
6-Acetyl-2,3,4,5-tetrahydropyridine
Encyclopedia
6-Acetyl-2,3,4,5-tetrahydropyridine, is an aroma compound
and flavor
that gives baked good
s such as white bread
, popcorn
, and tortilla
s their typical smell, together with its structural homolog 2-acetyl-1-pyrroline
.
6-Acetyl-2,3,4,5-tetrahydropyridine and 2-acetyl-1-pyrroline are usually formed by Maillard reaction
s during heating of food. Both compounds have odor thresholds below 0.06 ng/l
.
and a cyclic imine
as well as a ketone
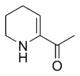
. The compound exists in a chemical equilibrium
with its tautomer
6-acetyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydropyridine that differs only by the position of the double bond
in the tetrahydropyridine ring:
Aroma compound
An aroma compound, also known as odorant, aroma, fragrance or flavor, is a chemical compound that has a smell or odor...
and flavor
Flavor
Flavor or flavour is the sensory impression of a food or other substance, and is determined mainly by the chemical senses of taste and smell. The "trigeminal senses", which detect chemical irritants in the mouth and throat as well as temperature and texture, are also very important to the overall...
that gives baked good
Baking
Baking is the technique of prolonged cooking of food by dry heat acting by convection, and not by radiation, normally in an oven, but also in hot ashes, or on hot stones. It is primarily used for the preparation of bread, cakes, pastries and pies, tarts, quiches, cookies and crackers. Such items...
s such as white bread
White bread
White bread is made from wheat flour from which the bran and the germ have been removed through a process known as milling. Milling gives white flour a longer shelf life by removing the bran which contains oil, allowing products made with it, like white bread, the ability to survive storage and...
, popcorn
Popcorn
Popcorn, or popping corn, is corn which expands from the kernel and puffs up when heated. Corn is able to pop because, like sorghum, quinoa and millet, its kernels have a hard moisture-sealed hull and a dense starchy interior. This allows pressure to build inside the kernel until an explosive...
, and tortilla
Tortilla
In Mexico and Central America, a tortilla is a type of thin, unleavened flat bread, made from finely ground maize...
s their typical smell, together with its structural homolog 2-acetyl-1-pyrroline
2-Acetyl-1-pyrroline
2-Acetyl-1-pyrroline, abbreviated 2AP, with the IUPAC name 1-ethanone, is an aroma compound and flavor that gives white bread, jasmine rice and basmati rice, the spice pandan , and bread flowers their typical smell...
.
6-Acetyl-2,3,4,5-tetrahydropyridine and 2-acetyl-1-pyrroline are usually formed by Maillard reaction
Maillard reaction
The Maillard reaction is a form of nonenzymatic browning similar to caramelization. It results from a chemical reaction between an amino acid and a reducing sugar, usually requiring heat....
s during heating of food. Both compounds have odor thresholds below 0.06 ng/l
Litér
- External links :*...
.
Structure and properties
6-Acetyl-2,3,4,5-tetrahydropyridine is a substituted tetrahydropyridinePyridine
Pyridine is a basic heterocyclic organic compound with the chemical formula C5H5N. It is structurally related to benzene, with one C-H group replaced by a nitrogen atom...
and a cyclic imine
Imine
An imine is a functional group or chemical compound containing a carbon–nitrogen double bond, with the nitrogen attached to a hydrogen atom or an organic group. If this group is not a hydrogen atom, then the compound is known as a Schiff base...
as well as a ketone
Ketone
In organic chemistry, a ketone is an organic compound with the structure RCR', where R and R' can be a variety of atoms and groups of atoms. It features a carbonyl group bonded to two other carbon atoms. Many ketones are known and many are of great importance in industry and in biology...
. The compound exists in a chemical equilibrium
Chemical equilibrium
In a chemical reaction, chemical equilibrium is the state in which the concentrations of the reactants and products have not yet changed with time. It occurs only in reversible reactions, and not in irreversible reactions. Usually, this state results when the forward reaction proceeds at the same...
with its tautomer
Tautomer
Tautomers are isomers of organic compounds that readily interconvert by a chemical reaction called tautomerization. This reaction commonly results in the formal migration of a hydrogen atom or proton, accompanied by a switch of a single bond and adjacent double bond...
6-acetyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydropyridine that differs only by the position of the double bond
Double bond
A double bond in chemistry is a chemical bond between two chemical elements involving four bonding electrons instead of the usual two. The most common double bond, that between two carbon atoms, can be found in alkenes. Many types of double bonds between two different elements exist, for example in...
in the tetrahydropyridine ring:
 |
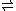 |
 |
| 6-Acetyl-2,3,4,5-tetrahydropyridine | (1 : 2) | 6-Acetyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydropyridine |

