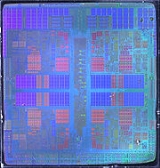
AMD K10
Encyclopedia
The AMD Family 10h is a microprocessor
microarchitecture
by AMD
. Though there were once reports that the K10 had been canceled, the first third-generation Opteron products for servers were launched on September 10, 2007, with the Phenom
processors for desktops following and launching on November 11, 2007 as the immediate successors to the K8 series of processors (Athlon 64
, Opteron
, 64-bit Sempron
).
or Athlon 64
processor family, AMD no longer uses K-nomenclatures (originally stood for Kryptonite) since no K-nomenclature naming convention beyond K8 has appeared in official AMD documents and press releases after the beginning of 2005.
The name "K8L" was first coined by Charlie Demerjian, one of the writers of The Inquirer
back in 2005, and was used by the wider IT community as a convenient shorthand while according to AMD official documents, the processor family was termed "AMD Next Generation Processor Technology".
The microarchitecture has also been referred to as Stars, as the codenames for desktop line of processors was named under stars or constellations (the initial Phenom models being codenamed Agena
and Toliman
).
In a video interview, Giuseppe Amato confirmed that the codename is K10.
It was revealed, by The Inquirer itself, that the codename "K8L" referred to a low-power version of the K8 family, later named Turion 64, and that K10 was the official codename for the microarchitecture.
AMD refers to it as Family 10h Processors, as it is the successor of the Family 0Fh Processors (codename K8). 10h and 0Fh refer to the main result of the CPUID
x86 processor instruction. In hexadecimal
numbering, 0Fh (h represents hexadecimal numbering) equals the decimal
number 15, and 10h equals decimal 16. (The "K10h" form that sometimes pops up is an improper hybrid of the "K" code and Family identifier number.)
On April 13, 2006, Henri Richard, AMD executive vice president and chief officer for marketing and sales, acknowledged the existence of the new microarchitecture in an interview.
In June 2006, AMD executive vice president Henri Richard had another interview with DigiTimes commented on the upcoming processor developments:
 On July 21, 2006, AMD President and Chief operating officer (COO) Dirk Meyer and Senior VP Marty Seyer confirmed that the launch date of new microprocessor
On July 21, 2006, AMD President and Chief operating officer (COO) Dirk Meyer and Senior VP Marty Seyer confirmed that the launch date of new microprocessor
s of Revision H under the new microarchitecture is slated for the middle of 2007; and that it will contain a quad core version for servers
, workstations, and high-end desktops
, as well as a dual core version for consumer Desktops. Some of the Revision H Opterons shipped in 2007 will have a thermal design power
of 68 W
.
On August 15, 2006, at the launch of the first Socket F
dual-core Opteron
s, AMD announced that the firm had reached the final design stage (tape-out
) of quad-core Opteron
parts. The next stages are testing and validation, with sampling to follow after several months.
On June 29, 2007, AMD stated that server processors codenamed Barcelona will ship in August 2007, and corresponding server systems from partners will ship in September of the same year.
On August 13, the reported ship dates for the first Barcelona processors were set for September 10, 2007. They announced the Opteron 2348 and 2350 will have core frequencies of 1.9 GHz and 2.0 GHz.
in the translation lookaside buffer
(TLB) of stepping B2 was discovered that could rarely lead to a race condition
and thus a system lockup. A patch allowed turning off the buffer in BIOS
or software, but was connected to a 5 to 20% performance penalty. Kernel patches
that would almost completely avoid this penalty were published for Linux
. In April 2008, the new stepping B3 was brought to the market by AMD, including a fix for the bug plus other minor enhancements. Now, delivery of K10 CPUs continues at full scale.
L2 cache each core, 2 MB
L3 cache, using HyperTransport 3.0, with a TDP of 125 W. In recent reports, single core variants (codenamed Spica) and dual core with or without L3 cache (codenamed Kuma and Rana respectively) are available under the same microarchitecture.
During the AMD Analyst Day 2006 on December 14, 2006, AMD announced their official timeline for server, desktop and mobile processors. For the servers segment, AMD will unveil two new processors based on the architecture codenamed "Barcelona" and "Budapest" for 8/4/2-way and 1-way servers respectively. For the second half of 2007, HyperTransport
3.0 and Socket AM2+
will be unveiled, which are designed for the specific implementation of the aforementioned consumer quad core desktop chip series, with naming convention changes from city names (up to middle of 2007) to stars or constellations after that, such as Agena; in addition, the AMD Quad FX platform and its immediate successor will support the high end enthusiast dual-processor versions of the chip, codenamed as Agena FX, updates the processors line for AMD Quad FX platform. As with the server chips codenamed Barcelona, the new desktop quad core series will feature a shared L3 cache, 128-bit floating point (FP) units and an enhanced microarchitecture. Agena will be the native quad-core processor for the desktop. Kuma, a dual-core variant will follow on in Q3 while Rana, the dual-core version with no shared L3 cache is expected at the end of the year.
technique of two "Shanghai" cores with a total of 12 MB L3-cache codenamed AMD K10.5. The desktop variant for Shanghai is codenamed Ridgeback. Afterwards is the release of products based on the Bulldozer
cores, which is optimized with integrated graphics core (AMD Fusion
) or native octal-core (8 core) server architecture (codenamed Sandtiger), and the Bobcat
core, optimized for low-power operations.
The model numbers of the new line of processors were apparently changed from the PR rating
s used by its predecessors, the Athlon 64
series processors (except Phenom FX series, being suggested to follow the nomenclature of Athlon 64 FX series). As reported by DailyTech, the model numbers are in alpha-numeric format as AA-@### where AA are alphabetical letters, the first letter indicating the processor class and the second indicating the typical TDP
power envelope. The character @ is the series indicator, which varies by branding (see below table), and the last three characters (###) are the model number, with higher numbers indicating greater performance.
Not much information was known about the details of the model numbers, but the processors will be divided into three segments: Premium, Intermediate, and Value. Premium segment model numbers have processor class "G", Intermediate segment "B", and Value level "L", as discovered on the web from the AsRock website. Similarly, three levels of TDP, "more than 65W", "65W", and "less than 65W", are indicated by the letters "P", "S", and "E" respectively.
As of November 2007, AMD has removed the letters from the model names and X2/X3/X4 monikers for depicting the number of cores of the processor, leaving just a four digit model number with the first character being the sole identification of the processor family, while Sempron remained using the LE prefix, as follows:
5355 processor codenamed Clovertown. More details regarding this first revision of the next generation AMD microprocessor architecture have surfaced on the web recently including their clock speeds.
On January 24, 2007, AMD Executive Vice President Randy Allen claimed that in live tests, in regard to a wide variety of workloads, "Barcelona" was able to demonstrate 40% performance advantage over the comparable Intel Xeon codenamed Clovertown dual-processor (2P) quad-core processors. The expected performance of floating point
per core would be approximately 1.8 times that of the K8 family, at the same clock speed.
On May 10, 2007, AMD held a private event demonstrating the upcoming processors codenamed Agena FX and chipsets, with one demonstrated system being AMD Quad FX platform with one Radeon HD 2900 XT
graphics card
on the upcoming RD790 chipset, the system was also demonstrated real-time converting a 720p
video clip into another undisclosed format while all 8 cores were maxed at 100% by other tasks.
, which will focus on lower power consumption chips in mobile platforms as well as small form factor
features. This microarchitecture will contain specialized features such as mobile optimized crossbar switch
and memory controller
and other on-die
components; link power management for HyperTransport
3.0; and others. At that time, AMD simply dubbed it "New Mobile Core", without giving a specific codename.
On the December 2006 analyst day, Executive vice president Marty Seyer announced the new mobile core codenamed Griffin launched in 2008 with inherited power optimizations technologies from the K10 microarchitecture, but based on a K8 design
support, Direct Connect Architecture
2.0, enhanced Reliability, Availability and Serviceability (RAS), and probably more for the processor die. The platform will also add support for I/O Virtualization, PCI Express
2.0, 10 Gigabit NIC
, larger caches, and more.
However, reports have suggested that FB-DIMM
support had been dropped from future roadmaps of the majority of AMD products since popularity is low. Also, FB-DIMM's future as an industry standard had been called into question.
An article published by The Inquirer
corroborates the earlier reports of the timeline (as cited in this article). According to the report, there will be three iterations of the server processor core: one named Barcelona, due in Q2 of 2007, with new CPU core components as well as the microarchitecture, but built on the old HyperTransport 2.0 infrastructure; the second is Budapest for single socket systems using socket AM2+
or socket AM3
, with HyperTransport
3.0; and the third, codenamed Shanghai is an update of the server chip, based on 45 nm process, probably also with HyperTransport
3.0 and DDR3 implementation, due in Q1-Q2 2008.
AMD, on September 17, 2007, announced that a three core (triple-core) processor will also be released under the Phenom brand lineup, codenamed Toliman. AMD official replied in an interview that this product is benefitted from ATI technologies to add fuses to the quad-core processor and shutting down one of the four cores to become a triple-core processor, which the technique has been popular for making one or more mainstream GPU cores from a single high-end GPU core by blowing out parts of the circuit to save R&D costs while targeting more markets some time ago. The triple-core processor still see the same specifications for quad-core variants, the naming of the processor lineup, according to the AMD branding scheme, will be named as Phenom triple-core 8000 series, the processor line will be focused on what AMD called the fourth market segment or the "High-end Mainstream" segment beside Value, Mainstream and Performance segments in an interview with BetaNews, which the targeted customers of the processors are "those who are willing to pay more for more performance but not required for too much processing power as required by gamers and system builders, while there are single core (Sempron) variants for low-end market, and dual-core (Athlon) variants for mid-range market, and quad-core (Phenom quad-core 9000 series and Phenom FX) variants should be seen in the high-end market at the same time frame.
Further in 2008, AMD will introduce Deneb FX for the replacement for the AMD Quad FX platform, as well as Deneb for the mainstream. Propos and Regor will also replace Kuma and Rana in the lower market segments. Socket AM2+
being named in the late 2006 might actually have been the original AM3 socket, but as naming conventions changed, so that the next generation of consumer desktop socket capable of DDR3
will be socket AM3
.
technology, since the release of K10 coincides with the volume ramp of this manufacturing process. The servers will be produced for Socket F(1207) or later 1207-pin socket infrastructure, the only server socket on AMD's near-term roadmap; the desktop parts will come on Socket AM2
or Socket AM2+
.
AMD announced during the Technology Analyst Day that the use of Continuous Transistor Improvement (CTI) and Shared Transistor Technology (STT) would finally lead to the implementation of Silicon-Germanium-On-Insulator (SGoI) on 65 nm process CPUs.
family was known to be particularly sensitive to memory latency
since its design gains performance by minimizing this through the use of an on-die memory controller
(integrated into the CPU); increased latency in the external modules negates the usefulness of the feature. DDR2 RAM
introduces some additional latency over traditional DDR RAM
since the DRAM
is internally driven by a clock at one quarter of the external data frequency, as opposed to one half that of DDR. However, since the command clock rate in DDR2 is doubled relative to DDR and other latency-reducing features (e.g. additive latency) have been introduced, common comparisons based on CAS latency
alone are not sufficient. For example, Socket AM2
processors are known to demonstrate similar performance using DDR2 SDRAM as Socket 939
processors that utilize DDR-400 SDRAM. K10 processors support DDR2 SDRAM
rated up to DDR2-1066 (1066 MHz).
, The Inquirer
and Geek.com) that the microprocessors implementing the microarchitecture will feature a doubling in the width of SSE
execution units in the cores. With the help of major improvements in the memory subsystem (such as load re-ordering and improved prefetch mechanisms) as well as the doubled instruction fetch and load, it is expected to increase the suitability of the processor to scientific and high-performance computing tasks and potentially improve its competitiveness with Intel's Xeon
, Core 2
, Itanium 2 and other contemporary microprocessors.
Many of the improvements in computational throughput
of each core are listed below.

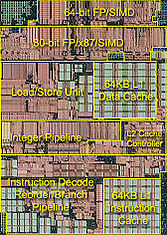
" is a CPU technology furthering the trend of continued system component integration onto CPU die (which was initiated by K8 with integrated System Request Queue (SRQ), cross-bar switch, memory controller as well as HyperTransport
links), planned beyond these two aforementioned families of products, and will be due sometime in 2011. The Fusion products will see new processor cores, codenamed "Bulldozer
" and "Bobcat
" incorporated into the die. Fusion will also see the debut of special purpose cores with a quad core cpu dedicating up to 3 cores to specialized tasks such as a graphics core, a physics core (for game physics) and a Java core (specialized for running managed code). Not all of these cores may be present in each chip and more speciality cores may be developed based on market demand.
Microprocessor
A microprocessor incorporates the functions of a computer's central processing unit on a single integrated circuit, or at most a few integrated circuits. It is a multipurpose, programmable device that accepts digital data as input, processes it according to instructions stored in its memory, and...
microarchitecture
Microarchitecture
In computer engineering, microarchitecture , also called computer organization, is the way a given instruction set architecture is implemented on a processor. A given ISA may be implemented with different microarchitectures. Implementations might vary due to different goals of a given design or...
by AMD
Advanced Micro Devices
Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. or AMD is an American multinational semiconductor company based in Sunnyvale, California, that develops computer processors and related technologies for commercial and consumer markets...
. Though there were once reports that the K10 had been canceled, the first third-generation Opteron products for servers were launched on September 10, 2007, with the Phenom
Phenom (processor)
Phenom is the 64-bit AMD desktop processor line based on the K10 microarchitecture, in what AMD calls family 10h processors, sometimes incorrectly called "K10h". Triple-core versions belong to the Phenom 8000 series and quad cores to the AMD Phenom X4 9000 series...
processors for desktops following and launching on November 11, 2007 as the immediate successors to the K8 series of processors (Athlon 64
Athlon 64
The Athlon 64 is an eighth-generation, AMD64-architecture microprocessor produced by AMD, released on September 23, 2003. It is the third processor to bear the name Athlon, and the immediate successor to the Athlon XP...
, Opteron
Opteron
Opteron is AMD's x86 server and workstation processor line, and was the first processor which supported the AMD64 instruction set architecture . It was released on April 22, 2003 with the SledgeHammer core and was intended to compete in the server and workstation markets, particularly in the same...
, 64-bit Sempron
Sempron
Sempron has been the marketing name used by AMD for several different budget desktop CPUs, using several different technologies and CPU socket formats. The Sempron replaced the AMD Duron processor and competes against Intel's Celeron series of processors...
).
Nomenclatures
It is commonly perceived that from the time after the use of the codename K8 for the AMD K8AMD K8
The AMD K8 is a computer processor microarchitecture designed by AMD as the successor to the AMD K7 microarchitecture. The K8 was the first implementation of the AMD64 64-bit extension to the x86 processor architecture.Processors based on the K8 core include:...
or Athlon 64
Athlon 64
The Athlon 64 is an eighth-generation, AMD64-architecture microprocessor produced by AMD, released on September 23, 2003. It is the third processor to bear the name Athlon, and the immediate successor to the Athlon XP...
processor family, AMD no longer uses K-nomenclatures (originally stood for Kryptonite) since no K-nomenclature naming convention beyond K8 has appeared in official AMD documents and press releases after the beginning of 2005.
The name "K8L" was first coined by Charlie Demerjian, one of the writers of The Inquirer
The Inquirer
The Inquirer is a British technology tabloid website founded by Mike Magee after his departure from The Register in 2001. In 2006 the site was acquired by Dutch publisher Verenigde Nederlandse Uitgeverijen...
back in 2005, and was used by the wider IT community as a convenient shorthand while according to AMD official documents, the processor family was termed "AMD Next Generation Processor Technology".
The microarchitecture has also been referred to as Stars, as the codenames for desktop line of processors was named under stars or constellations (the initial Phenom models being codenamed Agena
Agena
-Other:* RM-81 Agena, a rocket upper stage family developed by Lockheed, especially the Agena target vehicle used in preparation for the Apollo program lunar missions* Agena , a memory resident, file infecting computer virus...
and Toliman
Tolimán
Tolimán may refer to:*Tolimán , a town in the Mexican state of Jalisco.*Tolimán , a town in the Mexican state of Querétaro.*Volcán Tolimán, a stratovolcano in Guatemala....
).
In a video interview, Giuseppe Amato confirmed that the codename is K10.
It was revealed, by The Inquirer itself, that the codename "K8L" referred to a low-power version of the K8 family, later named Turion 64, and that K10 was the official codename for the microarchitecture.
AMD refers to it as Family 10h Processors, as it is the successor of the Family 0Fh Processors (codename K8). 10h and 0Fh refer to the main result of the CPUID
CPUID
The CPUID opcode is a processor supplementary instruction for the x86 architecture. It was introduced by Intel in 1993 when it introduced the Pentium and SL-Enhanced 486 processors....
x86 processor instruction. In hexadecimal
Hexadecimal
In mathematics and computer science, hexadecimal is a positional numeral system with a radix, or base, of 16. It uses sixteen distinct symbols, most often the symbols 0–9 to represent values zero to nine, and A, B, C, D, E, F to represent values ten to fifteen...
numbering, 0Fh (h represents hexadecimal numbering) equals the decimal
Decimal
The decimal numeral system has ten as its base. It is the numerical base most widely used by modern civilizations....
number 15, and 10h equals decimal 16. (The "K10h" form that sometimes pops up is an improper hybrid of the "K" code and Family identifier number.)
Historical information
In 2003, AMD outlined the features for upcoming generations of microprocessors after the K8 family of processors in various events and analyst meetings, including the Microprocessor Forum 2003. The outlined features to be deployed by the next-generation microprocessors are as follows:- Threaded architectures.
- Chip level multiprocessingMultiprocessingMultiprocessing is the use of two or more central processing units within a single computer system. The term also refers to the ability of a system to support more than one processor and/or the ability to allocate tasks between them...
. - Huge scale MP (multi-processor) machines.
- 10 GHz operation.
- Much higher performance superscalarSuperscalarA superscalar CPU architecture implements a form of parallelism called instruction level parallelism within a single processor. It therefore allows faster CPU throughput than would otherwise be possible at a given clock rate...
, out of order CPU core. - Huge caches.
- Media/vector processing extensions.
- Branch and memory hints.
- Security and virtualization.
- Enhanced Branch Predictors.
- Static and dynamic power management.
On April 13, 2006, Henri Richard, AMD executive vice president and chief officer for marketing and sales, acknowledged the existence of the new microarchitecture in an interview.
In June 2006, AMD executive vice president Henri Richard had another interview with DigiTimes commented on the upcoming processor developments:
Confirmation of time frames

Microprocessor
A microprocessor incorporates the functions of a computer's central processing unit on a single integrated circuit, or at most a few integrated circuits. It is a multipurpose, programmable device that accepts digital data as input, processes it according to instructions stored in its memory, and...
s of Revision H under the new microarchitecture is slated for the middle of 2007; and that it will contain a quad core version for servers
Server (computing)
In the context of client-server architecture, a server is a computer program running to serve the requests of other programs, the "clients". Thus, the "server" performs some computational task on behalf of "clients"...
, workstations, and high-end desktops
Desktop computer
A desktop computer is a personal computer in a form intended for regular use at a single location, as opposed to a mobile laptop or portable computer. Early desktop computers are designed to lay flat on the desk, while modern towers stand upright...
, as well as a dual core version for consumer Desktops. Some of the Revision H Opterons shipped in 2007 will have a thermal design power
Thermal Design Power
The thermal design power , sometimes called thermal design point, refers to the maximum amount of power the cooling system in a computer is required to dissipate. For example, a laptop's CPU cooling system may be designed for a 20 watt TDP, which means that it can dissipate up to 20 watts of heat...
of 68 W
Watt
The watt is a derived unit of power in the International System of Units , named after the Scottish engineer James Watt . The unit, defined as one joule per second, measures the rate of energy conversion.-Definition:...
.
On August 15, 2006, at the launch of the first Socket F
Socket F
Socket F is a CPU socket designed by AMD for its Opteron line of CPUs released on August 15, 2006. In 2010 Socket F was replaced by Socket C32 for entry-level servers and Socket G34 for high-end servers.-Technical specifications:...
dual-core Opteron
Opteron
Opteron is AMD's x86 server and workstation processor line, and was the first processor which supported the AMD64 instruction set architecture . It was released on April 22, 2003 with the SledgeHammer core and was intended to compete in the server and workstation markets, particularly in the same...
s, AMD announced that the firm had reached the final design stage (tape-out
Tape-out
In electronics design, tape-out or tapeout is the final result of the design cycle for integrated circuits or printed circuit boards, the point at which the artwork for the photomask of a circuit is sent for manufacture....
) of quad-core Opteron
Opteron
Opteron is AMD's x86 server and workstation processor line, and was the first processor which supported the AMD64 instruction set architecture . It was released on April 22, 2003 with the SledgeHammer core and was intended to compete in the server and workstation markets, particularly in the same...
parts. The next stages are testing and validation, with sampling to follow after several months.
On June 29, 2007, AMD stated that server processors codenamed Barcelona will ship in August 2007, and corresponding server systems from partners will ship in September of the same year.
On August 13, the reported ship dates for the first Barcelona processors were set for September 10, 2007. They announced the Opteron 2348 and 2350 will have core frequencies of 1.9 GHz and 2.0 GHz.
TLB Bug
In November 2007 AMD stopped delivery of Barcelona processors after a bugSoftware bug
A software bug is the common term used to describe an error, flaw, mistake, failure, or fault in a computer program or system that produces an incorrect or unexpected result, or causes it to behave in unintended ways. Most bugs arise from mistakes and errors made by people in either a program's...
in the translation lookaside buffer
Translation Lookaside Buffer
A translation lookaside buffer is a CPU cache that memory management hardware uses to improve virtual address translation speed. All current desktop and server processors use a TLB to map virtual and physical address spaces, and it is ubiquitous in any hardware which utilizes virtual memory.The...
