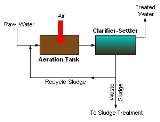
Activated sludge
Overview
Sewage
Sewage is water-carried waste, in solution or suspension, that is intended to be removed from a community. Also known as wastewater, it is more than 99% water and is characterized by volume or rate of flow, physical condition, chemical constituents and the bacteriological organisms that it contains...
and industrial wastewaters
Wastewater Treatment
Wastewater treatment may refer to:* Sewage treatment* Industrial wastewater treatment...
using air and a biological floc composed of bacteria and protozoans.
In a sewage (or industrial wastewater) treatment plant, the activated sludge process can be used for one or several of the following purposes:
- oxidizing carbonaceous matter: biological matter.
- oxidizing nitrogeneous matter: mainly ammoniumAmmoniumThe ammonium cation is a positively charged polyatomic cation with the chemical formula NH. It is formed by the protonation of ammonia...
and nitrogenNitrogenNitrogen is a chemical element that has the symbol N, atomic number of 7 and atomic mass 14.00674 u. Elemental nitrogen is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, and mostly inert diatomic gas at standard conditions, constituting 78.08% by volume of Earth's atmosphere...
in biological materials. - removing phosphatePhosphateA phosphate, an inorganic chemical, is a salt of phosphoric acid. In organic chemistry, a phosphate, or organophosphate, is an ester of phosphoric acid. Organic phosphates are important in biochemistry and biogeochemistry or ecology. Inorganic phosphates are mined to obtain phosphorus for use in...
. - driving off entrained gases carbon dioxideCarbon dioxideCarbon dioxide is a naturally occurring chemical compound composed of two oxygen atoms covalently bonded to a single carbon atom...
, ammoniaAmmoniaAmmonia is a compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the formula . It is a colourless gas with a characteristic pungent odour. Ammonia contributes significantly to the nutritional needs of terrestrial organisms by serving as a precursor to food and fertilizers. Ammonia, either directly or...
, nitrogen, etc. - generating a biological floc that is easy to settle.
- generating a liquor that is low in dissolved or suspended material.
The process involves air or oxygen
Oxygen
Oxygen is the element with atomic number 8 and represented by the symbol O. Its name derives from the Greek roots ὀξύς and -γενής , because at the time of naming, it was mistakenly thought that all acids required oxygen in their composition...
being introduced into a mixture of primary treated or screened sewage or industrial wastewater (called wastewater from now on) combined with organisms to develop a biological floc
Flocculation
Flocculation, in the field of chemistry, is a process wherein colloids come out of suspension in the form of floc or flakes by the addition of a clarifying agent. The action differs from precipitation in that, prior to flocculation, colloids are merely suspended in a liquid and not actually...
which reduces the organic
Organic matter
Organic matter is matter that has come from a once-living organism; is capable of decay, or the product of decay; or is composed of organic compounds...
content of the sewage
Sewage
Sewage is water-carried waste, in solution or suspension, that is intended to be removed from a community. Also known as wastewater, it is more than 99% water and is characterized by volume or rate of flow, physical condition, chemical constituents and the bacteriological organisms that it contains...
.
Unanswered Questions

