
A Mathematical Theory of Communication
Encyclopedia
"A Mathematical Theory of Communication" is an influential 1948 article by mathematician
Claude E. Shannon. As of November 2011, Google Scholar
has listed more than 48,000 unique citations of the article and the later-published book version. It was renamed "The Mathematical Theory of Communication" in the book, a small but significant title change after realizing the generality of this work.
 The article was one of the founding works of the field of information theory
The article was one of the founding works of the field of information theory
. Shannon expanded the ideas of this article in a 1949 book with Warren Weaver
titled The Mathematical Theory of Communication (ISBN 0-252-72546-8). The book was released as a paperback in 1963 (ISBN 0-252-72548-4). Shannon's article laid out the basic elements of communication:
It also developed the concepts of information entropy
and redundancy
, and introduced the term bit
as a unit of information.
Mathematician
A mathematician is a person whose primary area of study is the field of mathematics. Mathematicians are concerned with quantity, structure, space, and change....
Claude E. Shannon. As of November 2011, Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Google Scholar is a freely accessible web search engine that indexes the full text of scholarly literature across an array of publishing formats and disciplines. Released in beta in November 2004, the Google Scholar index includes most peer-reviewed online journals of Europe and America's largest...
has listed more than 48,000 unique citations of the article and the later-published book version. It was renamed "The Mathematical Theory of Communication" in the book, a small but significant title change after realizing the generality of this work.
Description

Information theory
Information theory is a branch of applied mathematics and electrical engineering involving the quantification of information. Information theory was developed by Claude E. Shannon to find fundamental limits on signal processing operations such as compressing data and on reliably storing and...
. Shannon expanded the ideas of this article in a 1949 book with Warren Weaver
Warren Weaver
Warren Weaver was an American scientist, mathematician, and science administrator...
titled The Mathematical Theory of Communication (ISBN 0-252-72546-8). The book was released as a paperback in 1963 (ISBN 0-252-72548-4). Shannon's article laid out the basic elements of communication:
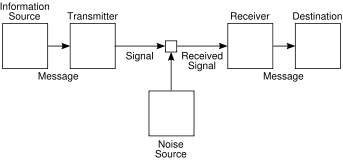
- An information source that produces a message
- A transmitter that operates on the message to create a signalSignal (electrical engineering)In the fields of communications, signal processing, and in electrical engineering more generally, a signal is any time-varying or spatial-varying quantity....
which can be sent through a channel - A channel, which is the medium over which the signal, carrying the information that composes the message, is sent
- A receiver, which transforms the signal back into the message intended for delivery
- A destination, which can be a person or a machine, for whom or which the message is intended
It also developed the concepts of information entropy
Information entropy
In information theory, entropy is a measure of the uncertainty associated with a random variable. In this context, the term usually refers to the Shannon entropy, which quantifies the expected value of the information contained in a message, usually in units such as bits...
and redundancy
Redundancy (information theory)
Redundancy in information theory is the number of bits used to transmit a message minus the number of bits of actual information in the message. Informally, it is the amount of wasted "space" used to transmit certain data...
, and introduced the term bit
Bit
A bit is the basic unit of information in computing and telecommunications; it is the amount of information stored by a digital device or other physical system that exists in one of two possible distinct states...
as a unit of information.

