
Abbey of Fontenay
Encyclopedia
Abbey
An abbey is a Catholic monastery or convent, under the authority of an Abbot or an Abbess, who serves as the spiritual father or mother of the community.The term can also refer to an establishment which has long ceased to function as an abbey,...
located in the commune of Marmagne
Marmagne, Côte-d'Or
Marmagne is a commune in the Côte-d'Or department in eastern France.The Abbey of Fontenay is located on the territory of the commune.-Population:-References:*...
, near Montbard
Montbard
Montbard is a commune and subprefecture of the Côte-d'Or department in the Bourgogne region in eastern France.Montbard is a small industrial town on the river Brenne. The Forges de Buffon, ironworks established by Buffon, are located in the nearby village of Buffon...
, in the département
Départements of France
The departments of France are French administrative divisions. The 101 departments form one of the three levels of local government, together with the 22 metropolitan and 5 overseas regions above them and more than 36 000 communes beneath them...
of Côte-d'Or
Côte-d'Or
Côte-d'Or is a department in the eastern part of France.- History :Côte-d'Or is one of the original 83 departments created during the French Revolution on 4 March 1790. It was formed from part of the former province of Burgundy.- Geography :...
in France
France
The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
. It was founded by Saint Bernard of Clairvaux in 1118, and built in the Romanesque style
Romanesque architecture
Romanesque architecture is an architectural style of Medieval Europe characterised by semi-circular arches. There is no consensus for the beginning date of the Romanesque architecture, with proposals ranging from the 6th to the 10th century. It developed in the 12th century into the Gothic style,...
. It is one of the oldest and most complete Cistercian abbeys in Europe, and became a UNESCO
UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations...
World Heritage Site
World Heritage Site
A UNESCO World Heritage Site is a place that is listed by the UNESCO as of special cultural or physical significance...
in 1981.
History
Bernard of Claivaux founded the Abbey of Fontenay only a few years after he left Cîteaux AbbeyCîteaux Abbey
Cîteaux Abbey is a Roman Catholic abbey located in Saint-Nicolas-lès-Cîteaux, south of Dijon, France. Today it belongs to the Trappists, or Cistercians of the Strict Observance . The Cistercian order takes its name from this mother house of Cîteaux, earlier Cisteaux, near Nuits-Saint-Georges...
to found Clairvaux Abbey
Clairvaux Abbey
Clairvaux Abbey is a Cistercian monastery in Ville-sous-la-Ferté, 15 km from Bar-sur-Aube, in the Aube département in northeastern France. The original building, founded in 1115 by St. Bernard, is now in ruins; a high-security prison, the Clairvaux Prison, now occupies the grounds...
. The abbey church was dedicated by Pope Eugene III
Pope Eugene III
Pope Blessed Eugene III , born Bernardo da Pisa, was Pope from 1145 to 1153. He was the first Cistercian to become Pope.-Early life:...
in 1147. Located in a small forested valley 60 kilometres northwest of Dijon
Dijon
Dijon is a city in eastern France, the capital of the Côte-d'Or département and of the Burgundy region.Dijon is the historical capital of the region of Burgundy. Population : 151,576 within the city limits; 250,516 for the greater Dijon area....
, it achieved great prosperity in the twelfth and thirteenth centuries. Fontenay enjoyed the protection of the Kings of France but was plundered in the Hundred Year's War and the Wars of Religion
French Wars of Religion
The French Wars of Religion is the name given to a period of civil infighting and military operations, primarily fought between French Catholics and Protestants . The conflict involved the factional disputes between the aristocratic houses of France, such as the House of Bourbon and House of Guise...
. Later, its fortunes declined, and the refectory
Refectory
A refectory is a dining room, especially in monasteries, boarding schools and academic institutions. One of the places the term is most often used today is in graduate seminaries...
was demolished by the monks in 1745. The abbey was closed in the French Revolution
French Revolution
The French Revolution , sometimes distinguished as the 'Great French Revolution' , was a period of radical social and political upheaval in France and Europe. The absolute monarchy that had ruled France for centuries collapsed in three years...
, and became a paper mill
Paper mill
A paper mill is a factory devoted to making paper from vegetable fibres such as wood pulp, old rags and other ingredients using a Fourdrinier machine or other type of paper machine.- History :...
until 1902, owned for most of its period of operation by the Montgolfier family. In 1905 the abbey was bought by Édouard Aynard and restored.
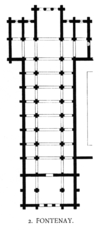
Architecture
The church of the abbey was built from 1139 to 1147 in the prevalent Romanesque style, and marked by the austerity typical of Cistercian architectureCistercian architecture
Cistercian architecture is a style of architecture associated with the churches, monasteries and abbeys of the Roman Catholic Cistercian Order. It was headed by Abbot Bernard of Clairvaux , who believed that churches should avoid superfluous ornamentation so as not to distract from the religious life...
. It has a cruciform
Cruciform
Cruciform means having the shape of a cross or Christian cross.- Cruciform architectural plan :This is a common description of Christian churches. In Early Christian, Byzantine and other Eastern Orthodox forms of church architecture this is more likely to mean a tetraconch plan, a Greek cross,...
plan, with a nave
Nave
In Romanesque and Gothic Christian abbey, cathedral basilica and church architecture, the nave is the central approach to the high altar, the main body of the church. "Nave" was probably suggested by the keel shape of its vaulting...
66 metres long and 8 metres wide, with two aisles, and a transept
Transept
For the periodical go to The Transept.A transept is a transverse section, of any building, which lies across the main body of the building. In Christian churches, a transept is an area set crosswise to the nave in a cruciform building in Romanesque and Gothic Christian church architecture...
measuring 19 metres. The cloister measures 36×38 metres. The chapterhouse is vaulted, with heavy ribs. There is a large dormitory which was re-roofed in the fifteenth century with an arched braced roof of chestnut
Chestnut
Chestnut , some species called chinkapin or chinquapin, is a genus of eight or nine species of deciduous trees and shrubs in the beech family Fagaceae, native to temperate regions of the Northern Hemisphere. The name also refers to the edible nuts they produce.-Species:The chestnut belongs to the...
timber.
Apart from the demolished refectory, the abbey retains almost all of its original buildings: church, dormitory
Dormitory
A dormitory, often shortened to dorm, in the United States is a residence hall consisting of sleeping quarters or entire buildings primarily providing sleeping and residential quarters for large numbers of people, often boarding school, college or university students...
, cloister
Cloister
A cloister is a rectangular open space surrounded by covered walks or open galleries, with open arcades on the inner side, running along the walls of buildings and forming a quadrangle or garth...
, chapter house
Chapter house
A chapter house or chapterhouse is a building or room attached to a cathedral or collegiate church in which meetings are held. They can also be found in medieval monasteries....
, caldarium
Caldarium
right|thumb|230px|Caldarium from the Roman Baths at [[Bath, England]]. The floor has been removed to reveal the empty space where the hot air flowed through to heat the floor....
or "warming room", dovecote
Dovecote
A dovecote or dovecot is a structure intended to house pigeons or doves. Dovecotes may be square or circular free-standing structures or built into the end of a house or barn. They generally contain pigeonholes for the birds to nest. Pigeons and doves were an important food source historically in...
and forge
Forge
A forge is a hearth used for forging. The term "forge" can also refer to the workplace of a smith or a blacksmith, although the term smithy is then more commonly used.The basic smithy contains a forge, also known as a hearth, for heating metals...
, all built in Romanesque style
Romanesque architecture
Romanesque architecture is an architectural style of Medieval Europe characterised by semi-circular arches. There is no consensus for the beginning date of the Romanesque architecture, with proposals ranging from the 6th to the 10th century. It developed in the 12th century into the Gothic style,...
, with later abbot's lodgings and infirmary
Hospital
A hospital is a health care institution providing patient treatment by specialized staff and equipment. Hospitals often, but not always, provide for inpatient care or longer-term patient stays....
. Today the abbey buildings are set in modern manicured parterre
Parterre
A parterre is a formal garden construction on a level surface consisting of planting beds, edged in stone or tightly clipped hedging, and gravel paths arranged to form a pleasing, usually symmetrical pattern. Parterres need not have any flowers at all...
s of lawn and gravel.

