
A value
Encyclopedia
A-Values are numerical values used in the determination of the most stable orientation of atoms in a molecule
(Conformational Analysis
), as well as a general representation of steric bulk. A-values are derived from energy measurements of a monosubstituted cyclohexane
ring.
Substituent
s on a cyclohexane
ring prefer to reside in the equatorial position to the axial. The difference in Gibbs free energy
(ΔG) between the higher energy conformation (axial substitution) and the lower energy conformation (equatorial substitution) is the A-value for that particular substituent.
of cyclohexane rings. The most stable conformation will be the one which has the substituent or substituents equatorial. When multiple substituents are taken into consideration, the conformation where the substituent with the largest A-value is equatorial is favored.
The utility of A-values can be generalized for use outside of cyclohexane conformations. A-values can help predict the steric effect of a substituent. In general, the larger a substituent’s A-value, the larger the steric effect of that substituent. Methyl has an A-value of 1.74 while tert-butyl
has an A-value of ~5. Because the A-value of tert-butyl is higher, tert-butyl has a larger steric effect than methyl. This difference in steric effects
can be used to help predict reactivity in chemical reactions.
There are generally considered three principle contributions to the conformational free energy
:
between conformations. Each 6-atom interaction is worth 0.9 kcal/mol and each 7-atom interaction is worth 4 kcal/mol.
also plays a role in a substituent’s preference for the equatorial position. The entropic component is determined by the following formula: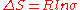
Where σ is equal to the number of micro states available for each conformation.
Due to the larger number of possible conformations of ethyl cyclohexane, the A value is reduced from what would be predicted based purely on enthalpic terms. Due to these favorable entropic conditions, the steric relevance of an ethyl group is similar to that of a methyl substituent.
of oxidation in trans and cis substituted rings using a Chromium catalyst. The large tBu group used locks the conformation of each molecule placing it equatorial (cis compound shown).
It was observed that the cis compound underwent oxidation at a much faster rate than the trans compound. The proposition was that the large hydroxyl group in the axial position was disfavored and formed the carbonyl more readily to relieve this strain. The trans compound had rates identical to those found in the monosubstituted cyclohexanol.
substituent shown below is axial in the ground state, despite a positive A-Value. From this observation, it is clear that there are other possible electronic interactions that stabilize the axial conformation.
group (A-value=2.5), yet the tert-butyl group actually occupies less space. This difference can be attributed to the longer length of the carbon-silicon bond as compared to the carbon-carbon bond
of the tert-butyl group. The longer bond allows for less interactions with neighboring substituents, which effectively makes the trimethylsilyl group less sterically hindering, thus, lowering it’s A-value. This can also be seen when comparing the halogen
s. Bromine, iodine, and chlorine all have similar A-values even though their atomic radii differ. A-values then, predict the apparent size of a substituent, and the relative apparent sizes determine the differences in steric effects between compounds. Thus, A-values are useful tools in determining compound reactivity in chemical reactions.
Molecule
A molecule is an electrically neutral group of at least two atoms held together by covalent chemical bonds. Molecules are distinguished from ions by their electrical charge...
(Conformational Analysis
Conformational isomerism
In chemistry, conformational isomerism is a form of stereoisomerism in which the isomers can be interconverted exclusively by rotations about formally single bonds...
), as well as a general representation of steric bulk. A-values are derived from energy measurements of a monosubstituted cyclohexane
Cyclohexane conformation
A cyclohexane conformation is any of several three-dimensional shapes that a cyclohexane molecule can assume while maintaining the integrity of its chemical bonds....
ring.
Substituent
Substituent
In organic chemistry and biochemistry, a substituent is an atom or group of atoms substituted in place of a hydrogen atom on the parent chain of a hydrocarbon...
s on a cyclohexane
Cyclohexane
Cyclohexane is a cycloalkane with the molecular formula C6H12. Cyclohexane is used as a nonpolar solvent for the chemical industry, and also as a raw material for the industrial production of adipic acid and caprolactam, both of which being intermediates used in the production of nylon...
ring prefer to reside in the equatorial position to the axial. The difference in Gibbs free energy
Gibbs free energy
In thermodynamics, the Gibbs free energy is a thermodynamic potential that measures the "useful" or process-initiating work obtainable from a thermodynamic system at a constant temperature and pressure...
(ΔG) between the higher energy conformation (axial substitution) and the lower energy conformation (equatorial substitution) is the A-value for that particular substituent.
Utility
A-values help predict the conformationConformational isomerism
In chemistry, conformational isomerism is a form of stereoisomerism in which the isomers can be interconverted exclusively by rotations about formally single bonds...
of cyclohexane rings. The most stable conformation will be the one which has the substituent or substituents equatorial. When multiple substituents are taken into consideration, the conformation where the substituent with the largest A-value is equatorial is favored.
The utility of A-values can be generalized for use outside of cyclohexane conformations. A-values can help predict the steric effect of a substituent. In general, the larger a substituent’s A-value, the larger the steric effect of that substituent. Methyl has an A-value of 1.74 while tert-butyl
Butyl
In organic chemistry, butyl is a four-carbon alkyl radical or substituent group with general chemical formula -C4H9, derived from either of the two isomers of butane....
has an A-value of ~5. Because the A-value of tert-butyl is higher, tert-butyl has a larger steric effect than methyl. This difference in steric effects
Steric effects
Steric effects arise from the fact that each atom within a molecule occupies a certain amount of space. If atoms are brought too close together, there is an associated cost in energy due to overlapping electron clouds , and this may affect the molecule's preferred shape and reactivity.-Steric...
can be used to help predict reactivity in chemical reactions.
Free energy considerations
Steric effects play a major role in the assignment of configurations in cyclohexanes. One can use steric hindrances to determine the propensity of a substituent to reside in the axial or equatorial plane. It is known that axial bonds are more hindered than the corresponding equatorial bonds. This is because substituents in the axial position are relatively close to two other axial substituents. This makes it very crowded when bulky substituents are oriented in the axial position. These types of steric interactions are commonly known as 1,3 diaxial interactions. These types of interactions are not present with substituents at the equatorial position.There are generally considered three principle contributions to the conformational free energy
Gibbs free energy
In thermodynamics, the Gibbs free energy is a thermodynamic potential that measures the "useful" or process-initiating work obtainable from a thermodynamic system at a constant temperature and pressure...
:
- Bayer strain, defined as the strain arising from deformation of bond angles.
- Pitzer strain, defined as the torsional strain arising from 1,2 interactions between groups attached to contiguous carbons,
- Van der Waals interactions, which are similar to 1,3 diaxial interactions.
Enthalpic components
When comparing relative stability, 6- and 7-atom interactions can be used to approximate differences in enthalpyEnthalpy
Enthalpy is a measure of the total energy of a thermodynamic system. It includes the internal energy, which is the energy required to create a system, and the amount of energy required to make room for it by displacing its environment and establishing its volume and pressure.Enthalpy is a...
between conformations. Each 6-atom interaction is worth 0.9 kcal/mol and each 7-atom interaction is worth 4 kcal/mol.
Entropic components
EntropyEntropy
Entropy is a thermodynamic property that can be used to determine the energy available for useful work in a thermodynamic process, such as in energy conversion devices, engines, or machines. Such devices can only be driven by convertible energy, and have a theoretical maximum efficiency when...
also plays a role in a substituent’s preference for the equatorial position. The entropic component is determined by the following formula:
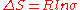
Where σ is equal to the number of micro states available for each conformation.
Due to the larger number of possible conformations of ethyl cyclohexane, the A value is reduced from what would be predicted based purely on enthalpic terms. Due to these favorable entropic conditions, the steric relevance of an ethyl group is similar to that of a methyl substituent.