(TLB) of stepping B2 was discovered that could rarely lead to a race condition
Race condition
A race condition or race hazard is a flaw in an electronic system or process whereby the output or result of the process is unexpectedly and critically dependent on the sequence or timing of other events...
and thus a system lockup. A patch allowed turning off the buffer in BIOS
BIOS
In IBM PC compatible computers, the basic input/output system , also known as the System BIOS or ROM BIOS , is a de facto standard defining a firmware interface....
or software, but was connected to a 5 to 20% performance penalty. Kernel patches
Patch (computing)
A patch is a piece of software designed to fix problems with, or update a computer program or its supporting data. This includes fixing security vulnerabilities and other bugs, and improving the usability or performance...
that would almost completely avoid this penalty were published for Linux
Linux
Linux is a Unix-like computer operating system assembled under the model of free and open source software development and distribution. The defining component of any Linux system is the Linux kernel, an operating system kernel first released October 5, 1991 by Linus Torvalds...
. In April 2008, the new stepping B3 was brought to the market by AMD, including a fix for the bug plus other minor enhancements. Now, delivery of K10 CPUs continues at full scale.
Internal codenames
As of November 2006, reports leaked the upcoming desktop part codenames Agena, Agena FX, and the core speeds of the parts range from 2.4 GHz - 2.9 GHz respectively, 512 KBKilobyte
The kilobyte is a multiple of the unit byte for digital information. Although the prefix kilo- means 1000, the term kilobyte and symbol KB have historically been used to refer to either 1024 bytes or 1000 bytes, dependent upon context, in the fields of computer science and information...
L2 cache each core, 2 MB
Megabyte
The megabyte is a multiple of the unit byte for digital information storage or transmission with two different values depending on context: bytes generally for computer memory; and one million bytes generally for computer storage. The IEEE Standards Board has decided that "Mega will mean 1 000...
L3 cache, using HyperTransport 3.0, with a TDP of 125 W. In recent reports, single core variants (codenamed Spica) and dual core with or without L3 cache (codenamed Kuma and Rana respectively) are available under the same microarchitecture.
During the AMD Analyst Day 2006 on December 14, 2006, AMD announced their official timeline for server, desktop and mobile processors. For the servers segment, AMD will unveil two new processors based on the architecture codenamed "Barcelona" and "Budapest" for 8/4/2-way and 1-way servers respectively. For the second half of 2007, HyperTransport
HyperTransport
HyperTransport , formerly known as Lightning Data Transport , is a technology for interconnection of computer processors. It is a bidirectional serial/parallel high-bandwidth, low-latency point-to-point link that was introduced on April 2, 2001...
3.0 and Socket AM2+
Socket AM2+
Socket AM2+ is a CPU socket, which is the immediate successor to Socket AM2 that is used by several AMD processors such as Athlon 64 X2. Socket AM2+ is a mid-migration from Socket AM2 to Socket AM3 and both AM2+ and AM2 socket CPUs and motherboards have the potential to operate together...
will be unveiled, which are designed for the specific implementation of the aforementioned consumer quad core desktop chip series, with naming convention changes from city names (up to middle of 2007) to stars or constellations after that, such as Agena; in addition, the AMD Quad FX platform and its immediate successor will support the high end enthusiast dual-processor versions of the chip, codenamed as Agena FX, updates the processors line for AMD Quad FX platform. As with the server chips codenamed Barcelona, the new desktop quad core series will feature a shared L3 cache, 128-bit floating point (FP) units and an enhanced microarchitecture. Agena will be the native quad-core processor for the desktop. Kuma, a dual-core variant will follow on in Q3 while Rana, the dual-core version with no shared L3 cache is expected at the end of the year.
Subsequent product launches
More information about the upcoming chip codenamed "Montreal" on the server roadmap using MCMMulti-Chip Module
A multi-chip module is a specialized electronic package where multiple integrated circuits , semiconductor dies or other discrete components are packaged onto a unifying substrate, facilitating their use as a single component...
technique of two "Shanghai" cores with a total of 12 MB L3-cache codenamed AMD K10.5. The desktop variant for Shanghai is codenamed Ridgeback. Afterwards is the release of products based on the Bulldozer
Bulldozer (processor)
Bulldozer is the codename Advanced Micro Devices has given to one of the next-generation CPU cores after the K10 microarchitecture for the company's M-SPACE design methodology, with the core specifically aimed at 10-watt to 125-watt TDP computing products. Bulldozer is a completely new design...
cores, which is optimized with integrated graphics core (AMD Fusion
AMD Fusion
AMD Fusion is the marketing name for a series of APUs by AMD. There are two flavors of Fusion currently available, one with its CPU logic based on the Bobcat core and the other its CPU logic based on the 10h core. In both cases the GPU logic is HD6xxx, which itself is based on the mobile variant of...
) or native octal-core (8 core) server architecture (codenamed Sandtiger), and the Bobcat
Bobcat (processor)
Bobcat is the latest x86 processor core from AMD aimed at low-power / low-cost market.It was revealed during a speech from AMD executive vice-president Henri Richard in Computex 2007 and was put into production Q1 2011. One of the major supporters was executive vice-president Mario A...
core, optimized for low-power operations.
Change of model nomenclatures
During Computex 2007 in early June, new information regarding the naming schemes of upcoming AMD microprocessors emerged. Additional letters indicating both performance and power envelope will precede the 4 digit model number.The model numbers of the new line of processors were apparently changed from the PR rating
PR rating
The PR system was developed by AMD in the mid-1990s as a method of comparing their x86 processors to those of rival Intel.-Branding:...
s used by its predecessors, the Athlon 64
AMD K8
The AMD K8 is a computer processor microarchitecture designed by AMD as the successor to the AMD K7 microarchitecture. The K8 was the first implementation of the AMD64 64-bit extension to the x86 processor architecture.Processors based on the K8 core include:...
series processors (except Phenom FX series, being suggested to follow the nomenclature of Athlon 64 FX series). As reported by DailyTech, the model numbers are in alpha-numeric format as AA-@### where AA are alphabetical letters, the first letter indicating the processor class and the second indicating the typical TDP
Thermal Design Power
The thermal design power , sometimes called thermal design point, refers to the maximum amount of power the cooling system in a computer is required to dissipate. For example, a laptop's CPU cooling system may be designed for a 20 watt TDP, which means that it can dissipate up to 20 watts of heat...
power envelope. The character @ is the series indicator, which varies by branding (see below table), and the last three characters (###) are the model number, with higher numbers indicating greater performance.
Not much information was known about the details of the model numbers, but the processors will be divided into three segments: Premium, Intermediate, and Value. Premium segment model numbers have processor class "G", Intermediate segment "B", and Value level "L", as discovered on the web from the AsRock website. Similarly, three levels of TDP, "more than 65W", "65W", and "less than 65W", are indicated by the letters "P", "S", and "E" respectively.
As of November 2007, AMD has removed the letters from the model names and X2/X3/X4 monikers for depicting the number of cores of the processor, leaving just a four digit model number with the first character being the sole identification of the processor family, while Sempron remained using the LE prefix, as follows:
| Processor series | Indicator |
|---|---|
| Phenom quad-core (Agena) | 9 |
| Phenom triple-core (Toliman) | 8 |
| Athlon dual-core (Kuma) | 7 |
| Athlon single-core (Lima) | 1 |
| Sempron LE single-core (Sparta) | 1 |
Live demonstrations
On November 30, 2006, AMD live demonstrated the native quad core chip known as "Barcelona" for the first time in public, while running Windows Server 2003 64-bit Edition. AMD claims 70% scaling of performance in real world loads, and better performance than Intel XeonXeon
The Xeon is a brand of multiprocessing- or multi-socket-capable x86 microprocessors from Intel Corporation targeted at the non-consumer server, workstation and embedded system markets.-Overview:...
5355 processor codenamed Clovertown. More details regarding this first revision of the next generation AMD microprocessor architecture have surfaced on the web recently including their clock speeds.
On January 24, 2007, AMD Executive Vice President Randy Allen claimed that in live tests, in regard to a wide variety of workloads, "Barcelona" was able to demonstrate 40% performance advantage over the comparable Intel Xeon codenamed Clovertown dual-processor (2P) quad-core processors. The expected performance of floating point
Floating point
In computing, floating point describes a method of representing real numbers in a way that can support a wide range of values. Numbers are, in general, represented approximately to a fixed number of significant digits and scaled using an exponent. The base for the scaling is normally 2, 10 or 16...
per core would be approximately 1.8 times that of the K8 family, at the same clock speed.
On May 10, 2007, AMD held a private event demonstrating the upcoming processors codenamed Agena FX and chipsets, with one demonstrated system being AMD Quad FX platform with one Radeon HD 2900 XT
Radeon R600
The graphics processing unit codenamed the Radeon R600 is the foundation of the Radeon HD 2000/3000 series and the FireGL 2007 series video cards developed by ATI Technologies...
graphics card
Video card
A video card, Graphics Card, or Graphics adapter is an expansion card which generates output images to a display. Most video cards offer various functions such as accelerated rendering of 3D scenes and 2D graphics, MPEG-2/MPEG-4 decoding, TV output, or the ability to connect multiple monitors...
on the upcoming RD790 chipset, the system was also demonstrated real-time converting a 720p
720p
720p is the shorthand name for 1280x720, a category of High-definition television video modes having a resolution of 1080 or 720p and a progressive scan...
video clip into another undisclosed format while all 8 cores were maxed at 100% by other tasks.
Sister microarchitecture
Also due in a similar time frame will be a sister microarchitectureMicroarchitecture
In computer engineering, microarchitecture , also called computer organization, is the way a given instruction set architecture is implemented on a processor. A given ISA may be implemented with different microarchitectures. Implementations might vary due to different goals of a given design or...
, which will focus on lower power consumption chips in mobile platforms as well as small form factor
Small form factor
A small form factor is a computer form factor designed to minimize the volume of a desktop computer. For comparison purposes, the size of an SFF case is usually measured in litres. SFFs are available in a variety of sizes and shapes, including shoeboxes, cubes, and book-sized PCs...
features. This microarchitecture will contain specialized features such as mobile optimized crossbar switch
Crossbar switch
In electronics, a crossbar switch is a switch connecting multiple inputs to multiple outputs in a matrix manner....
and memory controller
Memory controller
The memory controller is a digital circuit which manages the flow of data going to and from the main memory. It can be a separate chip or integrated into another chip, such as on the die of a microprocessor...
and other on-die
Integrated circuit
An integrated circuit or monolithic integrated circuit is an electronic circuit manufactured by the patterned diffusion of trace elements into the surface of a thin substrate of semiconductor material...
components; link power management for HyperTransport
HyperTransport
HyperTransport , formerly known as Lightning Data Transport , is a technology for interconnection of computer processors. It is a bidirectional serial/parallel high-bandwidth, low-latency point-to-point link that was introduced on April 2, 2001...
