
16 Cygni Bb
Encyclopedia
16 Cygni Bb or 16 Cyg Bb is an extrasolar planet
approximately 70 light-year
s away in the constellation
of Cygnus
. The planet was discovered orbiting the sun-like
star
16 Cygni B
, one of two solar-mass
components of the triple star system 16 Cygni. It makes one revolution every 799 days and was the first eccentric Jupiter
to be discovered.
ary-mass companion to the star 16 Cygni B was announced, with a mass at least 1.68 times that of Jupiter
. At the time, it had the highest orbital eccentricity of any known extrasolar planet. The discovery was made by measuring the star's radial velocity
. As the inclination of the orbit is unknown, only a lower limit on the mass is known.
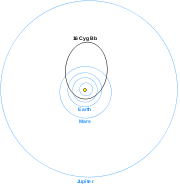
 Unlike the planets in our solar system
Unlike the planets in our solar system
, the planet's orbit is highly elliptical
, and its distance varies from 0.54 AU
at periastron to 2.8 AU at apastron. This high eccentricity may have been caused by tidal interactions in the binary star
system, and the planet's orbit may vary chaotically
between low and high-eccentricity states over a period of tens of millions of years.
The lower limit for the object's mass is well below the dividing line between planets and brown dwarf
s at 13 Jupiter masses. Preliminary astrometric
measurements in 2001 suggested the orbit of 16 Cygni Bb may be highly inclined with respect to our line of sight (at around 173°). This would mean the object's mass may be around 14 times that of Jupiter, making it a low-mass brown dwarf. However these measurements were later proved useful only for upper limits;.
, composition and temperature
are unknown.
al effects. Despite this, simulations suggest that an Earth
-like moon
would be able to support liquid water at its surface over the course of a year. Due to the eccentric orbit of this massive gas giant
, it is unlikely that a habitable planet could survive in this system.
Extrasolar planet
An extrasolar planet, or exoplanet, is a planet outside the Solar System. A total of such planets have been identified as of . It is now known that a substantial fraction of stars have planets, including perhaps half of all Sun-like stars...
approximately 70 light-year
Light-year
A light-year, also light year or lightyear is a unit of length, equal to just under 10 trillion kilometres...
s away in the constellation
Constellation
In modern astronomy, a constellation is an internationally defined area of the celestial sphere. These areas are grouped around asterisms, patterns formed by prominent stars within apparent proximity to one another on Earth's night sky....
of Cygnus
Cygnus (constellation)
Cygnus is a northern constellation lying on the plane of the Milky Way. Its name is the Latinized Hellenic word for swan. One of the most recognizable constellations of the northern summer and autumn, it features a prominent asterism known as the Northern Cross...
. The planet was discovered orbiting the sun-like
Sun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is almost perfectly spherical and consists of hot plasma interwoven with magnetic fields...
star
Star
A star is a massive, luminous sphere of plasma held together by gravity. At the end of its lifetime, a star can also contain a proportion of degenerate matter. The nearest star to Earth is the Sun, which is the source of most of the energy on Earth...
16 Cygni B
16 Cygni
16 Cygni or 16 Cyg is a triple star system approximately 70 light-years away from Earth in the constellation of Cygnus. It consists of two Sun-like yellow dwarf stars, 16 Cygni A and 16 Cygni B, together with a red dwarf, 16 Cygni C...
, one of two solar-mass
Mass
Mass can be defined as a quantitive measure of the resistance an object has to change in its velocity.In physics, mass commonly refers to any of the following three properties of matter, which have been shown experimentally to be equivalent:...
components of the triple star system 16 Cygni. It makes one revolution every 799 days and was the first eccentric Jupiter
Eccentric Jupiter
An eccentric Jupiter is a Jovian planet that orbits its star in an eccentric orbit. Eccentric Jupiters may disqualify a planetary system from having Earth-like planets in it because a massive gas giant with an eccentric orbit may remove all Earth mass planets from the habitable zone.To date, it...
to be discovered.
Discovery
In October 1996 the discovery of a planetPlanet
A planet is a celestial body orbiting a star or stellar remnant that is massive enough to be rounded by its own gravity, is not massive enough to cause thermonuclear fusion, and has cleared its neighbouring region of planetesimals.The term planet is ancient, with ties to history, science,...
ary-mass companion to the star 16 Cygni B was announced, with a mass at least 1.68 times that of Jupiter
Jupiter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the largest planet within the Solar System. It is a gas giant with mass one-thousandth that of the Sun but is two and a half times the mass of all the other planets in our Solar System combined. Jupiter is classified as a gas giant along with Saturn,...
. At the time, it had the highest orbital eccentricity of any known extrasolar planet. The discovery was made by measuring the star's radial velocity
Radial velocity
Radial velocity is the velocity of an object in the direction of the line of sight . In astronomy, radial velocity most commonly refers to the spectroscopic radial velocity...
. As the inclination of the orbit is unknown, only a lower limit on the mass is known.
Orbit and mass


Solar System
The Solar System consists of the Sun and the astronomical objects gravitationally bound in orbit around it, all of which formed from the collapse of a giant molecular cloud approximately 4.6 billion years ago. The vast majority of the system's mass is in the Sun...
, the planet's orbit is highly elliptical
Ellipse
In geometry, an ellipse is a plane curve that results from the intersection of a cone by a plane in a way that produces a closed curve. Circles are special cases of ellipses, obtained when the cutting plane is orthogonal to the cone's axis...
, and its distance varies from 0.54 AU
Astronomical unit
An astronomical unit is a unit of length equal to about or approximately the mean Earth–Sun distance....
at periastron to 2.8 AU at apastron. This high eccentricity may have been caused by tidal interactions in the binary star
Binary star
A binary star is a star system consisting of two stars orbiting around their common center of mass. The brighter star is called the primary and the other is its companion star, comes, or secondary...
system, and the planet's orbit may vary chaotically
Chaos theory
Chaos theory is a field of study in mathematics, with applications in several disciplines including physics, economics, biology, and philosophy. Chaos theory studies the behavior of dynamical systems that are highly sensitive to initial conditions, an effect which is popularly referred to as the...
between low and high-eccentricity states over a period of tens of millions of years.
The lower limit for the object's mass is well below the dividing line between planets and brown dwarf
Brown dwarf
Brown dwarfs are sub-stellar objects which are too low in mass to sustain hydrogen-1 fusion reactions in their cores, which is characteristic of stars on the main sequence. Brown dwarfs have fully convective surfaces and interiors, with no chemical differentiation by depth...
s at 13 Jupiter masses. Preliminary astrometric
Astrometry
Astrometry is the branch of astronomy that involves precise measurements of the positions and movements of stars and other celestial bodies. The information obtained by astrometric measurements provides information on the kinematics and physical origin of our Solar System and our Galaxy, the Milky...
measurements in 2001 suggested the orbit of 16 Cygni Bb may be highly inclined with respect to our line of sight (at around 173°). This would mean the object's mass may be around 14 times that of Jupiter, making it a low-mass brown dwarf. However these measurements were later proved useful only for upper limits;.
Physical characteristics
Since the planet has only been detected indirectly by measurements of its parent star, properties such as its radiusRadius
In classical geometry, a radius of a circle or sphere is any line segment from its center to its perimeter. By extension, the radius of a circle or sphere is the length of any such segment, which is half the diameter. If the object does not have an obvious center, the term may refer to its...
, composition and temperature
Temperature
Temperature is a physical property of matter that quantitatively expresses the common notions of hot and cold. Objects of low temperature are cold, while various degrees of higher temperatures are referred to as warm or hot...
are unknown.
Habitable zone
The planet's highly eccentric orbit means the planet would experience extreme seasonSeason
A season is a division of the year, marked by changes in weather, ecology, and hours of daylight.Seasons result from the yearly revolution of the Earth around the Sun and the tilt of the Earth's axis relative to the plane of revolution...
al effects. Despite this, simulations suggest that an Earth
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun, and the densest and fifth-largest of the eight planets in the Solar System. It is also the largest of the Solar System's four terrestrial planets...
-like moon
Extrasolar moon
An extrasolar moon, or exomoon, is a natural satellite that orbits an extrasolar planet or other extrasolar body. Although no extrasolar moons have yet been observed, it can be inferred from the empirical study of natural satellites in the Solar System that they are likely to be common elements of...
would be able to support liquid water at its surface over the course of a year. Due to the eccentric orbit of this massive gas giant
Gas giant
A gas giant is a large planet that is not primarily composed of rock or other solid matter. There are four gas giants in the Solar System: Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune...
, it is unlikely that a habitable planet could survive in this system.
See also
- 30 Arietis Bb30 Arietis Bb30 Arietis Bb is an extrasolar planet which orbits the F-type main sequence star 30 Arietis B, located approximately 129 light years away in the constellation Aries. This planet has minimum mass nearly 10 times that of Jupiter. Because inclination is not known, its true mass is unknown...
- 83 Leonis Bb83 Leonis Bb83 Leonis Bb, also catalogued as HD 99492 b or abbreviated 83 Leo Bb, is an extrasolar planet approximately 58 light-years away in the constellation of Leo . The planet was discovered in January 2005 by the California and Carnegie Planet Search team, who use the Doppler spectroscopy method to...
- HD 80606 bHD 80606 bHD 80606 b is a superjovian planet 190 light-years distant in the constellation of Ursa Major. The planet was discovered orbiting the star Struve 1341 B in April 2001 by a team led by Michel Mayor and Didier Queloz. Based on its mass, at 4 times that of Jupiter, it is a gas giant...
- List of extrasolar planets

