
Acoustic source localization
Encyclopedia
Acoustic source localization is the task of locating a sound
source given measurements of the sound field. The sound field can be described using physical quantities like sound pressure and particle velocity. By measuring these properties it is (indirectly) possible to obtain a source direction.
is measured using microphones. Microphones have a polar pattern describing their sensitivity as function of the direction of the incident sound. Many microphones have an omni-directional polar pattern which means their sensitivity is independent of the direction of the incident sound. Microphones with other polar patterns exist that are more sensitive in a certain direction. This however is still no solution for the sound localization problem as one tries to determine either an exact direction, or a point of origin. Besides considering microphones that measure sound pressure
, it is also possible to use a particle velocity probe
to measure the acoustic particle velocity
directly. The particle velocity is another quantity related to acoustic wave
s however, unlike sound pressure, particle velocity is a vector
. By measuring particle velocity one obtains a source direction directly. Other more complicated methods using multiple sensors is also possible. Many of these methods use the time difference of arrival (TDOA) technique.
Some have termed acoustic
source localization an "inverse problem
" in that the measured sound field is translated to the position of the sound source.
. The particle velocity is a vector
and thus also contains directional information.
With a sensor array (for instance a microphone array
) consisting of at least two probes it is possible to obtain the source direction using the cross-correlation
function between each probes' signal. The cross-correlation
function between two microphones is defined as
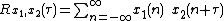
which defines the level of correlation
between the outputs of two sensors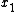 and
and 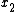 . In general, a higher level of correlation means that the argument
. In general, a higher level of correlation means that the argument  is relatively close to the actual time-difference-of-arrival. For two sensors next to each other the TDOA is given by
is relatively close to the actual time-difference-of-arrival. For two sensors next to each other the TDOA is given by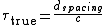
where is the speed of sound in the medium surrounding the sensors and the source.
is the speed of sound in the medium surrounding the sensors and the source.
A well known example of TDOA is the interaural time difference
. The interaural time difference is the difference in arrival time of a sound between two ears. The interaural time difference is given by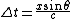
where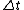 is the time difference in seconds
is the time difference in seconds is the distance between the two sensors (ears) in meters
is the distance between the two sensors (ears) in meters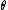 is the angle between the baseline of the sensors (ears) and the incident sound, in degrees
is the angle between the baseline of the sensors (ears) and the incident sound, in degrees
and geometry
, triangulation is the process of determining the location of a point by measuring angle
s to it from known points at either end of a fixed baseline, rather than measuring distances to the point directly (trilateration
). The point can then be fixed as the third point of a triangle with one known side and two known angles.
For acoustic localization this means that if the source direction is measured at at least two locations in space, it is possible to triangulate its location.
Acoustic location
Boomerang
Japanese war tuba
: Use of Acoustic location during World War I
Sound
Sound is a mechanical wave that is an oscillation of pressure transmitted through a solid, liquid, or gas, composed of frequencies within the range of hearing and of a level sufficiently strong to be heard, or the sensation stimulated in organs of hearing by such vibrations.-Propagation of...
source given measurements of the sound field. The sound field can be described using physical quantities like sound pressure and particle velocity. By measuring these properties it is (indirectly) possible to obtain a source direction.
Overview
Traditionally sound pressureSound pressure
Sound pressure or acoustic pressure is the local pressure deviation from the ambient atmospheric pressure caused by a sound wave. Sound pressure can be measured using a microphone in air and a hydrophone in water...
is measured using microphones. Microphones have a polar pattern describing their sensitivity as function of the direction of the incident sound. Many microphones have an omni-directional polar pattern which means their sensitivity is independent of the direction of the incident sound. Microphones with other polar patterns exist that are more sensitive in a certain direction. This however is still no solution for the sound localization problem as one tries to determine either an exact direction, or a point of origin. Besides considering microphones that measure sound pressure
Sound pressure
Sound pressure or acoustic pressure is the local pressure deviation from the ambient atmospheric pressure caused by a sound wave. Sound pressure can be measured using a microphone in air and a hydrophone in water...
, it is also possible to use a particle velocity probe
Particle velocity probe
A Particle velocity probe is a probe capable of measuring the acoustic particle velocity.The only particle velocity probe to date has been produced by Microflown Technologies and is called the Microflown....
to measure the acoustic particle velocity
Particle velocity
Particle velocity is the velocity v of a particle in a medium as it transmits a wave. In many cases this is a longitudinal wave of pressure as with sound, but it can also be a transverse wave as with the vibration of a taut string....
directly. The particle velocity is another quantity related to acoustic wave
Acoustic wave
Acoustic waves are a type of longitudinal waves that propagate by means of adiabatic compression and decompression. Longitudinal waves are waves that have the same direction of vibration as their direction of travel. Important quantities for describing acoustic waves are sound pressure, particle...
s however, unlike sound pressure, particle velocity is a vector
Vector
Vector, a Latin word meaning "carrier", may refer in English to:-In computer science:*A one-dimensional array**Vector , a data type in the C++ Standard Template Library...
. By measuring particle velocity one obtains a source direction directly. Other more complicated methods using multiple sensors is also possible. Many of these methods use the time difference of arrival (TDOA) technique.