3.0; and others. At that time, AMD simply dubbed it "New Mobile Core", without giving a specific codename.
On the December 2006 analyst day, Executive vice president Marty Seyer announced the new mobile core codenamed Griffin launched in 2008 with inherited power optimizations technologies from the K10 microarchitecture, but based on a K8 design
Iterations of the release
In late 2007 to second quarter of 2008, there will be a modification to the core to be fabricated at 45 nm process node, with enhancements such as FB-DIMMFully Buffered DIMM
Fully Buffered DIMM is a memory technology which can be used to increase reliability and density of memory systems. Conventionally, data lines from the memory controller have to be connected to data lines in every DRAM module. As memory width, as well as access speed, increases, the signal...
support, Direct Connect Architecture
Direct Connect Architecture
The Direct Connect Architecture is the I/O architecture of the Athlon 64 X2, Opteron, and Phenom microprocessors from AMD. It consists of the combination of three elements:...
2.0, enhanced Reliability, Availability and Serviceability (RAS), and probably more for the processor die. The platform will also add support for I/O Virtualization, PCI Express
PCI Express
PCI Express , officially abbreviated as PCIe, is a computer expansion card standard designed to replace the older PCI, PCI-X, and AGP bus standards...
2.0, 10 Gigabit NIC
Network card
A network interface controller is a computer hardware component that connects a computer to a computer network....
, larger caches, and more.
However, reports have suggested that FB-DIMM
Fully Buffered DIMM
Fully Buffered DIMM is a memory technology which can be used to increase reliability and density of memory systems. Conventionally, data lines from the memory controller have to be connected to data lines in every DRAM module. As memory width, as well as access speed, increases, the signal...
support had been dropped from future roadmaps of the majority of AMD products since popularity is low. Also, FB-DIMM's future as an industry standard had been called into question.
An article published by The Inquirer
The Inquirer
The Inquirer is a British technology tabloid website founded by Mike Magee after his departure from The Register in 2001. In 2006 the site was acquired by Dutch publisher Verenigde Nederlandse Uitgeverijen...
corroborates the earlier reports of the timeline (as cited in this article). According to the report, there will be three iterations of the server processor core: one named Barcelona, due in Q2 of 2007, with new CPU core components as well as the microarchitecture, but built on the old HyperTransport 2.0 infrastructure; the second is Budapest for single socket systems using socket AM2+
Socket AM2+
Socket AM2+ is a CPU socket, which is the immediate successor to Socket AM2 that is used by several AMD processors such as Athlon 64 X2. Socket AM2+ is a mid-migration from Socket AM2 to Socket AM3 and both AM2+ and AM2 socket CPUs and motherboards have the potential to operate together...
or socket AM3
Socket AM3
Socket AM3 is a CPU socket for AMD processors. AM3 was launched as the successor to Socket AM2+ on February 9, 2009, alongside the initial grouping of Phenom II processors designed for it...
, with HyperTransport
HyperTransport
HyperTransport , formerly known as Lightning Data Transport , is a technology for interconnection of computer processors. It is a bidirectional serial/parallel high-bandwidth, low-latency point-to-point link that was introduced on April 2, 2001...
3.0; and the third, codenamed Shanghai is an update of the server chip, based on 45 nm process, probably also with HyperTransport
HyperTransport
HyperTransport , formerly known as Lightning Data Transport , is a technology for interconnection of computer processors. It is a bidirectional serial/parallel high-bandwidth, low-latency point-to-point link that was introduced on April 2, 2001...
3.0 and DDR3 implementation, due in Q1-Q2 2008.
AMD, on September 17, 2007, announced that a three core (triple-core) processor will also be released under the Phenom brand lineup, codenamed Toliman. AMD official replied in an interview that this product is benefitted from ATI technologies to add fuses to the quad-core processor and shutting down one of the four cores to become a triple-core processor, which the technique has been popular for making one or more mainstream GPU cores from a single high-end GPU core by blowing out parts of the circuit to save R&D costs while targeting more markets some time ago. The triple-core processor still see the same specifications for quad-core variants, the naming of the processor lineup, according to the AMD branding scheme, will be named as Phenom triple-core 8000 series, the processor line will be focused on what AMD called the fourth market segment or the "High-end Mainstream" segment beside Value, Mainstream and Performance segments in an interview with BetaNews, which the targeted customers of the processors are "those who are willing to pay more for more performance but not required for too much processing power as required by gamers and system builders, while there are single core (Sempron) variants for low-end market, and dual-core (Athlon) variants for mid-range market, and quad-core (Phenom quad-core 9000 series and Phenom FX) variants should be seen in the high-end market at the same time frame.
Further in 2008, AMD will introduce Deneb FX for the replacement for the AMD Quad FX platform, as well as Deneb for the mainstream. Propos and Regor will also replace Kuma and Rana in the lower market segments. Socket AM2+
Socket AM2+
Socket AM2+ is a CPU socket, which is the immediate successor to Socket AM2 that is used by several AMD processors such as Athlon 64 X2. Socket AM2+ is a mid-migration from Socket AM2 to Socket AM3 and both AM2+ and AM2 socket CPUs and motherboards have the potential to operate together...
being named in the late 2006 might actually have been the original AM3 socket, but as naming conventions changed, so that the next generation of consumer desktop socket capable of DDR3
DDR3 SDRAM
In computing, DDR3 SDRAM, an abbreviation for double data rate type three synchronous dynamic random access memory, is a modern kind of dynamic random access memory with a high bandwidth interface. It is one of several variants of DRAM and associated interface techniques used since the early 1970s...
will be socket AM3
Socket AM3
Socket AM3 is a CPU socket for AMD processors. AM3 was launched as the successor to Socket AM2+ on February 9, 2009, alongside the initial grouping of Phenom II processors designed for it...
.
Fabrication technology
AMD has introduced the microprocessors manufactured at 65 nm feature width using Silicon-on-insulator (SOI)Silicon on insulator
Silicon on insulator technology refers to the use of a layered silicon-insulator-silicon substrate in place of conventional silicon substrates in semiconductor manufacturing, especially microelectronics, to reduce parasitic device capacitance and thereby improving performance...
technology, since the release of K10 coincides with the volume ramp of this manufacturing process. The servers will be produced for Socket F(1207) or later 1207-pin socket infrastructure, the only server socket on AMD's near-term roadmap; the desktop parts will come on Socket AM2
Socket AM2
The Socket AM2, renamed from Socket M2 , is a CPU socket designed by AMD for desktop processors, including the performance, mainstream and value segments...
or Socket AM2+
Socket AM2+
Socket AM2+ is a CPU socket, which is the immediate successor to Socket AM2 that is used by several AMD processors such as Athlon 64 X2. Socket AM2+ is a mid-migration from Socket AM2 to Socket AM3 and both AM2+ and AM2 socket CPUs and motherboards have the potential to operate together...
.
AMD announced during the Technology Analyst Day that the use of Continuous Transistor Improvement (CTI) and Shared Transistor Technology (STT) would finally lead to the implementation of Silicon-Germanium-On-Insulator (SGoI) on 65 nm process CPUs.
Supported DRAM standards
The K8AMD K8
The AMD K8 is a computer processor microarchitecture designed by AMD as the successor to the AMD K7 microarchitecture. The K8 was the first implementation of the AMD64 64-bit extension to the x86 processor architecture.Processors based on the K8 core include:...
family was known to be particularly sensitive to memory latency
SDRAM latency
SDRAM latency refers to delays in transmitting data between the CPU and SDRAM. SDRAM latency is often measured in memory bus clock cycles. However, the CPU operates faster than the memory, so it must wait while the proper segment of memory is located and read, before the data can be sent back...
since its design gains performance by minimizing this through the use of an on-die memory controller
Memory controller
The memory controller is a digital circuit which manages the flow of data going to and from the main memory. It can be a separate chip or integrated into another chip, such as on the die of a microprocessor...
(integrated into the CPU); increased latency in the external modules negates the usefulness of the feature. DDR2 RAM
DDR2 SDRAM
DDR2 SDRAM is a double data rate synchronous dynamic random-access memory interface. It supersedes the original DDR SDRAM specification and has itself been superseded by DDR3 SDRAM...
introduces some additional latency over traditional DDR RAM
DDR SDRAM
Double data rate synchronous dynamic random access memory is a class of memory integrated circuits used in computers. DDR SDRAM has been superseded by DDR2 SDRAM and DDR3 SDRAM, neither of which are either forward or backward compatible with DDR SDRAM, meaning that DDR2 or DDR3 memory modules...
since the DRAM
Dynamic random access memory
Dynamic random-access memory is a type of random-access memory that stores each bit of data in a separate capacitor within an integrated circuit. The capacitor can be either charged or discharged; these two states are taken to represent the two values of a bit, conventionally called 0 and 1...
is internally driven by a clock at one quarter of the external data frequency, as opposed to one half that of DDR. However, since the command clock rate in DDR2 is doubled relative to DDR and other latency-reducing features (e.g. additive latency) have been introduced, common comparisons based on CAS latency
CAS Latency
Column Address Strobe latency, or CL, is the delay time between the moment a memory controller tells the memory module to access a particular memory column on a RAM memory module, and the moment the data from given array location is available on the module's output pins...
alone are not sufficient. For example, Socket AM2
Socket AM2
The Socket AM2, renamed from Socket M2 , is a CPU socket designed by AMD for desktop processors, including the performance, mainstream and value segments...
processors are known to demonstrate similar performance using DDR2 SDRAM as Socket 939
Socket 939
Socket 939 is a CPU socket released by AMD in June 2004 to supersede the previous Socket 754 for Athlon 64 processors. Socket 939 was succeeded by Socket AM2 in May 2006. It is the second socket designed for AMD's AMD64 range of processors.-Availability:...
processors that utilize DDR-400 SDRAM. K10 processors support DDR2 SDRAM
DDR2 SDRAM
DDR2 SDRAM is a double data rate synchronous dynamic random-access memory interface. It supersedes the original DDR SDRAM specification and has itself been superseded by DDR3 SDRAM...
rated up to DDR2-1066 (1066 MHz).
Higher computational throughput
It was also reported by several sources (such as AnandTechAnandTech
AnandTech is an online computer hardware magazine. It was founded in 1997 by then 15-year-old Anand Lal Shimpi, who is the current editor-in-chief and CEO. The web site is recommended as a good resource of hardware reviews for off-the-shelf components addressed to computer building enthusiasts...
, The Inquirer
The Inquirer
The Inquirer is a British technology tabloid website founded by Mike Magee after his departure from The Register in 2001. In 2006 the site was acquired by Dutch publisher Verenigde Nederlandse Uitgeverijen...
and Geek.com) that the microprocessors implementing the microarchitecture will feature a doubling in the width of SSE
Streaming SIMD Extensions
In computing, Streaming SIMD Extensions is a SIMD instruction set extension to the x86 architecture, designed by Intel and introduced in 1999 in their Pentium III series processors as a reply to AMD's 3DNow! . SSE contains 70 new instructions, most of which work on single precision floating point...
execution units in the cores. With the help of major improvements in the memory subsystem (such as load re-ordering and improved prefetch mechanisms) as well as the doubled instruction fetch and load, it is expected to increase the suitability of the processor to scientific and high-performance computing tasks and potentially improve its competitiveness with Intel's Xeon
Xeon
The Xeon is a brand of multiprocessing- or multi-socket-capable x86 microprocessors from Intel Corporation targeted at the non-consumer server, workstation and embedded system markets.-Overview:...
, Core 2
Intel Core 2
Core 2 is a brand encompassing a range of Intel's consumer 64-bit x86-64 single-, dual-, and quad-core microprocessors based on the Core microarchitecture. The single- and dual-core models are single-die, whereas the quad-core models comprise two dies, each containing two cores, packaged in a...
, Itanium 2 and other contemporary microprocessors.
Many of the improvements in computational throughput
Throughput
In communication networks, such as Ethernet or packet radio, throughput or network throughput is the average rate of successful message delivery over a communication channel. This data may be delivered over a physical or logical link, or pass through a certain network node...
of each core are listed below.
Characteristics of the microarchitecture


- Form factors
- Socket AM2+Socket AM2+Socket AM2+ is a CPU socket, which is the immediate successor to Socket AM2 that is used by several AMD processors such as Athlon 64 X2. Socket AM2+ is a mid-migration from Socket AM2 to Socket AM3 and both AM2+ and AM2 socket CPUs and motherboards have the potential to operate together...
with DDR2DDR2 SDRAMDDR2 SDRAM is a double data rate synchronous dynamic random-access memory interface. It supersedes the original DDR SDRAM specification and has itself been superseded by DDR3 SDRAM...
for the 65 nm Phenom and Athlon 7000 Series - Socket AM3Socket AM3Socket AM3 is a CPU socket for AMD processors. AM3 was launched as the successor to Socket AM2+ on February 9, 2009, alongside the initial grouping of Phenom II processors designed for it...
with either DDR2 or DDR3 for the 45 nm Phenom II Series. Note while all K10 Phenom Processors are backwards compatible with Socket AM2+ and Socket AM2Socket AM2The Socket AM2, renamed from Socket M2 , is a CPU socket designed by AMD for desktop processors, including the performance, mainstream and value segments...
, some 45 nm Phenom II Processors are only available for Socket AM2+. - Socket FSocket FSocket F is a CPU socket designed by AMD for its Opteron line of CPUs released on August 15, 2006. In 2010 Socket F was replaced by Socket C32 for entry-level servers and Socket G34 for high-end servers.-Technical specifications:...
with DDR2, DDR3 with Shanghai and later
- Socket AM2+
- Instruction set additions and extensions
- New bit-manipulation instructions: Leading Zero Count (LZCNT) and Population Count (POPCNT)
- New SSEStreaming SIMD ExtensionsIn computing, Streaming SIMD Extensions is a SIMD instruction set extension to the x86 architecture, designed by Intel and introduced in 1999 in their Pentium III series processors as a reply to AMD's 3DNow! . SSE contains 70 new instructions, most of which work on single precision floating point...
instructions named as SSE4a: combined mask-shift instructions (EXTRQ/INSERTQ) and scalar streaming store instructions (MOVNTSD/MOVNTSS). These instructions are not found in Intel's SSE4SSE4SSE4 is a CPU instruction set used in the Intel Core microarchitecture and AMD K10 . It was announced on 27 September 2006 at the Fall 2006 Intel Developer Forum, with vague details in a white paper; more precise details of 47 instructions became available at the Spring 2007 Intel Developer Forum... - Support for unaligned SSE load-operation instructions (which formerly required 16-byte alignment)
- Execution pipeline enhancements
- 128-bit wide SSEStreaming SIMD ExtensionsIn computing, Streaming SIMD Extensions is a SIMD instruction set extension to the x86 architecture, designed by Intel and introduced in 1999 in their Pentium III series processors as a reply to AMD's 3DNow! . SSE contains 70 new instructions, most of which work on single precision floating point...
units - Wider L1 data cache interface allowing for two 128-bit loads per cycle (as opposed to two 64-bit loads per cycle with K8)
- Lower integer divide latency
- 512-entry indirect branch predictorBranch predictorIn computer architecture, a branch predictor is a digital circuit that tries to guess which way a branch will go before this is known for sure. The purpose of the branch predictor is to improve the flow in the instruction pipeline...
and a larger return stack (size doubled from K8) and branch target buffer - Side-Band Stack Optimizer, dedicated to perform increment/decrement of register stack pointer
- Fastpathed CALL and RET-Imm instructions (formerly microcoded) as well as MOVs from SIMD registers to general purpose registers
- 128-bit wide SSE
- Integration of new technologies onto CPU die:
- Four processor cores (Quad-core)Multi-core (computing)A multi-core processor is a single computing component with two or more independent actual processors , which are the units that read and execute program instructions...
- Split power planePower planeIn printed circuit board design, a power plane is the counterpart to the ground plane and behaves as an AC signal ground, whilst providing DC voltage for powering circuits mounted on the PCB.- Uses :...
s for CPU core and memory controller/northbridge for more effective power management, first dubbed Dynamic Independent Core Engagement or D. I. C. E. by AMD and now known as Enhanced PowerNow! (also dubbed Independent Dynamic Core Technology), allowing the cores and northbridge (integrated memory controller) to scale power consumption up or down independently. - Shutting down portions of the circuits in core when not in load, named "CoolCore" Technology.
- Four processor cores (Quad-core)
- Improvements in the memory subsystem:
- Improvements in access latency:
- Support for re-ordering loads ahead of other loads and stores
- More aggressive instruction prefetchInstruction prefetchIn computer architecture, instruction prefetch is a technique used in microprocessors to speed up the execution of a program by reducing wait states....
ing, 32 bytes instruction prefetch as opposed to 16 bytes in K8AMD K8The AMD K8 is a computer processor microarchitecture designed by AMD as the successor to the AMD K7 microarchitecture. The K8 was the first implementation of the AMD64 64-bit extension to the x86 processor architecture.Processors based on the K8 core include:... - DRAM prefetcher for buffering reads
- Buffered burst writeback to RAM in order to reduce contention
- Changes in memory hierarchy:
- Prefetch directly into L1 cache as opposed to L2 cache with K8 family
- 32-way set associative L3 victim cacheCPU cacheA CPU cache is a cache used by the central processing unit of a computer to reduce the average time to access memory. The cache is a smaller, faster memory which stores copies of the data from the most frequently used main memory locations...
sized at least 2 MB, shared between processing cores on a single die (each with 512 KB of independent exclusive L2 cache), with a sharing-aware replacement policy. - Extensible L3 cache design, with 6 MB planned for 45 nm process node, with the chips codenamed Shanghai.
- Changes in address space management:
- Two 64-bit independent memory controllers, each with its own physical address space; this provides an opportunity to better utilize the available bandwidth in case of random memory accesses occurring in heavily multi-threaded environments. This approach is in contrast to the previous "interleaved" design, where the two 64-bit data channels were bounded to a single common address space.
- Larger Tagged Lookaside Buffers; support for 1 GBGigabyteThe gigabyte is a multiple of the unit byte for digital information storage. The prefix giga means 109 in the International System of Units , therefore 1 gigabyte is...
page entries and a new 128-entry 2 MB page TLB - 48-bit memory addressing to allow for 256 TB memory subsystems
- Memory mirroring, data poisoning support and Enhanced RASReliability, Availability and Serviceabilityreliability, availability, and serviceability are computer hardware engineering terms. It originated from IBM to advertise the robustness of their mainframe computers. The concept is often known by the acronym RAS....
- AMD-V Nested Paging for improved MMU virtualization, claimed to have decreasing world switch time by 25%.
- Improvements in access latency:
- Improvements in system interconnect:
- HyperTransportHyperTransportHyperTransport , formerly known as Lightning Data Transport , is a technology for interconnection of computer processors. It is a bidirectional serial/parallel high-bandwidth, low-latency point-to-point link that was introduced on April 2, 2001...
retry support - Support for HyperTransport 3.0, with HyperTransport Link unganging which creates 8 point-to-point links per socket.
- HyperTransport
- Platform-level enhancements with additional functionality:
- Five p-states allowing for automatic clock rate modulation
- Increased clock gatingClock gatingClock gating is a power-saving technique used in many synchronous circuits-Description:Clock gating is a popular technique used in many synchronous circuits for reducing dynamic power dissipation. Clock gating saves power by adding more logic to a circuit to prune the clock tree...
- Official support for coprocessors via HTXHyperTransportHyperTransport , formerly known as Lightning Data Transport , is a technology for interconnection of computer processors. It is a bidirectional serial/parallel high-bandwidth, low-latency point-to-point link that was introduced on April 2, 2001...
slots and vacant CPU sockets through HyperTransportHyperTransportHyperTransport , formerly known as Lightning Data Transport , is a technology for interconnection of computer processors. It is a bidirectional serial/parallel high-bandwidth, low-latency point-to-point link that was introduced on April 2, 2001...
: TorrenzaTorrenzaTorrenza was an initiative announced by Advanced Micro Devices in 2006 to improve support for the integration of specialized coprocessors in systems based on AMD Opteron microprocessors...
initiative.
Agena (65 nm SOI)
- Four AMD K10 cores
- L1 cacheCPU cacheA CPU cache is a cache used by the central processing unit of a computer to reduce the average time to access memory. The cache is a smaller, faster memory which stores copies of the data from the most frequently used main memory locations...
: 64 KBKilobyteThe kilobyte is a multiple of the unit byte for digital information. Although the prefix kilo- means 1000, the term kilobyte and symbol KB have historically been used to refer to either 1024 bytes or 1000 bytes, dependent upon context, in the fields of computer science and information...
+ 64 KBKilobyteThe kilobyte is a multiple of the unit byte for digital information. Although the prefix kilo- means 1000, the term kilobyte and symbol KB have historically been used to refer to either 1024 bytes or 1000 bytes, dependent upon context, in the fields of computer science and information...
(dataData (computing)In computer science, data is information in a form suitable for use with a computer. Data is often distinguished from programs. A program is a sequence of instructions that detail a task for the computer to perform...
+ instructions) per core - L2 cache: 512 KBKilobyteThe kilobyte is a multiple of the unit byte for digital information. Although the prefix kilo- means 1000, the term kilobyte and symbol KB have historically been used to refer to either 1024 bytes or 1000 bytes, dependent upon context, in the fields of computer science and information...
per core, full-speed - L3 cache: 2 MBMegabyteThe megabyte is a multiple of the unit byte for digital information storage or transmission with two different values depending on context: bytes generally for computer memory; and one million bytes generally for computer storage. The IEEE Standards Board has decided that "Mega will mean 1 000...
shared between all cores - Memory controller: dual channel DDR2-1066 MHz with unganging option
- MMX, Extended 3DNow!3DNow!3DNow! is an extension to the x86 instruction set developed by Advanced Micro Devices . It adds single instruction multiple data instructions to the base x86 instruction set, enabling it to perform simple vector processing, which improves the performance of many graphic-intensive applications...