Table of A-Values
The following table lists some common A-values in kcal/mol:| Substituent | A-Value | Substituent | A-Value | Substituent | A-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D | 0.006 | CH2Br | 1.79 | OSi(CH3)3 | 0.74 |
| F | 0.15 | CH(CH3)2 | 2.15 | OH | 0.87 |
| Cl | 0.43 | c-C6H11 | 2.15 | OCH3 | 0.6 |
| Br | 0.38 | C(CH3)3 | >4 | OCD3 | 0.56 |
| I | 0.43 | Ph | 3 | OCH2CH3 | 0.9 |
| CN | 0.17 | C2H | 1.35 | O-Ac | 0.6 |
| NC | 0.21 | CO2- | 1.92 | O-TFA | 0.68 |
| NCO | 0.51 | CO2CH3 | 1.27 | OCHO | 0.27 |
| NCS | 0.28 | CO2Et | 1.2 | O-Ts | 0.5 |
| N=C=NR | 1 | CO2iPr | 0.96 | ONO2 | 0.59 |
| CH3 | 1.7 | COCl | 1.25 | NH2 | 1.6 |
| CF3 | 2.1 | COCH3 | 1.17 | NHCH3 | 1 |
| CH2CH3 | 1.75 | SH | 0.9 | N(CH3)3 | 2.1 |
| CH=CH2 | 1.35 | SMe | 0.7 | NH3+ | 1.9 |
| CCH | 0.41 | SPh | 0.8 | NO2 | 1.1 |
| CH2tBu | 2 | S- | 1.3 | HgBr | ~0 |
| CH2OTs | 1.75 | SOPh | 1.9 | HgCl | 0.3 |
| SO2Ph | 2.5 | Si(CH3)3 | 2.5 |
Predicting reactivity
One of the original experiments performed by Winston and Holness was measuring the rateReaction rate
The reaction rate or speed of reaction for a reactant or product in a particular reaction is intuitively defined as how fast or slow a reaction takes place...
of oxidation in trans and cis substituted rings using a Chromium catalyst. The large tBu group used locks the conformation of each molecule placing it equatorial (cis compound shown).
It was observed that the cis compound underwent oxidation at a much faster rate than the trans compound. The proposition was that the large hydroxyl group in the axial position was disfavored and formed the carbonyl more readily to relieve this strain. The trans compound had rates identical to those found in the monosubstituted cyclohexanol.
Approximating intramolecular force strength using A-Values
Using the A-Values of the hydroxyl and isopropyl subunit, the energetic value of a favorable intramolecular hydrogen bond can be calculated.Limitations
A-Values are measured using a mono-substituted cyclohexane ring, and are an indication of only the sterics a particular substituent imparts on the molecule. This leads to a problem when there are possible stabilizing electronic factors in a different system. The carboxylic acidCarboxylic acid
Carboxylic acids are organic acids characterized by the presence of at least one carboxyl group. The general formula of a carboxylic acid is R-COOH, where R is some monovalent functional group...
substituent shown below is axial in the ground state, despite a positive A-Value. From this observation, it is clear that there are other possible electronic interactions that stabilize the axial conformation.
Other considerations
It is important to note that A-values do not predict the physical size of a molecule, only the steric effect. For example, the tert-butyl group (A-value=4.9) has a larger A-value than the trimethylsilylTrimethylsilyl
A trimethylsilyl group is a functional group in organic chemistry. This group consists of three methyl groups bonded to a silicon atom [−Si3], which is in turn bonded to the rest of a molecule...
group (A-value=2.5), yet the tert-butyl group actually occupies less space. This difference can be attributed to the longer length of the carbon-silicon bond as compared to the carbon-carbon bond
Carbon-carbon bond
A carbon–carbon bond is a covalent bond between two carbon atoms. The most common form is the single bond: a bond composed of two electrons, one from each of the two atoms. The carbon–carbon single bond is a sigma bond and is said to be formed between one hybridized orbital from each...
of the tert-butyl group. The longer bond allows for less interactions with neighboring substituents, which effectively makes the trimethylsilyl group less sterically hindering, thus, lowering it’s A-value. This can also be seen when comparing the halogen
Halogen
The halogens or halogen elements are a series of nonmetal elements from Group 17 IUPAC Style of the periodic table, comprising fluorine , chlorine , bromine , iodine , and astatine...
s. Bromine, iodine, and chlorine all have similar A-values even though their atomic radii differ. A-values then, predict the apparent size of a substituent, and the relative apparent sizes determine the differences in steric effects between compounds. Thus, A-values are useful tools in determining compound reactivity in chemical reactions.