Some have termed acoustic
Acoustics
Acoustics is the interdisciplinary science that deals with the study of all mechanical waves in gases, liquids, and solids including vibration, sound, ultrasound and infrasound. A scientist who works in the field of acoustics is an acoustician while someone working in the field of acoustics...
source localization an "inverse problem
Inverse problem
An inverse problem is a general framework that is used to convert observed measurements into information about a physical object or system that we are interested in...
" in that the measured sound field is translated to the position of the sound source.
Particle velocity or intensity vector
The simplest but still a relatively new method is to measure the acoustic particle velocity using a particle velocity probeParticle velocity probe
A Particle velocity probe is a probe capable of measuring the acoustic particle velocity.The only particle velocity probe to date has been produced by Microflown Technologies and is called the Microflown....
. The particle velocity is a vector
Vector
Vector, a Latin word meaning "carrier", may refer in English to:-In computer science:*A one-dimensional array**Vector , a data type in the C++ Standard Template Library...
and thus also contains directional information.
Time difference of arrival
The traditional method to obtain the source direction is using the time difference of arrival (TDOA) method. This method can be used with pressure microphones as well as with particle velocity probes.With a sensor array (for instance a microphone array
Microphone array
A microphone array is any number of microphones operating in tandem. There are many applications:*Systems for extracting voice input from ambient noise *Surround sound and related technologies...
) consisting of at least two probes it is possible to obtain the source direction using the cross-correlation
Cross-correlation
In signal processing, cross-correlation is a measure of similarity of two waveforms as a function of a time-lag applied to one of them. This is also known as a sliding dot product or sliding inner-product. It is commonly used for searching a long-duration signal for a shorter, known feature...
function between each probes' signal. The cross-correlation
Cross-correlation
In signal processing, cross-correlation is a measure of similarity of two waveforms as a function of a time-lag applied to one of them. This is also known as a sliding dot product or sliding inner-product. It is commonly used for searching a long-duration signal for a shorter, known feature...
function between two microphones is defined as
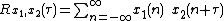
which defines the level of correlation
Correlation
In statistics, dependence refers to any statistical relationship between two random variables or two sets of data. Correlation refers to any of a broad class of statistical relationships involving dependence....
between the outputs of two sensors
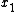 and
and 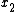 . In general, a higher level of correlation means that the argument
. In general, a higher level of correlation means that the argument  is relatively close to the actual time-difference-of-arrival. For two sensors next to each other the TDOA is given by
is relatively close to the actual time-difference-of-arrival. For two sensors next to each other the TDOA is given by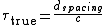
where
 is the speed of sound in the medium surrounding the sensors and the source.
is the speed of sound in the medium surrounding the sensors and the source.A well known example of TDOA is the interaural time difference
Interaural time difference
The interaural time difference when concerning humans or animals, is the difference in arrival time of a sound between two ears. It is important in the localisation of sounds, as it provides a cue to the direction or angle of the sound source from the head. If a signal arrives at the head from one...
. The interaural time difference is the difference in arrival time of a sound between two ears. The interaural time difference is given by
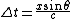
where
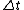 is the time difference in seconds
is the time difference in seconds is the distance between the two sensors (ears) in meters
is the distance between the two sensors (ears) in meters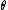 is the angle between the baseline of the sensors (ears) and the incident sound, in degrees
is the angle between the baseline of the sensors (ears) and the incident sound, in degreesTriangulation
In trigonometryTrigonometry
Trigonometry is a branch of mathematics that studies triangles and the relationships between their sides and the angles between these sides. Trigonometry defines the trigonometric functions, which describe those relationships and have applicability to cyclical phenomena, such as waves...
and geometry
Geometry
Geometry arose as the field of knowledge dealing with spatial relationships. Geometry was one of the two fields of pre-modern mathematics, the other being the study of numbers ....
, triangulation is the process of determining the location of a point by measuring angle
Angle
In geometry, an angle is the figure formed by two rays sharing a common endpoint, called the vertex of the angle.Angles are usually presumed to be in a Euclidean plane with the circle taken for standard with regard to direction. In fact, an angle is frequently viewed as a measure of an circular arc...
s to it from known points at either end of a fixed baseline, rather than measuring distances to the point directly (trilateration
Trilateration
In geometry, trilateration is the process of determinating absolute or relative locations of points by measurement of distances, using the geometry of circles, spheres or triangles. In addition to its interest as a geometric problem, trilateration does have practical applications in surveying and...
). The point can then be fixed as the third point of a triangle with one known side and two known angles.
For acoustic localization this means that if the source direction is measured at at least two locations in space, it is possible to triangulate its location.
See also
Sound localisationAcoustic location
Acoustic location
Acoustic location is the science of using sound to determine the distance and direction of something. Location can be done actively or passively, and can take place in gases , liquids , and in solids .* Active acoustic location involves the creation of sound in order to produce an echo, which is...
Boomerang
Boomerang (mobile shooter detection system)
Boomerang is a gunfire locator developed by DARPA and BBN Technologies primarily for use against snipers on mobile vehicles such as the Humvee, Stryker, and MRAP combat vehicles. There were future plans to integrate it into the Land Warrior system....
Japanese war tuba
Japanese War Tuba
The Japanese war tuba is a colloquial name sometimes applied to Imperial Japanese Army acoustic locators due to the visual resemblance to the musical tuba...
: Use of Acoustic location during World War I