, SSEStreaming SIMD ExtensionsIn computing, Streaming SIMD Extensions is a SIMD instruction set extension to the x86 architecture, designed by Intel and introduced in 1999 in their Pentium III series processors as a reply to AMD's 3DNow! . SSE contains 70 new instructions, most of which work on single precision floating point...
, SSE2SSE2SSE2, Streaming SIMD Extensions 2, is one of the Intel SIMD processor supplementary instruction sets first introduced by Intel with the initial version of the Pentium 4 in 2001. It extends the earlier SSE instruction set, and is intended to fully supplant MMX. Intel extended SSE2 to create SSE3...
, SSE3SSE3SSE3, Streaming SIMD Extensions 3, also known by its Intel code name Prescott New Instructions , is the third iteration of the SSE instruction set for the IA-32 architecture. Intel introduced SSE3 in early 2004 with the Prescott revision of their Pentium 4 CPU...
, SSE4a, AMD64, Cool'n'QuietCool'n'QuietCool'n'Quiet is a CPU speed throttling and power saving technology introduced by AMD with its Athlon 64 processor line. It works by reducing the processor's clock rate and voltage when the processor is idle. The aim of this technology is to reduce overall power consumption and lower heat...
, NX bitNX bitThe NX bit, which stands for No eXecute, is a technology used in CPUs to segregate areas of memory for use by either storage of processor instructions or for storage of data, a feature normally only found in Harvard architecture processors...
, AMD-V - Socket AM2+Socket AM2+Socket AM2+ is a CPU socket, which is the immediate successor to Socket AM2 that is used by several AMD processors such as Athlon 64 X2. Socket AM2+ is a mid-migration from Socket AM2 to Socket AM3 and both AM2+ and AM2 socket CPUs and motherboards have the potential to operate together...
, HyperTransportHyperTransportHyperTransport , formerly known as Lightning Data Transport , is a technology for interconnection of computer processors. It is a bidirectional serial/parallel high-bandwidth, low-latency point-to-point link that was introduced on April 2, 2001...
with 1600 to 2000 MHz - Power consumption (TDPThermal Design PowerThe thermal design power , sometimes called thermal design point, refers to the maximum amount of power the cooling system in a computer is required to dissipate. For example, a laptop's CPU cooling system may be designed for a 20 watt TDP, which means that it can dissipate up to 20 watts of heat...
): 65, 95, 125 and 140 Watt - First release
- November 19, 2007 (B2 Stepping)
- March 27, 2008 (B3 Stepping)
- Clock rate: 1800 to 2600 MHz
- Models: Phenom X4 9100e - 9950
Toliman (65 nm SOI)
- Three AMD K10 cores
- L1 cacheCPU cacheA CPU cache is a cache used by the central processing unit of a computer to reduce the average time to access memory. The cache is a smaller, faster memory which stores copies of the data from the most frequently used main memory locations...
: 64 KBKilobyteThe kilobyte is a multiple of the unit byte for digital information. Although the prefix kilo- means 1000, the term kilobyte and symbol KB have historically been used to refer to either 1024 bytes or 1000 bytes, dependent upon context, in the fields of computer science and information...
dataData (computing)In computer science, data is information in a form suitable for use with a computer. Data is often distinguished from programs. A program is a sequence of instructions that detail a task for the computer to perform...
and 64 KBKilobyteThe kilobyte is a multiple of the unit byte for digital information. Although the prefix kilo- means 1000, the term kilobyte and symbol KB have historically been used to refer to either 1024 bytes or 1000 bytes, dependent upon context, in the fields of computer science and information...
instruction cache per core - L2 cache: 512 KBKilobyteThe kilobyte is a multiple of the unit byte for digital information. Although the prefix kilo- means 1000, the term kilobyte and symbol KB have historically been used to refer to either 1024 bytes or 1000 bytes, dependent upon context, in the fields of computer science and information...
per core, full-speed - L3 cache: 2 MBMegabyteThe megabyte is a multiple of the unit byte for digital information storage or transmission with two different values depending on context: bytes generally for computer memory; and one million bytes generally for computer storage. The IEEE Standards Board has decided that "Mega will mean 1 000...
shared between all cores - Memory controller: dual channel DDR2-1066 MHz with unganging option
- MMX, Extended 3DNow!3DNow!3DNow! is an extension to the x86 instruction set developed by Advanced Micro Devices . It adds single instruction multiple data instructions to the base x86 instruction set, enabling it to perform simple vector processing, which improves the performance of many graphic-intensive applications...
, SSEStreaming SIMD ExtensionsIn computing, Streaming SIMD Extensions is a SIMD instruction set extension to the x86 architecture, designed by Intel and introduced in 1999 in their Pentium III series processors as a reply to AMD's 3DNow! . SSE contains 70 new instructions, most of which work on single precision floating point...
, SSE2SSE2SSE2, Streaming SIMD Extensions 2, is one of the Intel SIMD processor supplementary instruction sets first introduced by Intel with the initial version of the Pentium 4 in 2001. It extends the earlier SSE instruction set, and is intended to fully supplant MMX. Intel extended SSE2 to create SSE3...
, SSE3SSE3SSE3, Streaming SIMD Extensions 3, also known by its Intel code name Prescott New Instructions , is the third iteration of the SSE instruction set for the IA-32 architecture. Intel introduced SSE3 in early 2004 with the Prescott revision of their Pentium 4 CPU...
, SSE4a, AMD64, Cool'n'QuietCool'n'QuietCool'n'Quiet is a CPU speed throttling and power saving technology introduced by AMD with its Athlon 64 processor line. It works by reducing the processor's clock rate and voltage when the processor is idle. The aim of this technology is to reduce overall power consumption and lower heat...
, NX bitNX bitThe NX bit, which stands for No eXecute, is a technology used in CPUs to segregate areas of memory for use by either storage of processor instructions or for storage of data, a feature normally only found in Harvard architecture processors...
, AMD-V - Socket AM2+Socket AM2+Socket AM2+ is a CPU socket, which is the immediate successor to Socket AM2 that is used by several AMD processors such as Athlon 64 X2. Socket AM2+ is a mid-migration from Socket AM2 to Socket AM3 and both AM2+ and AM2 socket CPUs and motherboards have the potential to operate together...
, HyperTransportHyperTransportHyperTransport , formerly known as Lightning Data Transport , is a technology for interconnection of computer processors. It is a bidirectional serial/parallel high-bandwidth, low-latency point-to-point link that was introduced on April 2, 2001...
with 1600 to 1800 MHz - Power consumption (TDPThermal Design PowerThe thermal design power , sometimes called thermal design point, refers to the maximum amount of power the cooling system in a computer is required to dissipate. For example, a laptop's CPU cooling system may be designed for a 20 watt TDP, which means that it can dissipate up to 20 watts of heat...
): 65 and 95 Watt - First release
- March 27, 2008 (B2 Stepping)
- April 23, 2008 (B3 Stepping)
- Clock rate: 2100 to 2500 MHz
- Models: Phenom X3 8250e - 8850
Thuban (45 nm SOI with Immersion Lithography)
- Six AMD K10 cores
- L1 cacheCPU cacheA CPU cache is a cache used by the central processing unit of a computer to reduce the average time to access memory. The cache is a smaller, faster memory which stores copies of the data from the most frequently used main memory locations...
: 64 kBKilobyteThe kilobyte is a multiple of the unit byte for digital information. Although the prefix kilo- means 1000, the term kilobyte and symbol KB have historically been used to refer to either 1024 bytes or 1000 bytes, dependent upon context, in the fields of computer science and information...
+ 64 kB (dataData (computing)In computer science, data is information in a form suitable for use with a computer. Data is often distinguished from programs. A program is a sequence of instructions that detail a task for the computer to perform...
+ instructions) per core - L2 cache: 512 kB per core, full-speed
- L3 cache: 6 MBMegabyteThe megabyte is a multiple of the unit byte for digital information storage or transmission with two different values depending on context: bytes generally for computer memory; and one million bytes generally for computer storage. The IEEE Standards Board has decided that "Mega will mean 1 000...
shared between all cores. - Memory controller: dual channel DDR2-1066 MHz (AM2+), dual channel DDR3-1333 (AM3) with unganging option
- MMX, Extended 3DNow!3DNow!3DNow! is an extension to the x86 instruction set developed by Advanced Micro Devices . It adds single instruction multiple data instructions to the base x86 instruction set, enabling it to perform simple vector processing, which improves the performance of many graphic-intensive applications...
, SSEStreaming SIMD ExtensionsIn computing, Streaming SIMD Extensions is a SIMD instruction set extension to the x86 architecture, designed by Intel and introduced in 1999 in their Pentium III series processors as a reply to AMD's 3DNow! . SSE contains 70 new instructions, most of which work on single precision floating point...
, SSE2SSE2SSE2, Streaming SIMD Extensions 2, is one of the Intel SIMD processor supplementary instruction sets first introduced by Intel with the initial version of the Pentium 4 in 2001. It extends the earlier SSE instruction set, and is intended to fully supplant MMX. Intel extended SSE2 to create SSE3...
, SSE3SSE3SSE3, Streaming SIMD Extensions 3, also known by its Intel code name Prescott New Instructions , is the third iteration of the SSE instruction set for the IA-32 architecture. Intel introduced SSE3 in early 2004 with the Prescott revision of their Pentium 4 CPU...
, SSE4a, AMD64, Cool'n'QuietCool'n'QuietCool'n'Quiet is a CPU speed throttling and power saving technology introduced by AMD with its Athlon 64 processor line. It works by reducing the processor's clock rate and voltage when the processor is idle. The aim of this technology is to reduce overall power consumption and lower heat...
, NX bitNX bitThe NX bit, which stands for No eXecute, is a technology used in CPUs to segregate areas of memory for use by either storage of processor instructions or for storage of data, a feature normally only found in Harvard architecture processors...
, AMD-V - Socket AM2+Socket AM2+Socket AM2+ is a CPU socket, which is the immediate successor to Socket AM2 that is used by several AMD processors such as Athlon 64 X2. Socket AM2+ is a mid-migration from Socket AM2 to Socket AM3 and both AM2+ and AM2 socket CPUs and motherboards have the potential to operate together...
, Socket AM3Socket AM3Socket AM3 is a CPU socket for AMD processors. AM3 was launched as the successor to Socket AM2+ on February 9, 2009, alongside the initial grouping of Phenom II processors designed for it...
