5 | 250.4 | 201 | 300 | Very Unhealthy |
| 250.5 | 350.4 | 301 | 400 | Hazardous |
| 350.5 | 500.4 | 401 | 500 | Hazardous |
The equation above results in an AQI of:
 ,
,corresponding to air quality in the "Good" range.
If multiple pollutants are measured at a monitoring site, then the largest or "dominant" AQI value is reported for the location.
To convert an air pollutant concentration to an AQI, EPA has developed a calculator:
http://airnow.gov/index.cfm?action=aqi.conc_aqi_calc.
To convert an air quality index to an air pollutant concentration, see:
http://airnow.gov/index.cfm?action=aqi.aqi_conc_calc.
Current ambient monitoring data and forecasts of air quality that are color-coded in terms of the air quality index are available at: http://www.airnow.gov/.
The Clean Air Act (USA) (1990) requires EPA to review its National Ambient Air Quality Standards
National Ambient Air Quality Standards
The National Ambient Air Quality Standards are standards established by the United States Environmental Protection Agency under authority of the Clean Air Act that apply for outdoor air throughout the country...
every five years to reflect evolving health effects information. The Air Quality Index is adjusted periodically to reflect these changes.
Abbreviations in this article
In the context of this article about air quality:- ppbv=parts per billion by volume = a portion anomaly volume of pollutant gas per billion volumes of ambient air
- ppmv = parts per million by volume = volume of pollutant gas per million volumes of ambient air
- PM2.5 = particulate matter smaller than 2.5 μm in aerodynamic diameterAerodynamic diameterAerodynamic diameter is a physical property of a particle in a viscous fluid such as air. In general, particles have irregular shapes with actual geometric diameters that are difficult to measure. Aerodynamic diameter is an expression of a particle's aerodynamic behavior as if it were a perfect...
- PM10 = particulate matter smaller than 10 μm in aerodynamic diameter
- μg/m³ = micrograms per cubic metre of ambient air
- μm = micrometre
Air quality by country or region
- British ColumbiaAir pollution in British ColumbiaAir pollution is a concern in British Columbia, Canada because of its effects on health and visibility. Air quality is influenced in British Columbia by numerous mountain ranges and valleys, which complicate atmospheric pollution dispersion and can lead to high concentrations of pollutants such as...
- Hong KongAir pollution in Hong KongAir pollution in Hong Kong is considered a serious problem. Visibility is currently less than eight kilometres for 30% of the year. Cases of asthma and bronchial infections have soared in recent years due to reduced air quality....
See also
- Air pollutionAir pollutionAir pollution is the introduction of chemicals, particulate matter, or biological materials that cause harm or discomfort to humans or other living organisms, or cause damage to the natural environment or built environment, into the atmosphere....
- Air Pollution IndexAir Pollution IndexThe Air Pollution Index is a simple and generalized way to describe the air quality in mainland China, Hong Kong and Malaysia. It is calculated from several sets of air pollution data.-Mainland China:...
- Atmospheric dispersion modelingAtmospheric dispersion modelingAtmospheric dispersion modeling is the mathematical simulation of how air pollutants disperse in the ambient atmosphere. It is performed with computer programs that solve the mathematical equations and algorithms which simulate the pollutant dispersion...
- BarbecueBarbecueBarbecue or barbeque , used chiefly in the United States, Canada, the United Kingdom, New Zealand and Australia is a method and apparatus for cooking meat, poultry and occasionally fish with the heat and hot smoke of a fire, smoking wood, or hot coals of...
- GrillingGrillingGrilling is a form of cooking that involves dry heat applied to the surface of food, commonly from above or below.Grilling usually involves a significant amount of direct, radiant heat, and tends to be used for cooking meat quickly and meat that has already been cut into slices...
- Emission standardEmission standardEmission standards are requirements that set specific limits to the amount of pollutants that can be released into the environment. Many emissions standards focus on regulating pollutants released by automobiles and other powered vehicles but they can also regulate emissions from industry, power...
- Radon mitigationRadon mitigationRadon mitigation is any process used to reduce radon concentrations in the breathing zones of occupied buildings.-Testing:ASTM E-2121 is a standard for reducing radon in homes as far as practicable below 4 picocuries per liter in indoor air. Radon test kits are commercially available...
- European emission standardsEuropean emission standardsEuropean emission standards define the acceptable limits for exhaust emissions of new vehicles sold in EU member states. The emission standards are defined in a series of European Union directives staging the progressive introduction of increasingly stringent standards.Currently, emissions of...
- HazeHazeHaze is traditionally an atmospheric phenomenon where dust, smoke and other dry particles obscure the clarity of the sky. The World Meteorological Organization manual of codes includes a classification of horizontal obscuration into categories of fog, ice fog, steam fog, mist, haze, smoke, volcanic...
- Indoor air qualityIndoor air qualityIndoor air quality is a term referring to the air quality within and around buildings and structures, especially as it relates to the health and comfort of building occupants....
- National Ambient Air Quality StandardsNational Ambient Air Quality StandardsThe National Ambient Air Quality Standards are standards established by the United States Environmental Protection Agency under authority of the Clean Air Act that apply for outdoor air throughout the country...
- U.S. standards for EPA intervention - Pollutant Standards IndexPollutant Standards IndexThe Pollutant Standards Index, or PSI, provides a uniform system of measuring pollution levels for the major air pollutants. It is based on a scale devised by the United States Environmental Protection Agency to provide a way for broadcasts and newspapers to report air quality on a daily basis.The...
- SmogSmogSmog is a type of air pollution; the word "smog" is a portmanteau of smoke and fog. Modern smog is a type of air pollution derived from vehicular emission from internal combustion engines and industrial fumes that react in the atmosphere with sunlight to form secondary pollutants that also combine...
External links
- CAI at Airkorea.or.kr - website of South Korea Environmental Management Corp.
- AQI at airnow.gov - cross-agency U.S. Government site
- New Mexico Air Quality and API data - Example of how New Mexico Environment Department publishes their Air Quality and API data.
- AQI at Meteorological Service of Canada
- The UK Air Quality Archive
- The pollution index of the UK Met Office
- API at JAS (Malaysian Department of Environment)
- API at Hong Kong - Environmental Protection Department of the Government of the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region
- San Francisco Bay Area Spare-the-Air - AQI explanation
- Malaysia Air Pollution Index
- AQI in Thailand provinces and in Bangkok
- The American Lung Association declares EPA standards fall short.
The source of this article is wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. The text of this article is licensed under the GFDL.