, HyperTransportHyperTransportHyperTransport , formerly known as Lightning Data Transport , is a technology for interconnection of computer processors. It is a bidirectional serial/parallel high-bandwidth, low-latency point-to-point link that was introduced on April 2, 2001...
with 1800 to 2000 MHz - Power consumption (TDPThermal Design PowerThe thermal design power , sometimes called thermal design point, refers to the maximum amount of power the cooling system in a computer is required to dissipate. For example, a laptop's CPU cooling system may be designed for a 20 watt TDP, which means that it can dissipate up to 20 watts of heat...
): 95 or 125 Watt - First release
- 27 April 2010 (E0 Stepping)
- Clock rate: 2.6 - 3.3 GHz; up to 3.7 GHz with Turbo Core
- Models: Phenom II X6 1035T, 1045T, 1055T, 1075T, 1090T and 1100T
- Models: Phenom II X4 840T, 960T, 970 (Thuban-based Zosma core, OEM Only, 970 has unlocked multiplier but w/o Turbo Core)
Deneb (45 nm SOI with Immersion Lithography)
- Four AMD K10 cores
- L1 cacheCPU cacheA CPU cache is a cache used by the central processing unit of a computer to reduce the average time to access memory. The cache is a smaller, faster memory which stores copies of the data from the most frequently used main memory locations...
: 64 kBKilobyteThe kilobyte is a multiple of the unit byte for digital information. Although the prefix kilo- means 1000, the term kilobyte and symbol KB have historically been used to refer to either 1024 bytes or 1000 bytes, dependent upon context, in the fields of computer science and information...
+ 64 kB (dataData (computing)In computer science, data is information in a form suitable for use with a computer. Data is often distinguished from programs. A program is a sequence of instructions that detail a task for the computer to perform...
+ instructions) per core - L2 cache: 512 kB per core, full-speed
- L3 cache: 6 MBMegabyteThe megabyte is a multiple of the unit byte for digital information storage or transmission with two different values depending on context: bytes generally for computer memory; and one million bytes generally for computer storage. The IEEE Standards Board has decided that "Mega will mean 1 000...
shared between all cores. The 800 series have 2 MB of its L3 Cache disabled due to defects. - Memory controller: dual channel DDR2-1066 MHz (AM2+), dual channel DDR3-1333 (AM3) with unganging option
- MMX, Extended 3DNow!3DNow!3DNow! is an extension to the x86 instruction set developed by Advanced Micro Devices . It adds single instruction multiple data instructions to the base x86 instruction set, enabling it to perform simple vector processing, which improves the performance of many graphic-intensive applications...
, SSEStreaming SIMD ExtensionsIn computing, Streaming SIMD Extensions is a SIMD instruction set extension to the x86 architecture, designed by Intel and introduced in 1999 in their Pentium III series processors as a reply to AMD's 3DNow! . SSE contains 70 new instructions, most of which work on single precision floating point...
, SSE2SSE2SSE2, Streaming SIMD Extensions 2, is one of the Intel SIMD processor supplementary instruction sets first introduced by Intel with the initial version of the Pentium 4 in 2001. It extends the earlier SSE instruction set, and is intended to fully supplant MMX. Intel extended SSE2 to create SSE3...
, SSE3SSE3SSE3, Streaming SIMD Extensions 3, also known by its Intel code name Prescott New Instructions , is the third iteration of the SSE instruction set for the IA-32 architecture. Intel introduced SSE3 in early 2004 with the Prescott revision of their Pentium 4 CPU...
, SSE4a, AMD64, Cool'n'QuietCool'n'QuietCool'n'Quiet is a CPU speed throttling and power saving technology introduced by AMD with its Athlon 64 processor line. It works by reducing the processor's clock rate and voltage when the processor is idle. The aim of this technology is to reduce overall power consumption and lower heat...
, NX bitNX bitThe NX bit, which stands for No eXecute, is a technology used in CPUs to segregate areas of memory for use by either storage of processor instructions or for storage of data, a feature normally only found in Harvard architecture processors...
, AMD-V - Socket AM2+Socket AM2+Socket AM2+ is a CPU socket, which is the immediate successor to Socket AM2 that is used by several AMD processors such as Athlon 64 X2. Socket AM2+ is a mid-migration from Socket AM2 to Socket AM3 and both AM2+ and AM2 socket CPUs and motherboards have the potential to operate together...
, Socket AM3Socket AM3Socket AM3 is a CPU socket for AMD processors. AM3 was launched as the successor to Socket AM2+ on February 9, 2009, alongside the initial grouping of Phenom II processors designed for it...
, HyperTransportHyperTransportHyperTransport , formerly known as Lightning Data Transport , is a technology for interconnection of computer processors. It is a bidirectional serial/parallel high-bandwidth, low-latency point-to-point link that was introduced on April 2, 2001...
with 1800 to 2000 MHz - Power consumption (TDPThermal Design PowerThe thermal design power , sometimes called thermal design point, refers to the maximum amount of power the cooling system in a computer is required to dissipate. For example, a laptop's CPU cooling system may be designed for a 20 watt TDP, which means that it can dissipate up to 20 watts of heat...
): 65, 95, 125 and 140 Watt - First release
- 8 January 2009 (C2 Stepping)
- Clock rate: 2500 to 3700 MHz
- Models: Phenom II X4 805 - 980
Heka (45 nm SOI with Immersion Lithography)
- Three AMD K10 cores using chip harvesting technique, with one core disabled
- L1 cacheCPU cacheA CPU cache is a cache used by the central processing unit of a computer to reduce the average time to access memory. The cache is a smaller, faster memory which stores copies of the data from the most frequently used main memory locations...
: 64 kB + 64 kB (dataData (computing)In computer science, data is information in a form suitable for use with a computer. Data is often distinguished from programs. A program is a sequence of instructions that detail a task for the computer to perform...
+ instructions) per core - L2 cache: 512 kB per core, full-speed
- L3 cache: 6 MB shared between all cores
- Memory controller: dual channel DDR2-1066 MHz (AM2+), dual channel DDR3-1333 (AM3) with unganging option
- MMX, Extended 3DNow!3DNow!3DNow! is an extension to the x86 instruction set developed by Advanced Micro Devices . It adds single instruction multiple data instructions to the base x86 instruction set, enabling it to perform simple vector processing, which improves the performance of many graphic-intensive applications...
, SSEStreaming SIMD ExtensionsIn computing, Streaming SIMD Extensions is a SIMD instruction set extension to the x86 architecture, designed by Intel and introduced in 1999 in their Pentium III series processors as a reply to AMD's 3DNow! . SSE contains 70 new instructions, most of which work on single precision floating point...
, SSE2SSE2SSE2, Streaming SIMD Extensions 2, is one of the Intel SIMD processor supplementary instruction sets first introduced by Intel with the initial version of the Pentium 4 in 2001. It extends the earlier SSE instruction set, and is intended to fully supplant MMX. Intel extended SSE2 to create SSE3...
, SSE3SSE3SSE3, Streaming SIMD Extensions 3, also known by its Intel code name Prescott New Instructions , is the third iteration of the SSE instruction set for the IA-32 architecture. Intel introduced SSE3 in early 2004 with the Prescott revision of their Pentium 4 CPU...
, SSE4a, AMD64, Cool'n'QuietCool'n'QuietCool'n'Quiet is a CPU speed throttling and power saving technology introduced by AMD with its Athlon 64 processor line. It works by reducing the processor's clock rate and voltage when the processor is idle. The aim of this technology is to reduce overall power consumption and lower heat...
, NX bitNX bitThe NX bit, which stands for No eXecute, is a technology used in CPUs to segregate areas of memory for use by either storage of processor instructions or for storage of data, a feature normally only found in Harvard architecture processors...
, AMD-V - Socket AM3Socket AM3Socket AM3 is a CPU socket for AMD processors. AM3 was launched as the successor to Socket AM2+ on February 9, 2009, alongside the initial grouping of Phenom II processors designed for it...
, HyperTransportHyperTransportHyperTransport , formerly known as Lightning Data Transport , is a technology for interconnection of computer processors. It is a bidirectional serial/parallel high-bandwidth, low-latency point-to-point link that was introduced on April 2, 2001...
with 2000 MHz - Power consumption (TDPThermal Design PowerThe thermal design power , sometimes called thermal design point, refers to the maximum amount of power the cooling system in a computer is required to dissipate. For example, a laptop's CPU cooling system may be designed for a 20 watt TDP, which means that it can dissipate up to 20 watts of heat...
): 65 and 95 Watt - First release
- 9 February 2009 (C2 Stepping)
- Clock rate: 2500 to 3000 MHz
- Models: Phenom II X3 705e - 740
Callisto (45 nm SOI with Immersion Lithography)
- Two AMD K10 cores using chip harvesting technique, with two cores disabled
- L1 cacheCPU cacheA CPU cache is a cache used by the central processing unit of a computer to reduce the average time to access memory. The cache is a smaller, faster memory which stores copies of the data from the most frequently used main memory locations...
: 64 kB + 64 kB (dataData (computing)In computer science, data is information in a form suitable for use with a computer. Data is often distinguished from programs. A program is a sequence of instructions that detail a task for the computer to perform...
+ instructions) per core - L2 cache: 512 kB per core, full-speed
- L3 cache: 6 MB shared between all cores
- Memory controller: dual channel DDR2-1066 MHz (AM2+), dual channel DDR3-1333 (AM3) with unganging option
- MMX, Extended 3DNow!3DNow!3DNow! is an extension to the x86 instruction set developed by Advanced Micro Devices . It adds single instruction multiple data instructions to the base x86 instruction set, enabling it to perform simple vector processing, which improves the performance of many graphic-intensive applications...
, SSEStreaming SIMD ExtensionsIn computing, Streaming SIMD Extensions is a SIMD instruction set extension to the x86 architecture, designed by Intel and introduced in 1999 in their Pentium III series processors as a reply to AMD's 3DNow! . SSE contains 70 new instructions, most of which work on single precision floating point...
, SSE2SSE2SSE2, Streaming SIMD Extensions 2, is one of the Intel SIMD processor supplementary instruction sets first introduced by Intel with the initial version of the Pentium 4 in 2001. It extends the earlier SSE instruction set, and is intended to fully supplant MMX. Intel extended SSE2 to create SSE3...
, SSE3SSE3SSE3, Streaming SIMD Extensions 3, also known by its Intel code name Prescott New Instructions , is the third iteration of the SSE instruction set for the IA-32 architecture. Intel introduced SSE3 in early 2004 with the Prescott revision of their Pentium 4 CPU...
, SSE4a, AMD64, Cool'n'QuietCool'n'QuietCool'n'Quiet is a CPU speed throttling and power saving technology introduced by AMD with its Athlon 64 processor line. It works by reducing the processor's clock rate and voltage when the processor is idle. The aim of this technology is to reduce overall power consumption and lower heat...
, NX bitNX bitThe NX bit, which stands for No eXecute, is a technology used in CPUs to segregate areas of memory for use by either storage of processor instructions or for storage of data, a feature normally only found in Harvard architecture processors...
, AMD-V - Socket AM3Socket AM3Socket AM3 is a CPU socket for AMD processors. AM3 was launched as the successor to Socket AM2+ on February 9, 2009, alongside the initial grouping of Phenom II processors designed for it...
, HyperTransportHyperTransportHyperTransport , formerly known as Lightning Data Transport , is a technology for interconnection of computer processors. It is a bidirectional serial/parallel high-bandwidth, low-latency point-to-point link that was introduced on April 2, 2001...
with 2000 MHz - Power consumption (TDPThermal Design PowerThe thermal design power , sometimes called thermal design point, refers to the maximum amount of power the cooling system in a computer is required to dissipate. For example, a laptop's CPU cooling system may be designed for a 20 watt TDP, which means that it can dissipate up to 20 watts of heat...
): 80 Watt - First release
- 1 June 2009 (C2 Stepping)
- Clock rate: 3000 to 3500 MHz
- Models: Phenom II X2 545 - 570
Regor (45 nm SOI with Immersion Lithography)
- Two AMD K10 cores
- L1 cacheCPU cacheA CPU cache is a cache used by the central processing unit of a computer to reduce the average time to access memory. The cache is a smaller, faster memory which stores copies of the data from the most frequently used main memory locations...
: 64 kBKilobyteThe kilobyte is a multiple of the unit byte for digital information. Although the prefix kilo- means 1000, the term kilobyte and symbol KB have historically been used to refer to either 1024 bytes or 1000 bytes, dependent upon context, in the fields of computer science and information...
+ 64 kB (dataData (computing)In computer science, data is information in a form suitable for use with a computer. Data is often distinguished from programs. A program is a sequence of instructions that detail a task for the computer to perform...
+ instructions) per core - L2 cache: 1024 kB per core, full-speed
- Memory controller: dual channel DDR2-1066 MHz (AM2+), dual channel DDR3-1333 (AM3) with unganging option
- MMX, Extended 3DNow!3DNow!3DNow! is an extension to the x86 instruction set developed by Advanced Micro Devices . It adds single instruction multiple data instructions to the base x86 instruction set, enabling it to perform simple vector processing, which improves the performance of many graphic-intensive applications...
, SSEStreaming SIMD ExtensionsIn computing, Streaming SIMD Extensions is a SIMD instruction set extension to the x86 architecture, designed by Intel and introduced in 1999 in their Pentium III series processors as a reply to AMD's 3DNow! . SSE contains 70 new instructions, most of which work on single precision floating point...
, SSE2SSE2SSE2, Streaming SIMD Extensions 2, is one of the Intel SIMD processor supplementary instruction sets first introduced by Intel with the initial version of the Pentium 4 in 2001. It extends the earlier SSE instruction set, and is intended to fully supplant MMX. Intel extended SSE2 to create SSE3...
, SSE3SSE3SSE3, Streaming SIMD Extensions 3, also known by its Intel code name Prescott New Instructions , is the third iteration of the SSE instruction set for the IA-32 architecture. Intel introduced SSE3 in early 2004 with the Prescott revision of their Pentium 4 CPU...
, SSE4a, AMD64, Cool'n'QuietCool'n'QuietCool'n'Quiet is a CPU speed throttling and power saving technology introduced by AMD with its Athlon 64 processor line. It works by reducing the processor's clock rate and voltage when the processor is idle. The aim of this technology is to reduce overall power consumption and lower heat...
, NX bitNX bitThe NX bit, which stands for No eXecute, is a technology used in CPUs to segregate areas of memory for use by either storage of processor instructions or for storage of data, a feature normally only found in Harvard architecture processors...
, AMD-V - Socket AM3Socket AM3Socket AM3 is a CPU socket for AMD processors. AM3 was launched as the successor to Socket AM2+ on February 9, 2009, alongside the initial grouping of Phenom II processors designed for it...
, HyperTransportHyperTransportHyperTransport , formerly known as Lightning Data Transport , is a technology for interconnection of computer processors. It is a bidirectional serial/parallel high-bandwidth, low-latency point-to-point link that was introduced on April 2, 2001...
with 2000 MHz - Power consumption (TDPThermal Design PowerThe thermal design power , sometimes called thermal design point, refers to the maximum amount of power the cooling system in a computer is required to dissipate. For example, a laptop's CPU cooling system may be designed for a 20 watt TDP, which means that it can dissipate up to 20 watts of heat...
): 65 Watt - First release
- June 2009 (C2 Stepping)
- Clock rate: 2800 - 3200 MHz
- Models: Athlon II X2 240 - 260
Propus (45 nm SOI with Immersion Lithography)
- Four AMD K10 cores
- L1 cacheCPU cacheA CPU cache is a cache used by the central processing unit of a computer to reduce the average time to access memory. The cache is a smaller, faster memory which stores copies of the data from the most frequently used main memory locations...
: 64 kBKilobyteThe kilobyte is a multiple of the unit byte for digital information. Although the prefix kilo- means 1000, the term kilobyte and symbol KB have historically been used to refer to either 1024 bytes or 1000 bytes, dependent upon context, in the fields of computer science and information...
+ 64 kB (dataData (computing)In computer science, data is information in a form suitable for use with a computer. Data is often distinguished from programs. A program is a sequence of instructions that detail a task for the computer to perform...
+ instructions) per core - L2 cache: 512 kB per core, full-speed
- Memory controller: dual channel DDR2-1066 MHz (AM2+), dual channel DDR3-1333 (AM3) with unganging option
- MMX, Extended 3DNow!3DNow!3DNow! is an extension to the x86 instruction set developed by Advanced Micro Devices . It adds single instruction multiple data instructions to the base x86 instruction set, enabling it to perform simple vector processing, which improves the performance of many graphic-intensive applications...
, SSEStreaming SIMD ExtensionsIn computing, Streaming SIMD Extensions is a SIMD instruction set extension to the x86 architecture, designed by Intel and introduced in 1999 in their Pentium III series processors as a reply to AMD's 3DNow! . SSE contains 70 new instructions, most of which work on single precision floating point...
, SSE2SSE2SSE2, Streaming SIMD Extensions 2, is one of the Intel SIMD processor supplementary instruction sets first introduced by Intel with the initial version of the Pentium 4 in 2001. It extends the earlier SSE instruction set, and is intended to fully supplant MMX. Intel extended SSE2 to create SSE3...
, SSE3SSE3SSE3, Streaming SIMD Extensions 3, also known by its Intel code name Prescott New Instructions , is the third iteration of the SSE instruction set for the IA-32 architecture. Intel introduced SSE3 in early 2004 with the Prescott revision of their Pentium 4 CPU...
, SSE4a, AMD64, Cool'n'QuietCool'n'QuietCool'n'Quiet is a CPU speed throttling and power saving technology introduced by AMD with its Athlon 64 processor line. It works by reducing the processor's clock rate and voltage when the processor is idle. The aim of this technology is to reduce overall power consumption and lower heat...
, NX bitNX bitThe NX bit, which stands for No eXecute, is a technology used in CPUs to segregate areas of memory for use by either storage of processor instructions or for storage of data, a feature normally only found in Harvard architecture processors...
, AMD-V - Socket AM3Socket AM3Socket AM3 is a CPU socket for AMD processors. AM3 was launched as the successor to Socket AM2+ on February 9, 2009, alongside the initial grouping of Phenom II processors designed for it...
, HyperTransportHyperTransportHyperTransport , formerly known as Lightning Data Transport , is a technology for interconnection of computer processors. It is a bidirectional serial/parallel high-bandwidth, low-latency point-to-point link that was introduced on April 2, 2001...
with 2000 MHz - Power consumption (TDP): 45 Watt or 95 Watt
- First release
- September 2009 (C2 Stepping)
- Clock rate: 2200 - 3100 MHz
- Models: Athlon II X4 600e - 645
Successor
Codenamed "FusionAMD Fusion
AMD Fusion is the marketing name for a series of APUs by AMD. There are two flavors of Fusion currently available, one with its CPU logic based on the Bobcat core and the other its CPU logic based on the 10h core. In both cases the GPU logic is HD6xxx, which itself is based on the mobile variant of...
" is a CPU technology furthering the trend of continued system component integration onto CPU die (which was initiated by K8 with integrated System Request Queue (SRQ), cross-bar switch, memory controller as well as HyperTransport
HyperTransport
HyperTransport , formerly known as Lightning Data Transport , is a technology for interconnection of computer processors. It is a bidirectional serial/parallel high-bandwidth, low-latency point-to-point link that was introduced on April 2, 2001...
links), planned beyond these two aforementioned families of products, and will be due sometime in 2011. The Fusion products will see new processor cores, codenamed "Bulldozer
Bulldozer (processor)
Bulldozer is the codename Advanced Micro Devices has given to one of the next-generation CPU cores after the K10 microarchitecture for the company's M-SPACE design methodology, with the core specifically aimed at 10-watt to 125-watt TDP computing products. Bulldozer is a completely new design...
" and "Bobcat
Bobcat (processor)
Bobcat is the latest x86 processor core from AMD aimed at low-power / low-cost market.It was revealed during a speech from AMD executive vice-president Henri Richard in Computex 2007 and was put into production Q1 2011. One of the major supporters was executive vice-president Mario A...
" incorporated into the die. Fusion will also see the debut of special purpose cores with a quad core cpu dedicating up to 3 cores to specialized tasks such as a graphics core, a physics core (for game physics) and a Java core (specialized for running managed code). Not all of these cores may be present in each chip and more speciality cores may be developed based on market demand.
Media discussions
Note: These media discussions are listed in ascending date of publication.See also
- Phenom (processor)Phenom (processor)Phenom is the 64-bit AMD desktop processor line based on the K10 microarchitecture, in what AMD calls family 10h processors, sometimes incorrectly called "K10h". Triple-core versions belong to the Phenom 8000 series and quad cores to the AMD Phenom X4 9000 series...
- Phenom IIPhenom IIPhenom II is a family of AMD's multi-core 45 nm processors using the AMD K10 microarchitecture, succeeding the original Phenom. Advanced Micro Devices released the Socket AM2+ version of Phenom II in December 2008, while Socket AM3 versions with DDR3 support, along with an initial batch of...
- List of AMD Phenom microprocessors
- List of AMD Athlon X2 microprocessors
External links
- AMD Official Website
- AMD Quad-core processors introduction
- DarkVision Hardware: AMD talks about K9, K10 future innovations
- Next-Generation AMD Opteron Processors Introduced with Record OEM Design Wins and Native Quad-Core Upgrade Path (Official AMD press release on 15 August 2006)
- PC Watch report about K10 based on AMD Technology Analyst Day 2004 and 2005
- PC Watch report about K10 based on Slides presented in Microprocessor Forum 2003
- Software Optimization Guide for AMD Family 10h Processors
- TechReport: AMD outlines Future Goals
- TweakTown Discussions (2003)
- X-bit labs: AMD K10 Micro-Architecture

